What are teacher competencies? Competencies are the skills and knowledge that enable a teacher to be successful. To maximize student learning, teachers must have expertise in a wide-ranging array of competencies in an especially complex environment where hundreds of critical decisions are required each day (Jackson, 1990). Few jobs demand the integration of professional judgment and the proficient use of evidence-based competencies as does teaching.
Why is this important? The transformational power of an effective teacher is something many of us have experienced. Intuitively, the link between teaching and student academic achievement may seem obvious, but what is the evidence for it?
Research confirms this common perception of a link and reveals that of all factors under the control of a school, teachers are the most powerful influence on student success (Babu & Mendro, 2003; Sanders & Rivers, 1996). What separates effective teachers from ineffective ones, and how can this information be used to support better teaching? We can now begin to build a profile of exemplary classroom instruction derived from effectiveness research (Wenglinsky, 2002; Hattie, 2009).
Which competencies make the biggest difference? An examination of the research on education practices that make a difference shows that four classes of competencies yield the greatest results.
- Instructional delivery
- Classroom management
- Formative assessment
- Personal competencies (soft skills)
Further, the research indicates that these competencies can be used to organize the numerous specific skills and knowledge available for building effective teacher development.
Instructional delivery: Research tells us what can be expected from a teacher employing instructional strategies and practices that are proven to lead to increased mastery of lessons. Better learning happens in a dynamic setting in which teachers offer explicit active instruction than in situations in which teachers do not actively guide instruction and instead turn control over content and pace of instruction to students (Hattie, 2009).
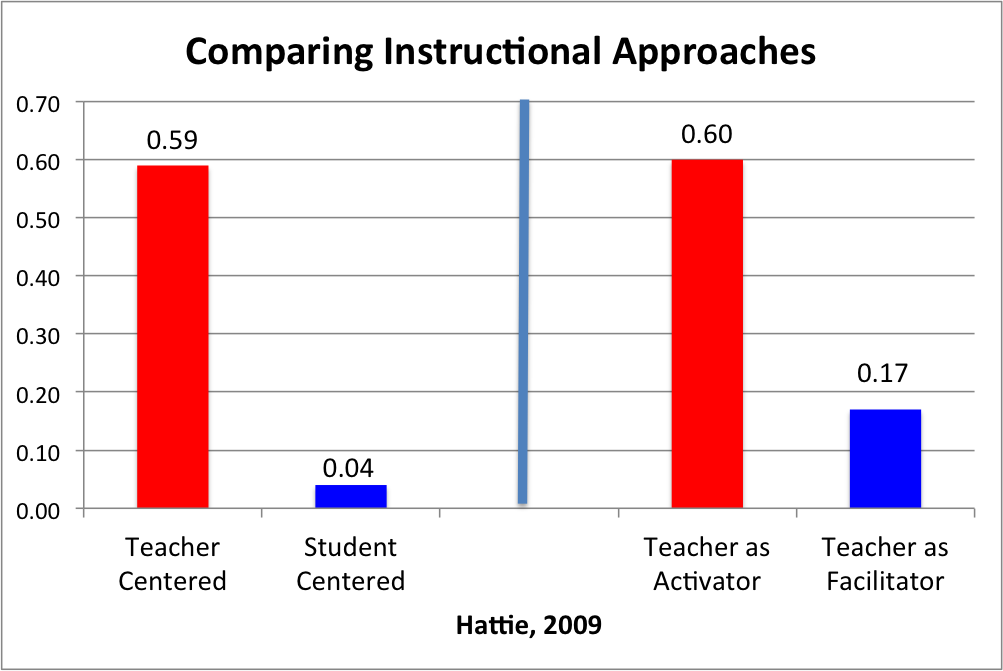
Is there a diverse set of practices that teachers can efficiently and effectively use to increase mastery of content for a variety of curricula? The structured and systematic approach of explicit instruction emphasizes mastery of the lesson to ensure that students understand what has been taught, become fluent in new material, and can generalize what they learn to novel situations they encounter in the future.
The following are hallmarks of an explicit approach for teachers (Archer & Hughes, 2011; Knight, 2012).
- Teacher selects the learning area to be taught.
- Teacher sets criteria for success.
- Teacher informs students of criteria ahead of the lesson.
- Teacher demonstrates to the students successful use of the knowledge/skills through modeling.
- Teacher evaluates student acquisition.
- Teacher provides remedial opportunities for acquiring the knowledge/skills, if necessary.
- Teacher provides closure at the end of the lesson.
A common complaint of an explicit instruction approach is that it does not offer sufficient opportunities for students to build on acquired knowledge/skills in creative and novel ways that help them to assimilate the material. The reality is that all effective instruction, regardless of philosophy, must aid students in generalizing newly taught knowledge/skills in a context that is greater than a single lesson. An explicit model accomplishes the goal of building toward “big ideas” by first emphasizing mastery of foundation skills such as reading and mathematics, and then systematically introducing opportunities to integrate these critical skills in discovery-based lessons to maximize students’ experience of success.
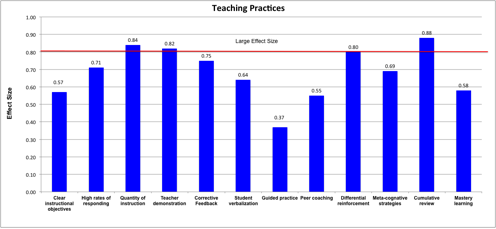
Effective explicit instruction practices include these features.
- Well-designed and planned instruction: Instruction that is well planned moves students from their current level of competency toward explicit criteria for success.
- Instructional design with clear instructional objectives: The teacher should present these objectives to students for each lesson.
- Scope and sequencing: The teacher should teach the range of related skills and the order in which they should be learned.
- Instruction that offers sufficient opportunities for successful acquisition:
- High rates of responding for each student to practice the skill: The teacher should provide sufficient opportunities for unpunished errors and ample reinforcement for success.
- Sufficient quantity of instruction: The teacher should allocate enough time to teach a topic.
- Teaching to mastery: Students need to learn the knowledge/skills to criteria that are verified by teachers or students’ peers.
- Teaching foundation knowledge/skills that become the basis for teaching big ideas: Current lessons should be built on past knowledge to increase fluency and maintain mastery of material. The teacher should relate lessons to complex issues and big ideas that provide deeper meaning and give students better understanding of the content.
To enlarge chart
Classroom management: Classroom management is one of the most persistent areas of concern voiced by school administrators, the public, and teachers (Evertson & Weinstein, 2013). Research consistently places classroom management among the top five issues that affect student achievement.
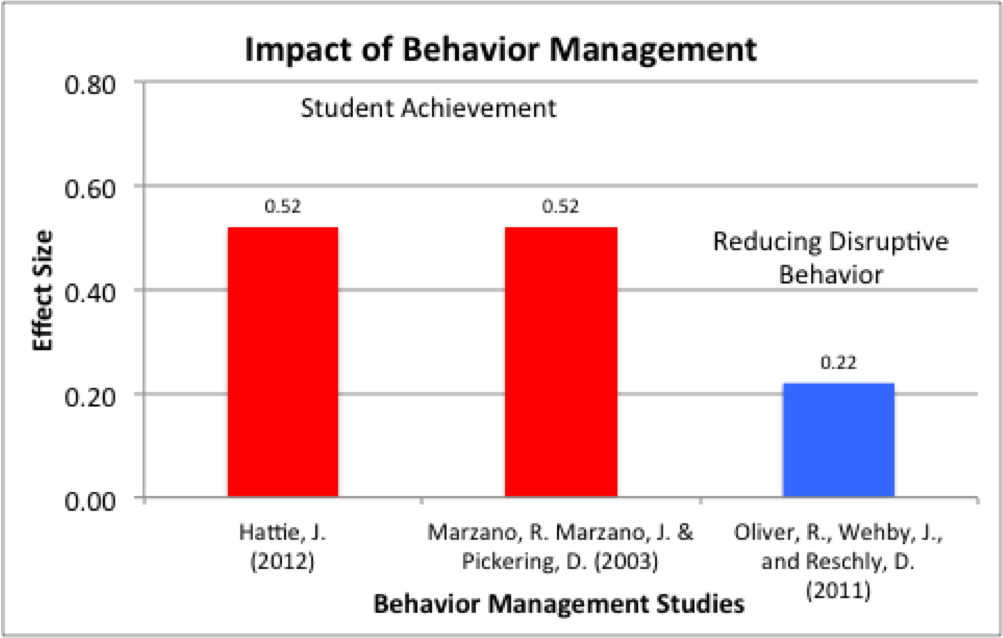
To put its in perspective, classroom management was associated with an increase of 20% in student achievement when classroom rules and procedures were applied systematically (Hattie, 2005).
A good body of research highlights four important areas that classroom teachers should be proficient in to create a climate that maximizes learning and induces a positive mood and tone.
- Rules and procedures: Effective rules and procedures identify expectations and appropriate behavior for students. To be effective, these practices must be observable and measurable.
- Schoolwide rules and procedures: Clearly stated rules identify, define, and operationalize acceptable behavior specific to a school. These rules, applicable to all students, are designed to build pro-social behavior and reduce problem behavior in a school. They distinguish appropriate from problem behavior as well as specify consequences for infractions.
- Classroom rules and procedures: Another set of clearly stated rules establishes acceptable behavior specific in a classroom. These rules need to be consistent with schoolwide rules, but may be unique to meet the needs of an individual classroom.
- Proactive classroom management: These are the practices that teachers and administrators can employ to teach and build acceptable behavior that is positive and helpful, promotes social acceptance, and leads to greater success in school. The key to proactive classroom management is active teacher supervision. The practice elements that constitute active supervision require staff to observe and interact with students regularly. The goal is to build a positive teacher-student relationship by providing timely and frequent positive feedback for appropriate behavior, and to swiftly and consistently respond to inappropriate behaviors.
- Effective classroom instruction: The key to maintaining a desirable classroom climate is to provide students with quality instructional delivery aligned to the skill level of each student. This enables students to experience success and keeps them attentive.
- Behavior reduction: These practices, designed to reduce problem and unacceptable behavior, are employed in the event the first three strategies fail. Behavior reduction strategies include giving students corrective feedback at the time of an infraction, minimizing reinforcement of a student’s unacceptable behavior, and guiding students in how to behave appropriately.
Formative assessment: Effective ongoing assessment, referred to in education literature as formative assessment and progress monitoring, is indispensable in promoting teacher and student success. It is frequently listed at the top of interventions for school improvement (Walberg, 1999).
Feedback, a core component of formative assessment, is recognized as an essential tool for improving performance in sports, business, and education. Hattie (2009) identified feedback as the single most powerful educational tool available for improving student performance, with a medium to large effect size ranging from 0.66 to 0.94.
Formative assessment consists of a range of formal and informal diagnostic testing procedures, conducted by teachers throughout the learning process, for modifying teaching and adapting activities to improve student attainment. Systemic interventions such as Response to Intervention (RtI) and Data-Based Decision Making depend heavily on the use of formative assessment (Hattie, 2009; Marzano, Pickering, & Pollock, 2001).
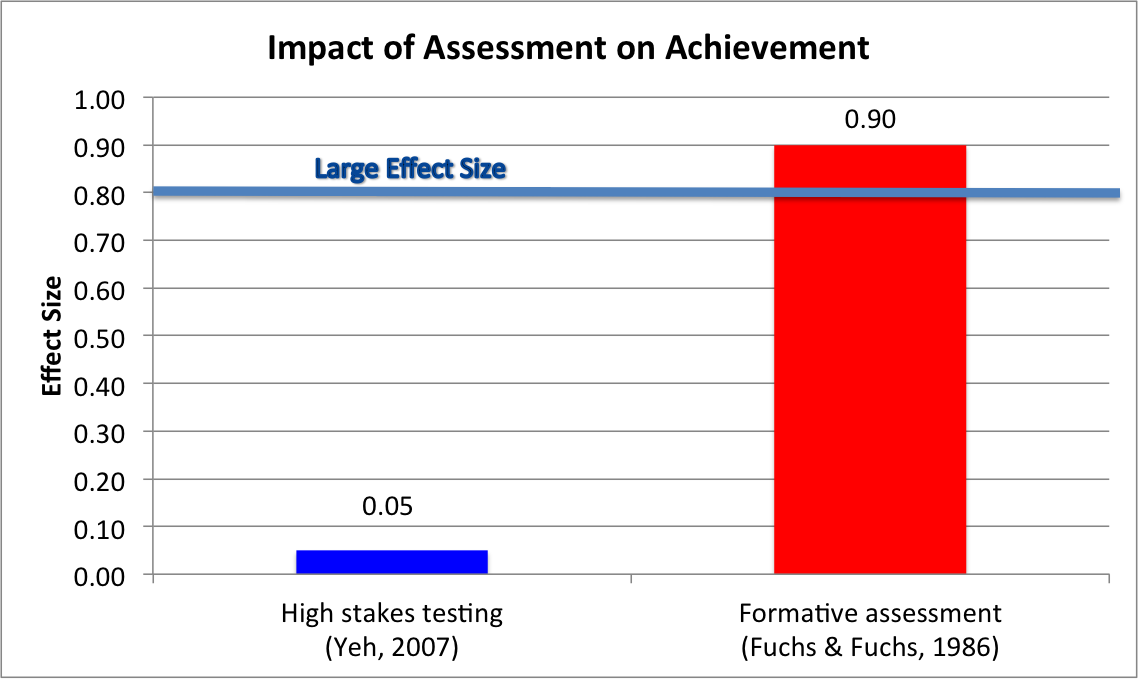
The following are the practice elements of formative assessment (Fuchs & Fuchs, 1986).
- Assessment: (Effect size 0.26) Assessing a student’s performance throughout a lesson offers a teacher insight into who is succeeding and who is falling behind. It is important that teachers collect and maintain data gained through both informal and formal assessments.
- Data display: (Effect size 0.70) Displaying the data in the form of a graphic has a surprisingly powerful effect on formative assessment’s usefulness as a tool.
- Data analysis following defined rules: (Effect size 0.90) Formative assessment is most valuable when teachers use evidence-based research and their own professional judgment to develop specific remedial interventions, before it is too late, for those falling behind.
Personable competencies (soft skills): An inspiring teacher can affect students profoundly by stimulating their interest in learning. It is equally true that most students have encountered teachers who were uninspiring and for whom they performed poorly. Unfortunately, effective and ineffective teachers have no readily discernable personality differences. Some of the very best teachers are affable, but many ineffective instructors can be personable and caring. Conversely, some of the best teachers appear as stern taskmasters, but whose influence is enormous in motivating students to accomplish things they never thought possible.
What soft skills do successful teachers have in common? Typically, the finest teachers display enthusiasm and excitement for the subjects they teach. More than just generating excitement, they provide a road map for students to reach the goals set before them. The best teachers are proficient in the technical competencies of teaching: instructional delivery, formative assessment, and classroom management. Equally significant, they are fluent in a multilayered set of social skills that students recognize and respond to, which leads to greater learning (Attakorn, Tayut, Pisitthawat, & Kanokorn, 2014). These skills must be defined as clear behaviors that teachers can master for use in classrooms.
Indispensable soft skills include:
- Establishing high but achievable expectations
- Encouraging a love for learning
- Listening to others
- Being flexible and capable of adjusting to novel situations
- Showing empathy
- Being culturally sensitive
- Embedding and encouraging higher order thinking along with teaching foundation skills
- Having a positive regard for students
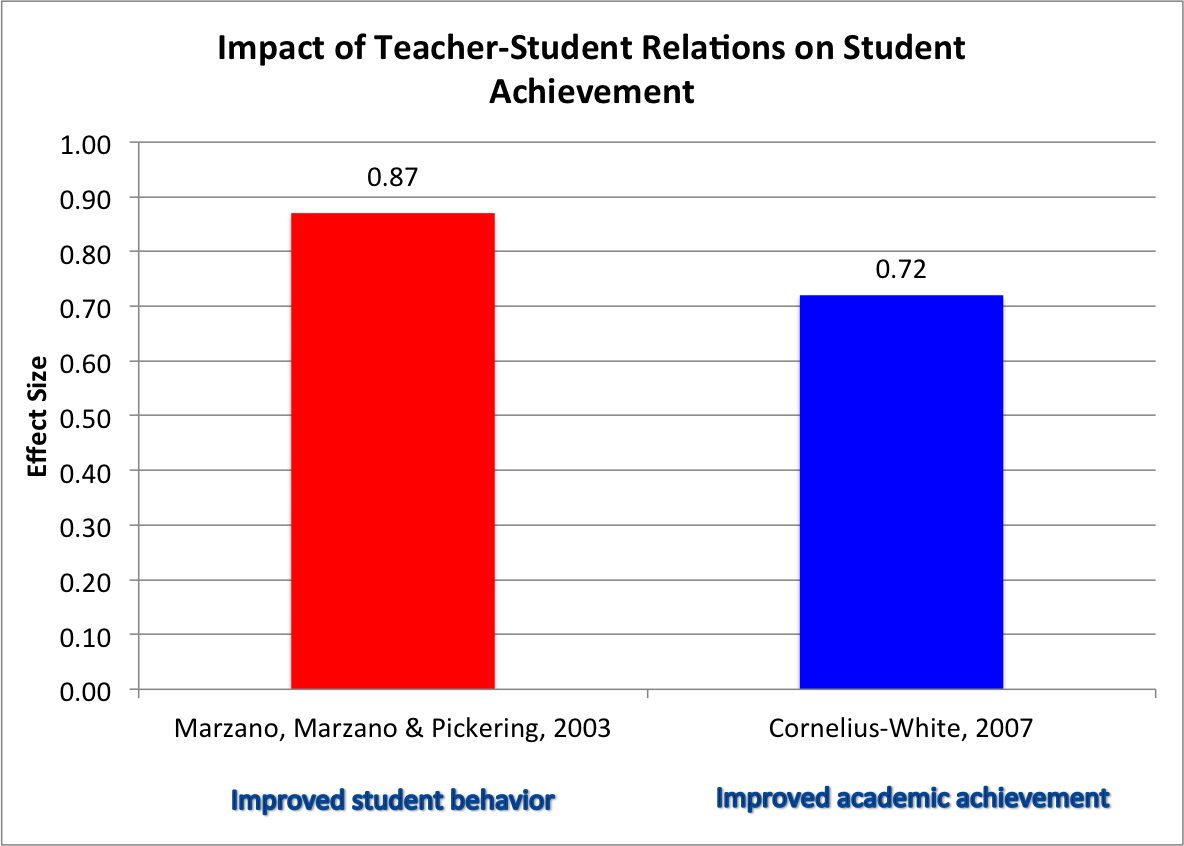
What does research tell us about personal competencies? Quantitative studies provide an overall range of effect sizes from 0.72 to 0.87 for effective teacher-student relations. Better teacher-student relations promote increased student academic performance and improve classroom climate by reducing disruptive student behavior (Cornelius-White, 2007; Marzano, Marzano & Pickering, 2003).
Conclusion
There is abundant research to support the notion that teachers play the critical role in improving student achievement in schools. What teachers do in the classroom is crucial in this process. The breadth of high-quality research accumulated over the past 40 years offers educators a clear picture of how to maximize teacher competency in four critical categories: instructional delivery, classroom management, formative assessment, and personal competencies. There is now ample evidence to recommend these competencies as the core around which to build teacher preparation, teacher hiring, teacher development, and teacher and school evaluations.
Citations
Archer, A. L., & Hughes, C. A. (2011). Explicit instruction: Efficient and effective teaching. New York, NY: Guilford Publications.
Attakorn, K., Tayut, T., Pisitthawat, K., & Kanokorn, S. (2014). Soft skills of new teachers in the secondary schools of Khon Kaen Secondary Educational Service Area 25, Thailand. Procedia—Social and Behavioral Sciences, 112, 1010–1013.
Babu, S., & Mendro, R. (2003). Teacher accountability: HLM-based teacher effectiveness indices in the investigation of teacher effects on student achievement in a state assessment program. Presented at the annual meeting of the American Educational Research Association (AERA), Chicago, IL, April.
Cornelius-White, J. (2007). Learner-centered teacher-student relationships are effective: A meta-analysis. Review of educational research, 77(1), 113–143.
Evertson, C. M., & Weinstein, C. S. (Eds.). (2013). Handbook of classroom management: Research, practice, and contemporary issues. New York, NY: Routledge.
Fuchs, L. S., & Fuchs, D. (1986). Effects of systematic formative evaluation: A meta-analysis. Exceptional Children, 53(3), 199–208.
Hattie, J., (2009). Visible learning: A synthesis of over 800 meta-analyses related to achievement. New York, NY: Routledge.
Jackson, P. W. (1990). Life in classrooms. New York, NY: Teachers College Press.
Knight, J. (2012). High-impact instruction: A framework for great teaching. Thousand Oaks, CA: Corwin Press.
Marzano, R. J., Marzano, J. S., & Pickering, D. (2003). Classroom management that works: Research-based strategies for every teacher. Alexandria, VA: Association for Supervision and Curriculum Development (ASCD).
Marzano, R. J., Pickering, D., & Pollock, J. E. (2001). Classroom instruction that works: Research-based strategies for increasing student achievement. Alexandria, VA: Association for Supervision and Curriculum Development (ASCD).
Sanders, W. L., & Rivers, J. C. (1996). Cumulative and residual effects of teachers on future student academic achievement. Knoxville, TN: University of Tennessee Value-Added Research and Assessment Center. Retrieved from http://heartland.org/policy-documents/cumulative-and-residual-effects-teachers-future-student-academic-achievement.
Walberg, H. (1999). Productive teaching. In H. C. Waxman & H. J. Walberg (Eds.), New directions for teaching practice and research (pp. 75–104). Berkeley, CA: McCutchen Publishing.
Wenglinsky, H. (2002). How schools matter: The link between teacher classroom practices and student academic performance. Education Policy Analysis Archives, 10(12).
White, W. A. T. (1988). A meta-analysis of the effects of direct instruction in special education. Education and Treatment of Children, 11(4), 364–374.
Yeh, S. S. (2007). The cost-effectiveness of five policies for improving student achievement. American Journal of Evaluation, 28(4), 416–436.
Publications
TITLE
SYNOPSIS
CITATION
LINK
Assessment Overview
Research recognizes the power of assessment to amplify learning and skill acquisition. This overview describes and compares two types of Assessments educators rely on: Formative Assessment and Summative Assessment.
Multitiered System of Support
This overview describe Multitiered system of support (MTSS) as a conceptual framework for organizing service delivery to students.
Seeking the Magic Metric: Using Evidence to Identify and Track School System Progress
This paper discusses the search for a “magic metric” in education: an index/number that would be generally accepted as the most efficient descriptor of school’s performance in a district.
Celio, M. B. (2013). Seeking the Magic Metric: Using Evidence to Identify and Track School System Quality. In Performance Feedback: Using Data to Improve Educator Performance (Vol. 3, pp. 97-118). Oakland, CA: The Wing Institute.
Overview of Teacher Evaluation
This overview provides information about teacher evaluation as it relates to collecting information about teacher practice and using it to improve student outcomes. The history of teacher evaluation and current research findings and implications are included.
Cleaver, S., Detrich, R. & States, J. (2018). Overview of Teacher Evaluation. Oakland, CA: The Wing Institute. https://www.winginstitute.org/quality-teachers-evaluation.
Teaching Functional Life Skills to Children with Developmental Disabilities
In this chapter we describe systematic instructional practices that are necessary for individuals with disabilities to benefit from educational services.
Detrich, R., & Higbee, T. S. (2009). Teaching Functional Life Skills to Children with Developmental Disabilities. Practical Handbook of School Psychology: Effective Practices for the 21st Century, 371.
Treatment Integrity in the Problem Solving Process
The usual approach to determining if an intervention is effective for a student is to review student outcome data; however, this is only part of the task. Student data can only be understood if we know something about how well the intervention was implemented. Student data without treatment integrity data are largely meaningless because without knowing how well an intervention has been implemented, no judgments can be made about the effectiveness of the intervention. Poor outcomes can be a function of an ineffective intervention or poor implementation of the intervention. Without treatment integrity data, the is a risk that an intervention will be judged as ineffective when, in fact, the quality of implementation was so inadequate that it would be unreasonable to expect positive outcomes.
Detrich, R., States, J. & Keyworth, R. (2017). Treatment Integrity in the Problem Solving Process. Oakland, Ca. The Wing Institute.
Decreasing Inappropriate Behavior Overview.
This overview describes strategies for how school personnel can respond when disruptive behavior occurs, including (1) negative consequences that can be applied as primary interventions, (2) functional behavior assessment, and (3) function-based, individualized interventions characteristic of the secondary or tertiary tiers of a multitiered system of support.
Guinness, K., Detrich, R., Keyworth, R. & States, J. (2020). Overview of Decreasing Inppropriate Behavior. Oakland, CA: The Wing Institute. https://www.winginstitute.org/classroom-inappropriate-behaviors.
Why Education Practices Fail?
This paper examines a range of education failures: common mistakes in how new practices are selected, implemented, and monitored. The goal is not a comprehensive listing of all education failures but rather to provide education stakeholders with an understanding of the importance of vigilance when implementing new practices.
States, J., & Keyworth, R. (2020). Why Practices Fail. Oakland, CA: The Wing Institute. https://www.winginstitute.org/roadmap-overview
Classroom Management
In this overview, classroom management strategies have been grouped into four essential areas: rules and procedures, proactive management, well-designed and delivered instruction, and disruptive behavior management. These strategies are devised for use at both school and classroom levels.
States, J., Detrich, R. & Keyworth, R. (2017). Overview of Classroom Management.Oakland, CA: The Wing Institute. https://www.winginstitute.org/effective-instruction-classroom.
Effective Instruction Overview
A summary of the available studies accumulated over the past 40 years on a key education driver, teacher competencies offers practical strategies, practices, and rules to guide teachers in ways to improve instruction that improves student performance and the quality of the work experience.
States, J., Detrich, R. & Keyworth, R. (2017). Effective Instruction Overview. Oakland, CA: The Wing Institute. Retrieved from https://www.winginstitute.org/effective-instruction-overview
Teacher Soft Skills Overview
This overview examines the available research on the topic of soft skills (personal competencies) and how these proficiencies support the technical competencies required for success in school
States, J., Detrich, R. & Keyworth, R. (2018). Overview of Teacher Soft Skills.Oakland, CA: The Wing Institute. https://www.winginstitute.org/teacher-compentencies-soft-skills.
Active Student Responding (ASR)
Active Student Responding (ASR) is a strategy designed to engage all students regardless of class size. ASR avoids the common problem of having only high achievers answer questions while low achievers remain silent, thus escaping detection. ASR strategies include; guided notes, response slates, response cards, and choral responding.
States, J., Detrich, R. & Keyworth, R. (2019). Active Student Responding (ASR) Overview.Oakland, CA: The Wing Institute. https://www.winginstitute.org/instructional-delivery-student-respond
Effective Teachers Make a Difference
This analysis examines the available research on effective teaching, how to impart these skills, and how to best transition teachers from pre-service to classroom with an emphasis on improving student achievement. It reviews current preparation practices and examine the research evidence on how well they are preparing teachers
States, J., Detrich, R. & Keywroth, R. (2012). Effective Teachers Make a Difference. In Education at the Crossroads: The State of Teacher Preparation (Vol. 2, pp. 1-46). Oakland, CA: The Wing Institute.
Are we making the differences that matter in education?
This paper argues that ineffective practices in schools carry a high price for consumers and suggests that school systems consider the measurable yield in terms of gains in student achievement for their schooling effort.
VanDerHeyden, A. (2013). Are we making the differences that matter in education. In R. Detrich, R. Keyworth, & J. States (Eds.),Advances in evidence-‐based education: Vol 3(pp. 119–138). Oakland, CA: The Wing Institute. Retrieved from http://www.winginstitute.org/uploads/docs/Vol3Ch4.pdf
Data Mining
TITLE
SYNOPSIS
CITATION
LINK
How do students of different socio-economic status learn during the school year and over the summer break? (Math Learning Seasonality vs Socio-economic Status)
An analysis of math test results compared at the beginning and end of each school year and the impact on learning of summer break by socio-economic status.
Alexander, K. L., Entwisle, D. R., & Olson, L. S. (2001). Schools, achievement, and inequality: A seasonal perspective. Educational evaluation and policy analysis, 23(2), 171-191.
Do we get better results when teachers match individual learning styles to instructional methods?
This analysis looks at the importance of learning styles impact on student achievement.
States, J. (2010). Do we get better results when teachers match individual learning styles to instructional methods? Retrieved from do-we-get-better.
Does a longer school year or longer school day improve student achievement scores?
This reviews looks at the issue, do longer school days and longer school years improve student achievement?
States, J. (2011). Does a longer school year or longer school day improve student achievement scores? Retrieved from does-longer-school-year.
Does learning style make a difference?
This analysis examines the research on learning styles.
States, J. (2011). Does learning style make a difference? Retrieved from does-learning-style-make935.
Which approaches to teaching science have the greatest impact on student achievement?
This analysis compares the effectiveness of differing approaches to teaching science.
States, J. (2013). Which approaches to teaching science have the greatest impact on student achievement? Retrieved from which-approaches-teaching-science944.
How do students of different socio-economic status learn during the school year and over the summer break? (Reading Learning Seasonality vs Socio-economic Status)
An analysis of reading test results compared at the beginning and end of each school year and the impact on learning of summer break by socio-economic status .
Gibson, S. (2011). How do students of different socio-economic status learn during the school year and over the summer break? (Reading Learning Seasonality vs Socio-economic Status) Retrieved from how-do-students-of822.
How big will be the impact of an intervention?
The analysis shows how effect size can be used to understand the impact of educational interventions.
States, J. (2010). How big will be the impact of an intervention? Retrieved from how-big-will-be.
What are the critical influences in a classroom that result in improved student performance?
The analysis examines direct influences tht have the greatest impact on student performance. 28 categories were distilled by combining the effect size along professional judgment of educational experts.
States, J. (2010). What are the critical influences in a classroom that result in improved student performance? Retrieved from what-are-critical-influences808.
Does Caffeine Affect Classroom Behavior and Student Performance?
This review looks at the impact that caffeine has on student behavior and academic performance.
States, J. (2011). Does Caffeine Affect Classroom Behavior and Student Performance? Retrieved from does-caffeine-affect-classroom.
Does Sugar Affect Student Behavior or Achievement?
This analysis examines the impact that sugar has on student behavior and academic achievement.
States, J. (2011). Does Sugar Affect Student Behavior or Achievement? Retrieved from does-sugar-affect-student.
Does the use of coaching as a professional development strategy improve student performance?
This review examines research on the effectiveness of coaching as a teacher training tool that can improve student performance.
States, J. (2011). Does the use of coaching as a professional development strategy improve student performance? Retrieved from does-use-of-coaching.
How important are teachers in improving student performance?
This analysis examines the impact that teachers have on low-achieving student's performance.
States, J. (2011). How important are teachers in improving student performance? Retrieved from how-important-are-teachers.
How Important is Classroom Management?
This review looks at meta-analyses on the impact of classroom management and it's role in student achievement.
States, J. (2011). How Important is Classroom Management? Retrieved from how-important-is-classroom.
What are the most effective ways for teachers to teach reading?
This analysis examines the critical practice elements for effective teaching of reading. The piece also looks at practices that have been shown to be less effective.
States, J. (2011). What are the most effective ways for teachers to teach reading? Retrieved from what-are-most-effective.
What behavior management factors reduce disruptive behavior?
This review looks behavior management practice elements that have the greatest impact on reducing disruptive student conduct.
States, J. (2011). What behavior management factors reduce disruptive behavior? Retrieved from what-behavior-management-factors.
Presentations
TITLE
SYNOPSIS
CITATION
LINK
Seeking the Magic Metric: Using Evidence to Identify and Track School System Progress
This paper discusses the search for a “magic metric” in education: an index/number that would be generally accepted as the most efficient descriptor of school’s performance in a district.
Celio, MB. (2011). Seeking the Magic Metric: Using Evidence to Identify and Track School System Progress [Powerpoint Slides]. Retrieved from 2011-wing-presentation-mary-beth-celio.
What We Know About Teacher Preparation Programs
This paper examines effective teaching, how to impart these skills, and how to best transition teachers into the classroom. Preparation practices are analyzed to determine how well we are succeeding in preparing teachers.
States, J. (2010). What We Know About Teacher Preparation Programs [Powerpoint Slides]. Retrieved from 2010-aba-presentation-jack-states.
Teaching Skills That Make a Difference
This paper provides checklist of evidence-based skills that should be the foundation of every teacher's preparation.
States, J. (2013). Teaching Skills That Make a Difference [Powerpoint Slides]. Retrieved from 2013-aba-presentation-jack-states.
Student Research
TITLE
SYNOPSIS
CITATION
LINK
Evaluating a Multimedia Professional Development Package for Improving Implementation of Evidence-Based Instructional Practices
Three 8th grade English teachers participated in this single-case multiple baseline experiment. These teachers were observed daily during classes that were inclusive to students with disabilities. Observations were conducted using the Classroom Teaching Scan. Within the Classroom Teaching Scan, a checklist of quality indicators for modeling was the primary dependent variable. Additionally, observations were scored using the Protocol for Language Arts Teaching Observations (PLATO, 2017). Participating students responded to curriculum-based measurement writing prompts throughout the study.
Minor changes in performance on the PLATO and CBM measures were demonstrated. However, these measures were descriptive in nature, not experimental. Therefore, more research over a sustained period of time is necessary to determine the effect of this professional development package on distal measures of teacher quality and student outcomes.
Elwood, J.R. (2017). Evaluating a Multimedia Professional Development Package for Improving Implementation of Evidence-Based Instructional Practices:Oakland, CA: The Wing Institute. https://www.winginstitute.org.
Effects of a problem solving team intervention on the problem-solving process: Improving concept knowledge, implementation integrity, and student outcomes.
This study evaluated the effects of a problem solving intervention package that included problem-solving information, performance feedback, and coaching in a student intervention planning protocol.
Vaccarello, C. A. (2011). Effects of a problem solving team intervention on the problem-solving process: Improving concept knowledge, implementation integrity, and student outcomes. Retrieved from student-research-2011.
TITLE
SYNOPSIS
CITATION
LINK
Assessment Overview
Research recognizes the power of assessment to amplify learning and skill acquisition. This overview describes and compares two types of Assessments educators rely on: Formative Assessment and Summative Assessment.
Multitiered System of Support
This overview describe Multitiered system of support (MTSS) as a conceptual framework for organizing service delivery to students.
Relationships matter: Linking teacher support to student engagement and achievement
This study was guided by a reduced version of the Self-System Process Model developed by Connell. This paper report the optimal and risk thresholds for the Student Performance and Commitment Index (SPCI) and engagement, and then data on how much engagement matters for later success in school are presented.
Klem, A. M., & Connell, J. P. (2004). Relationships matter: Linking teacher support to student engagement and achievement. Journal of school health, 74(7), 262-273.
Transforming the culture of schools: Yup’ik Eskimo examples
This book share issues of equity and school transformation, and shows how one indigenous minority teachers' group engaged in a process of transforming schooling in their community. Documented in one small locale far-removed from mainstream America, the personal narratives by Yupík Eskimo teachers.
Lipka, J., & Ilutsik, E. (2014). Transforming the Culture of Schools: Yup¡ k Eskimo Examples. Routledge.
The impact of communication factors on job satisfaction among Icelandic employees in the public sector
The main purpose of the present study was to explore the impact of communicative factors on job satisfaction and employee’s desired need for new ways of communicating.
Þorkelsson, J. The Impact of Communication Factors on Job Satisfaction Among Icelandic Employees in the Public Sector (Doctoral dissertation).
Learning About Learning: What Every New Teacher Needs to Know
This paper examines teacher education textbooks for discussion of research-based strategies that every teacher candidate should learn in order to promote student learning and retention.
Learning About Learning: What Every New Teacher Needs to Know Retrieved from http://www.nctq.org/dmsView/Learning_About_Learning_Report.
Knowledge of diverse learners: Implications for the practice of teaching
Knowledge of Diverse Learners (KDL) is increasingly recognized as an essential component of knowledge base for effective teaching as in today's schools, teachers must be prepared to teach a diverse population of student (Banks et al. 2005). In other words, teachers need to be aware that their students in a classroom are and always have been different from one another in a variety of ways. KDL refers to an understanding of diversity of students in terms of their abilities and interests and how they respond to diverse situations; an application of different teaching strategies; and how various types of classroom activities might be managed.
Abd Rahman, F., Scaife, J., Yahya, N. A., & Ab Jalil, H. (2010). Knowledge of diverse learners: Implications for the practice of teaching. International Journal of Instruction, 3(2).
Comparing Reading Research to Program Design: An Examination of Teachers College Units of Study.
This report is the first of a new initiative by Student Achievement Partners to review different reading instructional programs that have been adopted and are widely used in schools.
Adams, M.J., Fillmore, L.W., Goldenberg, C., Oakhill, J., Paige, D.D., Rasinski, T., & Shanahan, T. (2020). Comparing Reading Research to Program Design: An Examination of Teachers College Units of Study. Student Achievement Partners.
Cultural Diversity and School Equity. A Model to Evaluate and Develop Educational Practices in Multicultural Education Contexts
The main purpose of this research is to explore whether the proper strategies to deal with cultural diversity in school is being implemented, and to assess how cultural diversity is addressed in our school.
Aguado, T., Ballesteros, B., & Malik, B. (2003). Cultural diversity and school equity. A model to evaluate and develop educational practices in multicultural education contexts. Equity &Excellence in Education, 36(1), 50-63.
Teachers' Subject Matter Knowledge as a Teacher Qualification: A Synthesis of the Quantitative Literature on Students' Mathematics Achievement
The aim of this paper is to examine a variety of features of research that might account for mixed findings of the relationship between teachers' subject matter knowledge and student achievement based on meta-analytic technique.
Ahn, S., & Choi, J. (2004). Teachers' Subject Matter Knowledge as a Teacher Qualification: A Synthesis of the Quantitative Literature on Students' Mathematics Achievement. Online Submission.
Is the three-term contingency trial a predictor of effective instruction?
Two experiments are reported which test the effect of increased three-term contingency trials on students' correct and incorrect math responses. The results warrant further research to test whether or not rates of presentation of three-term contingency trials are predictors of effective instruction.
Albers, A. E., & Greer, R. D. (1991). Is the three-term contingency trial a predictor of effective instruction?. Journal of Behavioral Education, 1(3), 337-354.
Investigating the influence of distributed leadership on school effectiveness: A mediating role of teachers’ commitment.
The purpose of this study is to investigate the influence of distributed leadership (DL) on school effectiveness (SE) in junior secondary schools in Katsina State, Nigeria. The study also investigates if teachers’ commitment (TC) mediates the relationship between DL and SE.
Ali, H. M., & Yangaiya, S. A. (2015). Investigating the influence of distributed leadership on school effectiveness: A mediating role of teachers’ commitment. Journal of Educational and Social Research, 5(1), 163–174.
Observations of effective teacher-student interactions in secondary school classrooms: Predicting student achievement with the classroom assessment scoring system–secondary
Multilevel modeling techniques were used with a sample of 643 students enrolled in 37 secondary school classrooms to predict future student achievement (controlling for baseline achievement) from observed teacher interactions with students in the classroom, coded using the Classroom Assessment Scoring System—Secondary.
Allen, J., Gregory, A., Mikami, A., Lun, J., Hamre, B., & Pianta, R. (2013). Observations of effective teacher–student interactions in secondary school classrooms: Predicting student achievement with the classroom assessment scoring system—secondary. School Psychology Review, 42(1), 76.
Pushing the horizons of student teacher supervision: Can a bug-in-ear system be an effective plug-and-play tool for a novice electronic coach to use in student teacher supervision? ProQuest Dissertations and Theses.
This case study explored the use of the Bug-in-Ear (BIE) tool for undergraduate student-teacher supervision in the hands of a novice BIE2 coach, including the ease with which BIE equipment can be set up and operated by a novice coach and naïve users in the classroom.
Almendarez, M. B., Zigmond, N., Hamilton, R., Lemons, C., Lyon, S., McKeown, M., Rock, M. (2012). Pushing the horizons of student teacher supervision: Can a bug-in-ear system be an effective plug-and-play tool for a novice electronic coach to use in student teacher supervision? ProQuest Dissertations and Theses.
Characteristics of effective classroom rules: A review of the literature.
The purpose of this review of effective practices is to compare what information teachers are being given either in their preservice coursework or in-service training via textbooks and practitioner-oriented articles with actual empirical research that used classroom rules as an independent variable.
Alter, P., & Haydon, T. (2017). Characteristics of effective classroom rules: A review of the literature. Teacher Education and Special Education, 40(2), 114–127. https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Todd_Haydon/publication/315628091_Characteristics_of_Effective_Classroom_Rules_A_Review_of_the_Literature/links/59c4f704a6fdccc719149d6e/Characteristics-of-Effective-Classroom-Rules-A-Review-of-the-Literature.pdf
The effectiveness of a technologically facilitated classroom-based early reading intervention.
The purpose of this study was to evaluate the efficacy of a classroom-teacher-delivered reading intervention for struggling readers called the Targeted Reading Intervention (TRI), designed particularly for kindergarten and first-grade teachers and their struggling students in rural, low-wealth communities.
Amendum, S. J., Vernon-Faegans, L. V., & Ginsberg, M. C. (2011). The effectiveness of a technologically facilitated classroom-based early reading intervention. The Elementary School Journal, 112, 107-131.
Explicit instruction: Efficient and effective teaching.
Explicit instruction is systematic, direct, engaging, and success oriented--and has been shown to promote achievement for all students. This highly practical and accessible resource gives special and general education teachers the tools to implement explicit instruction in any grade level or content area.
Archer, A. L., & Hughes, C. A. (2010). Explicit instruction: Effective and efficient teaching. Guilford Publications.
Explicit Instruction: Effective and Efficient Teaching
This book gives special and general education teachers the tools to implement explicit instruction in any grade level or content area. The authors provide clear guidelines for identifying key concepts, skills, and routines to teach; designing and delivering effective lessons; and giving students opportunities to practice and master new material.
Archer, A., & Hughes, C. A. (2011). Explicit instruction: Efficient and effective teaching. New York, NY: Guilford Publications.
ACHIEVEMENT AND ENROLLMENT STATUS OF SUSPENDED STUDENTS: Outcomes in a Large, Multicultural School District
This article presents the results of longitudinal retrospective analyses on suspensions, achievement, and long-term enrollment status of students in a large, urban school district. Findings indicated that suspended students had substantially lower presuspension achievement than did students in the comparison group, gained considerably less academically throughout 3 years with suspensions, and had high drop-out rates.
Arcia, E. (2006). Achievement and enrollment status of suspended students: Outcomes in a large, multicultural school district. Education and Urban Society, 38(3), 359-369.
Soft skills of new teachers in the secondary schools of Khon Kaen Secondary Educational Service Area 25, Thailand.
This research objective was to study soft skills of new teachers in the secondary schools of Khon Kaen Secondary Educational Service Area 25, Thailand. The data were collected from 60 purposive samples of new teachers by interviewing and questionnaires. The results of this study were informed that new teachers have all of soft skills at high level totally. Communicative skills were highest among seven of soft skills and next Life-long learning and information management skills, Critical and problem solving skills, Team work skills, Ethics, moral and professional skills, Leadership skills and Innovation invention and development skills were lowest in all skills. Based on the research findings obtained, the sub-skills of seven soft skills will be considered and utilized in the package of teacher development program of next research.
Attakorn, K., Tayut, T., Pisitthawat, K., & Kanokorn, S. (2014). Soft skills of new teachers in the secondary schools of Khon Kaen Secondary Educational Service Area 25, Thailand. Procedia-Social and Behavioral Sciences, 112, 1010-1013.
The flip side of the coin: Understanding the school’s contribution to dropout and completion.
Using a structural perspective from organizational theory, the authors review aspects of schooling associated with dropout. They then briefly review selected reform initiatives that restructure the school environment to improve student achievement and retention.
Baker, J. A., Derrer, R. D., Davis, S. M., Dinklage-Travis, H. E., Linder, D. S., & Nicholson, M. D. (2001). The flip side of the coin: Understanding the school's contribution to dropout and completion. School psychology quarterly, 16(4), 406.
A Synthesis of Empirical Research on Teaching Mathematics to Low-Achieving Students
This meta-analysis synthesized research on the effects of interventions to improve mathematics achievement of students considered at risk for academic failure. It found that effective interventions included providing teachers and students with student performance data; using peer tutors; providing clear, specific feedback to parents on children's mathematics success; and using explicit instruction to teach math.
Baker, S., Gersten, R., & Lee, D. S. (2002). A synthesis of empirical research on teaching mathematics to low-achieving students. The Elementary School Journal, 51-73.
Effects of active student response during error correction on the acquisition and maintenance of geography facts by elementary students with learning disabilities.
This study compares the effects of Active Student Response error correction and No Response (NR) error correction during.
Barbetta, P. M., & Heward, W. L. (1993). Effects of active student response during error correction on the acquisition and maintenance of geography facts by elementary students with learning disabilities. Journal of Behavioral Education, 3(3), 217-233.
Teacher–Student Relationship Climate and School Outcomes: Implications for Educational Policy Initiatives
This study examined whether associations between teacher policies and student achievement were mediated by the teacher–student relationship climate. Results of this study were threefold. These findings are discussed in light of their educational policy implications.
Barile, J. P., Donohue, D. K., Anthony, E. R., Baker, A. M., Weaver, S. R., & Henrich, C. C. (2012). Teacher–student relationship climate and school outcomes: Implications for educational policy initiatives. Journal of Youth and Adolescence, 41(3), 256-267.
Identifying and Implementing Education Practices Supported by Rigorous Evidence: A User Friendly Guide.
This Guide seeks to provide assistance to educational practitioners in evaluating whether an educational intervention is backed by rigorous evidence of effectiveness, and in implementing evidence-based interventions in their schools or classrooms.
Baron, J. (2004). Identifying and Implementing Education Practices Supported by Rigorous Evidence: A User Friendly Guide. Journal for Vocational Special Needs Education, 26, 40-54.
Enhancing Adherence to a Problem Solving Model for Middle-School Pre-Referral Teams: A Performance Feedback and Checklist Approach
This study looks at the use of performance feedback and checklists to improve middle-school teams problem solving.
Bartels, S. M., & Mortenson, B. P. (2006). Enhancing adherence to a problem-solving model for middle-school pre-referral teams: A performance feedback and checklist approach. Journal of Applied School Psychology, 22(1), 109-123.
School Selection and the Social Class Divide: How Tracking Contributes to the Reproduction of Inequalities
Selection practices in education, such as tracking, may represent a structural obstacle that contributes to the social class achievement gap. The authors hypothesized that school’s function of selection leads evaluators to reproduce social inequalities in tracking decisions, even when performance is equal.
Batruch, A., Autin, F., Bataillard, F., & Butera, F. (2018). School Selection and the Social Class Divide: How Tracking Contributes to the Reproduction of Inequalities. Personality and Social Psychology Bulletin, 0146167218791804.
A follow-up of Follow Through: The later effects of the Direct Instruction model on children in fifth and sixth grades.
The later effects of the Direct Instruction Follow Through program were assessed at five diverse sites. Low-income fifth and sixth graders who had completed the full 3 years of this first- through third-grade program were tested on the Metropolitan Achievement Test (Intermediate level) and the Wide Range Achievement Test (WRAT).
Becker, W. C., & Gersten, R. (1982). A follow-up of Follow Through: The later effects of the Direct Instruction Model on children in fifth and sixth grades. American Educational Research Journal, 19(1), 75-92.
Reimagining the School Day: Innovative Schedules for Teaching and Learning
A new report from the Center for American Progress suggests American students would be better served by allowing teachers more time to collaborate with colleagues, planning lessons, and reviewing the effects of instruction.
Benner, M. & Partelow, L. (2017). Reimagining the School Day: Innovative Schedules for Teaching and Learning. Washington, D.C.: Center for American Progress.
Formative assessment: A critical review.
Six issues presented in this presentation are (1) The definitional issue (2) The effectiveness issue (3) The domain issue (4) The measurement issue (5) The professional development issue (6) The system issue
Bennett, R. E. (2011). Formative assessment: A critical review. Assessment in Education: Principles, Policy & Practice, 18(1), 5-25.
Implicit discrimination
What drives people to discriminate? Economists focus on two main reasons: "taste-based" and "statistical" discrimination. Motivated by a growing body of psychological evidence, the authors put forward a third interpretation: implicit discrimination. The authors argue that discrimination may be unintentional and outside of the discriminator's awareness.
Bertrand, M., Chugh, D., & Mullainathan, S. (2005). Implicit discrimination. American Economic Review, 95(2), 94-98.
Assertive supervision: Building involved teamwork.
This well-written book on assertiveness clearly describes the non assertive, assertive, and aggressive styles of supervision. Each chapter provides numerous examples, practice exercises, and self-tests. The author identifies feelings and beliefs that support aggressiveness, non aggressiveness, or non assertiveness which help the reader "look beyond the words themselves."
Black, M. K. (1991). Assertive Supervision-Building Involved Teamwork. The Journal of Continuing Education in Nursing, 22(5), 224-224.
Assessment and classroom learning. Assessment in Education: principles, policy & practice
This is a review of the literature on classroom formative assessment. Several studies show firm evidence that innovations designed to strengthen the frequent feedback that students receive about their learning yield substantial learning gains.
Black, P., & Wiliam, D. (1998). Assessment and classroom learning. Assessment in Education: principles, policy & practice, 5(1), 7-74.
Civil rights data show more work is needed to reduce inequities in K–12 schools
Gaps in educational opportunities persist, and more work is needed to make sure that every child has a fair shot at success. Earlier CEA analysis highlights that gaps in learning outcomes have already emerged at the time of school entry, and they persist or even widen as children progress through school.
Black, S., Giuliano, L., & Narayan, A, (2016, December 9). Civil rights data show more work is needed to reduce inequities in K–12 schools.
Preparing general education teachers to improve outcomes for students with disabilities.
This policy brief lays out five components of a vision for the future and identifies opportunities to support teacher education reform. Examples of promising developments are also addressed that involve full-scale program redesign featuring collaboration across general and special education.
Blanton, L. P., Pugach, M. C., & Florian, L. (2011). Preparing general education teachers to improve outcomes for students with disabilities. Washington, DC: American Association of Colleges for Teacher Education; National Center for Learning Disabilities. Retrieved from https://www.ncld.org/wp-content/uploads/2014/11/aacte_ncld_recommendation.pdf
Human characteristics and school learning
This paper theorizes that variations in learning and the level of learning of students are determined by the students' learning histories and the quality of instruction they receive.
Bloom, B. (1976). Human characteristics and school learning. New York: McGraw-Hill.
Development and validation of the clarity indicators scale
This study was conducted to create a reliable and valid low- to medium-inference, multidimensional measure of instructor clarity from seminal work across several academic fields. The five factors were explored in regards to their ability to predict the outcomes. Implications for instructional communication researchers are discussed.
Bolkan, S. (2017). Development and validation of the clarity indicators scale. Communication Education, 66(1), 19-36.
Nine Competencies for Teaching Empathy.
The author shares nine teachable competencies that can serve as a principal's guide for empathy education. This paper will help answer which practices enhance empathy and how will principals know if teachers are implementing them effectively.
Borba, M. (2018). Nine Competencies for Teaching Empathy. Educational Leadership, 76(2), 22-28.
Comprehensive school reform and achievement: A meta-analysis
This study is a meta-analysis of the research on the impact of comprehensive school reform (CSR) on student achievement. The research summarizes the specific effects of 29 widely implemented models.
Borman, G. D., Hewes, G. M., Overman, L. T., & Brown, S. (2003). Comprehensive school reform and achievement: A meta-analysis. Review of educational research, 73(2), 125-230.
Weighing the benefits of anchored math instruction for students with disabilities in general education classes
The purpose of this study was to examine the effectiveness of enhanced anchor-instruction and traditional problem instruction in improving problem-solving performance.
Bottge, B. A., Heinrichs, M., Mehta, Z. D., & Hung, Y. H. (2002). Weighing the benefits of anchored math instruction for students with disabilities in general education classes. The Journal of Special Education, 35(4), 186-200.
Formative assessment strategies for every classroom: An ASCD action tool (2nd ed.)
The best formative assessment involves both students and teachers in a recursive process. It starts with the teacher, who models the process for the students. At first, the concept of what good work "looks like" belongs to the teacher. The teacher describes, explains, or demonstrates the concepts or skills to be taught, or assigns student investigations—reading assigned material, locating and reading materials to answer a question, doing activities or experiments—to put content into students' hands.
Brookhart, S. M. (2010). Formative assessment strategies for every classroom: An ASCD action tool. ASCD.
Teacher behavior and student achievement
This paper, prepared as a chapter for the "Handbook of Research on Teaching" (third edition), reviews correlational and experimental research linking teacher behavior to student achievement. It focuses on research done in K-12 classrooms during 1973-83, highlighting several large-scale, programmatic efforts.
Brophy, J., & Good, T. L. (1984). Teacher Behavior and Student Achievement. Occasional Paper No. 73.
Multilevel analysis of multiple baseline data evaluating precision teaching as an intervention for improving fluency in foundational reading skills for at risk readers.
In this article, multiple-baseline across participants designs were used to evaluate the impact of a precision teaching (PT) program, within a Tier 2 Response to Intervention framework, targeting fluency in foundational reading skills with at risk kindergarten readers. From the outcomes of the multilevel model, PT can be considered as a promising Tier 2 intervention to increase reading fluency with individuals who are at risk of reading failure.
Brosnan, J., Moeyaert, M., Brooks Newsome, K., Healy, O., Heyvaert, M., Onghena, P., & Van den Noortgate, W. (2018). Multilevel analysis of multiple-baseline data evaluating precision teaching as an intervention for improving fluency in foundational reading skills for at risk readers. Exceptionality, 26(3), 137-161.
Parochial Empathy Predicts Reduced Altruism and the Endorsement of Passive Harm
This paper predicted that out-group empathy would inhibit inter-group harm and promote inter-group helping, whereas in-group empathy would have the opposite effect. In all samples, in-group and out-group empathy had independent, significant, and opposite effects on inter-group outcomes, controlling for trait empathic concern.
Bruneau, E. G., Cikara, M., & Saxe, R. (2017). Parochial empathy predicts reduced altruism and the endorsement of passive harm. Social Psychological and Personality Science, 8(8), 934-942.
Methods for effective teaching: Meeting the needs of all students
Methods for Effective Teaching helps teachers with every aspect of their day-to-day responsibilities. Readers learn about everything from planning and choosing the right instructional strategies, to delivering lessons, managing the classroom, disciplining students, assessing progress, and collaborating with colleagues and parents to actively engage students in learning. Numerous features, tables, and lists of recommendations help readers apply concepts and think critically about the decisions they'll have to make in their teaching careers.
Burden, P. R., & Byrd, D. M. (2010). Methods for effective teaching: Meeting the needs of all students (p. 408). Allyn & Bacon.
Guidelines for Determining if a Reading Intervention Is Consistent With the Science of Reading
How do you know if an intervention is consistent with research? Given that the science of reading is a vast, interdisciplinary body of research about reading, the consequences of using interventions that are not aligned are potentially tragic. This article provides clear guidelines for practitioners, a rating scale tool, and worked examples to demonstrate the use of the tool.
Burns, M. K., & Contesse, V. A. (2024). Guidelines for Determining if a Reading Intervention Is Consistent With the Science of Reading. The Reading League Journal.
Using performance feedback to enhance implementation fidelity of the problem-solving team process
This study examines the importance of implementation integrity for problem-solving teams (PST) and response-to-intervention models.
Burns, M. K., Peters, R., & Noell, G. H. (2008). Using performance feedback to enhance implementation fidelity of the problem-solving team process. Journal of School Psychology, 46(5), 537-550.
Burnout: Testing for the validity, replication, and invariance of causal structure across elementary, intermediate, and secondary teachers
The study investigated the impact of organizational and personality factors on three facets of burnout—Emotional Exhaustion, Depersonalization, and reduced Personal Accomplishment within one conceptual framework.
Byrne, B. M. (1994). Burnout: Testing for the validity, replication, and invariance of causal structure across elementary, intermediate, and secondary teachers. American Educational Research Journal, 31(3), 645–673.
Teacher Professional Development Challenges Faced by Rural Superintendents
Effective teacher professional development is defined as structured professional learning
activities which result in changes in teacher practice and improvements in student learning
outcomes. Superintendents face common challenges unique to the rural environment which
hinder the delivery of effective teacher professional development in rural school districts.
Cadero-Smith, L. (2019). Teacher Professional Development Challenges Faced by Rural Superintendents in Western Washington State: A Phenomenological Study (Doctoral dissertation, American College of Education).
Reinforcement, reward, and intrinsic motivation: A meta-analysis.
This article reviews research on the effects of reinforcement/reward on intrinsic motivation. The main meta-analysis included 96 experimental stud- ies that used between-groups designs to compare rewarded subjects to nonrewarded controls on four measures of intrinsic motivation.
Cameron, J., & Pierce, W. D. (1994). Reinforcement, reward, and intrinsic motivation: A meta-analysis. Review of Educational research, 64(3), 363-423.
The debate about rewards and intrinsic motivation: Protests and accusations do not alter the results.
Cameron, J., & Pierce, W. D. (1996). The debate about rewards and intrinsic motivation: Protests and accusations do not alter the results. Review of Educational Research, 66(1), 39–51.
Amazing Results! Teacher Expectations and Student Achievement (TESA) Follow-Up Survey of TESA-Trained Teachers in 45 States and the District of Columbia.
This paper describes a survey of teachers trained in Teacher Expectations and Student Achievement (TESA). The study examined whether teachers: agreed that TESA interactions were useful with today's children; continued to practice the TESA coding and observation process after being trained; and would recommend TESA to colleagues.
Cantor, J., Kester, D., & Miller, A. (2000). Amazing Results! Teacher Expectations and Student Achievement (TESA) Follow-Up Survey of TESA-Trained Teachers in 45 States and the District of Columbia.
Why Education Experts Resist Effective Practices (And What It Would Take To Make Education More Like Medicine
The first section of this essay provides examples from reading and mathematics curricula that show experts dispensing unproven methods and flitting from one fad to another. The middle section describes how experts, for ideological reasons, have shunned some solutions that do display robust evidence of efficacy. The following sections show how public impatience has forced other professions to "grow up" and accept accountability and scientific evidence. The paper concludes with a plea to develop education into a mature profession.
Carnine, D. (2000). Why Education Experts Resist Effective Practices (And What It Would Take To Make Education More Like Medicine).
Student cultural diversity: Understanding and meeting the challenge
In this article, the author argues convincingly for a view of American's cultural diversity as a self-evident reality - one that must be effectively addressed by inservice and preservice teacher education programmes.
Carrington, V. (1999). Student Cultural Diversity: Understanding and Meeting the Challenge. Journal of Adolescent & Adult Literacy, 43(4), 386.
Culturally responsive classrooms for culturally diverse students with and at risk for disabilities.
This article discusses culturally responsive classrooms for Culturally and linguistically diverse (CLD) students with and at risk for disabilities within the context of culturally competent teachers, culturally effective instructional principles, and culturally appropriate behavior development. It discusses implications for educators and suggestions for a future agenda
Cartledge, G., & Kourea, L. (2008). Culturally responsive classrooms for culturally diverse students with and at risk for disabilities. Exceptional children, 74(3), 351-371.
Core Features of Multi-tiered Systems of reading and Behavioral Support
Showcasing evidence-based models for schoolwide prevention of reading and behavior problems, this book is highly informative, practical, and grounded in research.
Chard, D. J., Harn, B. A., Sugai, G., Horner, R. H., Simmons, D. C., & Kame’enui, E. J. (2008). Core features of multi-tiered systems of reading and behavioral support. In C. R. Greenwood, T. R. Kratochwill, & M. Clemens (Eds.), Schoolwide prevention models: Lessons learned in elementary schools (pp. 31–58). New York, NY: Guildford Press.
A multilevel study of leadership, empowerment, and performance in teams
A multilevel model of leadership, empowerment, and performance was tested using a sample of 62 teams, 445 individual members, 62 team leaders, and 31 external managers from 31 stores of a Fortune 500 company. Leader-member exchange and leadership climate-related differently to individual and team empowerment and interacted to influence individual empowerment.
Chen, G., Kirkman, B. L., Kanfer, R., Allen, D., & Rosen, B. (2007). A multilevel study of leadership, empowerment, and performance in teams. Journal of Applied Psychology, 92(2), 331–346.
The 2018 EdNext poll on school reform
Few issues engender stronger opinions in the American population than education, and the number and complexity of issues continue to grow. The annual Education Next Survey of Public Opinion examines the opinions of parents and teachers across a wide range of topic areas such as: student performance, common core curriculum, charter schools, school choice, teacher salaries, school spending, school reform, etc. The 12thAnnual Survey was completed in May, 2018.
Cheng, A., Henderson, M. B., Peterson, P.E. & West, M. R. (2019). The 2018 EdNext poll on school reform. Education Next, 19(1).
The Development of The Teacher Clarity Short Inventory (TCSI) to Measure Clear Teaching in The Classroom
This study presents the Teacher Clarity Short Inventory (TCSI) as an alternative to existing measures of teacher clarity. Analyses revealed a 10 item scale with an acceptable factor structure, acceptable reliability and validity.
Chesebro, J. L., & McCroskey, J. C. (1998). The development of the teacher clarity short inventory (TCSI) to measure clear teaching in the classroom. Communication Research Reports, 15(3), 262-266.
The Development of The Teacher Clarity Short Inventory (TCSI) to Measure Clear Teaching in The Classroom
This study presents the Teacher Clarity Short Inventory (TCSI) as an alternative to existing measures of teacher clarity. Analyses revealed a 10 item scale with an acceptable factor structure, acceptable reliability and validity.
Chesebro, J. L., & McCroskey, J. C. (1998). The development of the teacher clarity short inventory (TCSI) to measure clear teaching in the classroom. Communication Research Reports, 15(3), 262-266.
The relationship of teacher clarity and teacher immediacy with students’ experiences of state receiver apprehension
This study examined the impact of state receiver apprehension in the instructional context. Because of its negative relationship with information processing effectiveness, receiver apprehension is an experience which can act as a barrier to elective learning.
Chesebro, J. L., & McCroskey, J. C. (1998). The relationship of teacher clarity and teacher immediacy with students’ experiences of state receiver apprehension. Communication Quarterly, 46(4), 446–456.
Evaluation of the Teacher Incentive Fund: Implementation and impacts of pay-for-performance after two years
Recent efforts to attract and retain effective educators and to improve teacher practices have focused on reforming evaluation and compensation systems for teachers and principals. In 2006, Congress established the Teacher Incentive Fund (TIF), which provides grants.
Chiang, H., Wellington, A., Hallgren, K., Speroni, C., Herrmann, M., Glazerman, S., & Constantine, J. (2015). Evaluation of the Teacher Incentive Fund: Implementation and Impacts of Pay-for-Performance after Two Years. NCEE 2015-4020. National Center for Education Evaluation and Regional Assistance.
Understanding the common elements of evidence-based practice:
At this manual level of analysis, practitioners may choose from a variety of specific treatment programs that have demonstrated their efficacy in research trials.
Chorpita, B. F., Becker, K. D., & Daleiden, E. L.. (2007). Understanding the common elements of evidence-based practice: Misconceptions and clinical examples. Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry, 46(5), 647–652.
Access and persistence: Findings from 10 years of longitudinal research on students
To answer questions about who goes to college, who persists toward a degree or credential, and what happens to students after they enroll, the National Center for Education Statistics launched three national longitudinal studies to track students movements into and through the postsecondary education system. These three surveys, the National Education Longitudinal Study, the Beginning Postsecondary Student Longitudinal Study, and the Baccalaureate and Beyond Study, provide findings about college access, student characteristics, and academic persistence.
Choy, S. P. (2002). Access and persistence: Findings from 10 years of longitudinal research on students.Washington, DC: American Council on Education, Center for Policy Analysis.
Opportunities suspended: The devastating consequences of zero tolerance and school discipline policies. Report from a national summit on zero tolerance.
This is the first comprehensive national report to scrutinize the impact of strict Zero Tolerance approach in the America public school. This report illustrate that Zero Tolerance is unfair, is contrary to developmental needs of children, denies children educational opportunities, and often results in the criminalization of children.
Civil Rights Project. (2000). Opportunities suspended: The devastating consequences of zero tolerance and school discipline policies.
A review of the time management literature. Personnel Review
The purpose of this article is to provide an overview for those interested in the current state‐of‐the‐art in time management research. The review demonstrates that time management behaviours relate positively to perceived control of time, job satisfaction, and health, and negatively to stress.
Claessens, B. J., Van Eerde, W., Rutte, C. G., & Roe, R. A. (2007). A review of the time management literature. Personnel Review, 36(2), 255–276.
Early career teacher attrition: Intentions of teachers beginning
This study considered early career teacher attrition as an identity making process that involves a complex negotiation between individual and contextual factors.
Clandinin, D. J., Long, J., Schaefer, L., Downey, C. A., Steeves, P., Pinnegar, E., ... & Wnuk, S. (2015). Early career teacher attrition: Intentions of teachers beginning. Teaching Education, 26(1), 1-16.
Effective schools and school improvement: A comparative analysis of two lines of inquiry
The history and the intra-and inter-literature consensus of these two lines of inquiry will be examined in this review. The purpose is to determine whether the findings and generalizations of those bodies of research can be used conjointly in order to understand how schools strive to change to attain more effective instructional outcomes.
Clark, D. L., Lotto, L. S., & Astuto, T. A. (1984). Effective schools and school improvement: A comparative analysis of two lines of inquiry. Educational Administration Quarterly, 20(3), 41–68.
Fostering the work motivation of individuals and teams
Solid evidence supports claims that motivational programs can increase the quality and quantity of performance from 20 to 40 percent. Motivation can solve three types of performance problems: 1) people are refusing to change; and/or 2) allowing themselves to be distracted and not persist at a key task; and/or 3) treating a novel task as familiar, making mistakes but not investing mental effort and taking responsibility because of overconfidence. After describing a number of general strategies for fostering individual motivation, the article focuses on the unique motivational issues faced by teams and how to overcome them.
Clark, R. E. (2003). Fostering the work motivation of individuals and teams. Performance Improvement, 42(3), 21–29.
Overview of Teacher Evaluation
This overview provides information about teacher evaluation as it relates to collecting information about teacher practice and using it to improve student outcomes. The history of teacher evaluation and current research findings and implications are included.
Cleaver, S., Detrich, R. & States, J. (2018). Overview of Teacher Evaluation. Oakland, CA: The Wing Institute. https://www.winginstitute.org/quality-teachers-evaluation.
School climate and social-emotional learning: Predicting teacher stress, job satisfaction, and teaching efficacy.
The aims of this study were to investigate whether and how teachers’ perceptions of social-emotional learning and climate in their schools influenced three outcome variables—teachers’ sense of stress, teaching efficacy, and job satisfaction—and to examine the interrelationships among the three outcome variables
Collie, R. J., Shapka, J. D., & Perry, N. E. (2012). School climate and social–emotional learning: Predicting teacher stress, job satisfaction, and teaching efficacy. Journal of educational psychology, 104(4), 1189.
“I don’t have enough time”—Teachers’ interpretations of time as a key to learning and school change
This study investigated inner-city middle school teachers' perceptions of the importance of time in learning and sharing information. The survey identified ways that teachers shared what they had learned and discussed factors that helped or hindered them in sharing. Teacher interviews examined: knowledge, skills, and insights gained by participating in the EELC.
Collinson, V., & Fedoruk Cook, T. (2001). “I don’t have enough time”—Teachers’ interpretations of time as a key to learning and school change. Journal of Educational Administration, 39(3), 266–281.
On evaluating curricular effectiveness: Judging the quality of K–12 mathematics evaluations
This book reviews the evaluation research literature that has accumulated around 19 K-12 mathematics curricula and breaks new ground in framing an ambitious and rigorous approach to curriculum evaluation that has relevance beyond mathematics.
Confrey, J., & Stohl, V. (2004). On Evaluating Curricular Effectiveness: Judging the Quality of K-12 Mathematics Evaluations. National Academies Press.
Promoting Open Science to Increase the Trustworthiness of Evidence in Special Education.
The past two decades has seen an explosion of research to guide special educators improve the lives for individuals with disabilities. At the same time society is wrestling with the challenges posed by a post-truth age in which the public is having difficulty discerning what to believe and what to consider as untrustworthy. In this environment it becomes ever more important that researchers find ways to increase special educator’s confidence in the available knowledge base of practices that will reliably produce positive outcomes. This paper offers methods to increase confidence through transparency, openness, and reproducibility of the research made available to special educators. To accomplish this the authors propose that researchers in special education adopt emerging open science reforms such as preprints, data and materials sharing, preregistration of studies and analysis plans, and Registered Reports.
Cook, B. G., Lloyd, J. W., Mellor, D., Nosek, B. A., & Therrien, W. (2018). Promoting Open Science to Increase the Trustworthiness of Evidence in Special Education.
Evidence-based practices in learning and behavioral disabilities: The search for effective instruction
In this 26th volume of Advances in Learning and Behavioral Disabilities we address one of the most important educational reforms of recent years evidence-based practices (EBPs).
Cook, B. G., Tankersley, M., & Landrum, T. J. (Eds.). (2013). Evidence-based practices in learning and behavioral disabilities: The search for effective instruction (Vol. 26). Bingley, UK: Emerald Group Publishing.
Learner-centered teacher-student relationships are effective: A meta-analysis.
This is a meta-analysis that examines teacher-student relations impact on student performance. The author reviewed about 1,000 articles to synthesize 119 studies from 1948 to 2004 with 1,450 findings and 355,325 students.
Person-centered education is a counseling-originated, educational psychology model, overripe for meta-analysis, that posits that positive teacher-student relationships are associated with optimal, holistic learning. It includes classical, humanistic education and today’s constructivist learner-centered model.
Cornelius-White, J. (2007). Learner-centered teacher-student relationships are effective: A meta-analysis. Review of educational research, 77(1), 113-143.
Learner-centered teacher-student relationships are effective: A meta-analysis.
This is a meta-analysis that examines teacher-student relations impact on student performance. The author reviewed about 1,000 articles to synthesize 119 studies from 1948 to 2004 with 1,450 findings and 355,325 students.
Person-centered education is a counseling-originated, educational psychology model, overripe for meta-analysis, that posits that positive teacher-student relationships are associated with optimal, holistic learning. It includes classical, humanistic education and today’s constructivist learner-centered model.
Cornelius-White, J. (2007). Learner-centered teacher-student relationships are effective: A meta-analysis. Review of educational research, 77(1), 113-143.
Improving reading skills of students with disabilities using Headsprout Comprehension
Reading comprehension is a critical skill for school success. Struggling readers can benefit from computer-assisted instruction that utilizes components of effective instruction (e.g., frequent practice, immediate feedback). The purpose of this study was to examine the effects of Headsprout Comprehension, a computer-assisted reading program, on the reading comprehension of six elementary students with high-incidence disabilities (i.e., learning disabilities, emotional disturbance, and other health impairment–attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (OHI-ADHD).
Cullen, J. M., Alber-Morgan, S. R., Schnell, S. T., & Wheaton, J. E. (2014). Improving reading skills of students with disabilities using Headsprout comprehension. Remedial and Special Education, 35(6), 356-365.
On the teachability of communication strategies.
This article describes what communication strategies are and provides an overview of the teachability issue, discussing the arguments for and against strategy instruction, and suggests three possible reasons for the existing controversy.
Dörnyei, Z. (1995). On the teachability of communication strategies. TESOL quarterly, 29(1), 55-85.
Motivational Strategies in the language classroom
This book is the first of its kind in the second/foreign language (L2) ®eldthat is entirely devoted to discussing
motivational strategies, that is, methods and techniques to generate and maintain the learners' motivation.
Dörnyei, Z. (2001). Motivational strategies in the language classroom.Cambridge, UK: Cambridge University Press.
Bringing Out The Best In People
This book by organizational psychologist Aubrey C. Daniels is a guide for anyone who is required to supervise people and is particularly relevant to school principals. It is based on applying positive consequences to improve performance and offers strategies to reduce undesirable behavior so your school and employees can be successful.
Daniels, A. C., Tapscott, D., & Caston, A. (2000). Bringing out the best in people. Columbus, OH: McGraw-Hill.
Developing and assessing beginning teacher effectiveness: The potential of performance assessments.
The Performance Assessment for California Teachers (PACT) is an authentic tool for evaluating prospective teachers by examining their abilities to plan, teach, assess, and reflect on instruction in actual classroom practice. The PACT seeks both to measure and develop teacher effectiveness, and this study of its predictive and consequential validity provides information on how well it achieves these goals.
Darling-Hammond, L., Newton, S. P., & Wei, R. C. (2013). Developing and assessing beginning teacher effectiveness: The potential of performance assessments. Educational Assessment, Evaluation and Accountability, 25(3), 179-204.
Superintendents’ perspectives on the involuntary departure of public school principals: The most frequent reasons why principals lose their jobs
Few studies have examined factors relating to ineffective school leadership. Such knowledge can help principals refine leadership behaviors and enhance job security. This study used experiences and perceptions from 99 California public school superintendents to examine the reasons why some principals lose their jobs.
Davis, S. H. (1998). Superintendents’ perspectives on the involuntary departure of public school principals: The most frequent reasons why principals lose their jobs. Educational Administration Quarterly, 34(1), 58–90.
Effects of externally mediated rewards on intrinsic motivation
Conducted 2 laboratory and 1 field experiment with 24, 24, and 8 undergraduates to investigate the effects of external rewards on intrinsic motivation to perform an activity. In each experiment, Ss performed an activity during 3 different periods, and observations relevant to their motivation were made. External rewards were given to the experimental Ss during the 2nd period only, while the control Ss received no rewards.
Deci, E. L. (1971). Effects of externally mediated rewards on intrinsic motivation. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 18,105–115.
The effects of team training on team outcomes: A meta‐analysis
A meta‐analysis was conducted to determine relationships between team training and team effectiveness. Results from the 21 studies provided evidence that training is positively related to team effectiveness and effectiveness in five outcome categories: affective, cognitive, subjective task‐based skill, objective task‐based skill, and teamwork skill.
Delise, L. A., Allen Gorman, C., Brooks, A. M., Rentsch, J. R., & Steele‐Johnson, D. (2010). The effects of team training on team outcomes: A meta‐analysis. Performance Improvement Quarterly, 22(4), 53–80.
Classwide peer tutoring
The purpose of this article is to discuss classwide peer tutoring as an effective instructional procedure. The article is organized into three major sections:(a) general principles of instruction,(b) description of classwide peer tutoring procedures, and (c) review of effectiveness data concerning classroom process (ie, ecological and behavioral factors) and student achievement outcomes.
Delquadri, J., Greenwood, C. R., Whorton, D., Carta, J. J., & Hall, R. V. (1986). Classwide peer tutoring. Exceptional children, 52(6), 535-542.
Chicago
Some theory of sampling.
Analysis of the problems, theory, and design of sampling techniques for social scientists, industrial managers, and others who find statistics increasingly important in their work. Only college algebra assumed. Illustrated with dozens of actual large-scale surveys in government and industry. "The 'bible' of sampling statisticians."
Deming, W. E. (1966). Some theory of sampling. North Chelmsford, MA: Courier Corporation.
A million new teachers are coming: Will they be ready to teach
Research shows that the most powerful, in-school influence on learning is the quality of instruction that teachers bring to their students. In the next decade, more than 1.5 million new teachers will be hired for our schools; unfortunately, teacher preparation programs may not be up to the task of delivering the teacher workforce we need, and critics have identified lax selection of teacher candidates, coursework disconnected from classroom practice, and weak clinical opportunities as indications that we are inadequately preparing teachers.
DeMonte, J. (2015). A Million New Teachers Are Coming: Will They Be Ready to Teach?. American Institutes for Research.
School psychologist as problem solver
Deno, S. L. (1995). School psychologist as problem solver. In A. Thomas & J. Grimes (Eds.), Best practices in school psychology III(pp. 471–484). Bethesda, MD: National Association of School Psychologists.
Innovation, Implementation Science, and Data-Based Decision Making: Components of Successful Reform
Over the last fifty years, there have been many educational reform efforts, most of which have had a relatively short lifespan and failed to produce the promised results. One possible reason for this is for the most part these innovations have been poorly implemented. In this chapter, the author proposes a data-based decision making approach to assuring high quality implementation.
Detrich, R. Innovation, Implementation Science, and Data-Based Decision Making: Components of Successful Reform. In M. Murphy, S. Redding, and J. Twyman (Eds). Handbook on Innovations in Learning, 31. Charlotte, NC: Information Age Publishing
Treatment Integrity: A Fundamental Unit of Sustainable Educational Programs.
Reform efforts tend to come and go very quickly in education. This paper makes the argument that the sustainability of programs is closely related to how well those programs are implemented.
Detrich, R., Keyworth, R. & States, J. (2010). Treatment Integrity: A Fundamental Unit of Sustainable Educational Programs. Journal of Evidence-Based Practices for Schools, 11(1), 4-29.
Treatment Integrity in the Problem Solving Process
The usual approach to determining if an intervention is effective for a student is to review student outcome data; however, this is only part of the task. Student data can only be understood if we know something about how well the intervention was implemented. Student data without treatment integrity data are largely meaningless because without knowing how well an intervention has been implemented, no judgments can be made about the effectiveness of the intervention. Poor outcomes can be a function of an ineffective intervention or poor implementation of the intervention. Without treatment integrity data, there is a risk that an intervention will be judged as ineffective when, in fact, the quality of implementation was so inadequate that it would be unreasonable to expect positive outcomes.
Detrich, R., States, J. & Keyworth, R. (2017). Treatment Integrity in the Problem Solving Process. Oakland, Ca. The Wing Institute.
Building the university/public school partnership: A workshop for mentor teachers
Strong teacher education programs acknowledge the importance of a partnership between teacher education and public school faculties and the important role mentor teachers play in the education of student teachers. Studies suggest that mentor teachers trained in supervision are more effective than those who are not.
Dever, M. T., Hager, K. D., & Klein, K. (2003). Building the university/public school partnership: A workshop for mentor teachers. The Teacher Educator, 38(4), 245-255.
Do smarter teams do better? A meta-analysis of team-level the cognitive ability and team performance
This study reports the results of several meta-analyses examining the relationship between four operational definitions of cognitive ability within teams (highest member score, lowest member score, mean score, standard deviation of scores) and team performance.
Devine, D. J., & Phillips, J. L. (2000). Do smarter teams do better? A meta-analysis of team-level the cognitive ability and team performance. Paper presented at the 15th Annual Conference of the Society for Industrial and Organizational Psychology, New Orleans, LA.
Long-term reduction in implicit race bias: A prejudice habit-breaking intervention
The authors developed a multi-faceted prejudice habit-breaking intervention to produce long-term reductions in implicit race bias. The intervention is based on the premise that implicit bias is like a habit that can be broken through a combination of awareness of implicit bias, concern about the effects of that bias, and the application of strategies to reduce bias.
Devine, P. G., Forscher, P. S., Austin, A. J., & Cox, W. T. (2012). Long-term reduction in implicit race bias: A prejudice habit-breaking intervention. Journal of Experimental Social Psychology, 48(6), 1267–1278.
How we think
Our schools are troubled with a multiplication of studies, each in turn having its own multiplication of materials and principles. Our teachers find their tasks made heavier in that they have come to deal with pupils individually and not merely in mass. Unless these steps in advance are to end in distraction, some clew of unity, some principle that makes for simplification, must be found.
Dewey, J. (1910). How we think. DC Heath & Co. Boston, Mass, 224.
It’s about Time!! A Report on the Impact of Workload on Teachers and Students
Studying teacher workload issues has become somewhat of a trend in recent years with studies having already been completed in most other Canadian provinces. The consistency in teacher workload across the country is remarkable (see Appendix 2), and many of the findings in this study are supported by research in other jurisdictions. However, this discussion of the findings will deal primarily with the issues in Newfoundland and Labrador.
Dibbon, D. C. (2004). It’s about Time!! A Report on the Impact of Workload on Teachers and Students. St. John’s, NL: Memorial University of Newfoundland.
Getting beneath the veil of effective schools: Evidence from New York City
This paper examines data on 39 charter schools and correlates these data with school effectiveness. We find that class size, per-pupil expenditure, teacher certification, and teacher training—are not correlated with school effectiveness. In stark contrast, we show that frequent teacher feedback, the use of data to guide instruction, high-dosage tutoring, increased instructional time, and high expectations—explains approximately 45 percent of the variation in school effectiveness.
Dobbie, W., & Fryer Jr, R. G. (2013). Getting beneath the veil of effective schools: Evidence from New York City. American Economic Journal: Applied Economics, 5(4), 28-60.
School Improvement Grants: Implementation and Effectiveness
The Institute of Education Sciences (IES) recently released a summary report of the impact of School Improvement Grants (SIG). The American Recovery and Reinvestment Act of 2009 provided states and school districts with $3 Billion for SIG. By accepting SIG grants states agreed to implement one of four interventions to improve the lowest performing schools: transformation, turnaround, restart, or closure. The goals of SIG were to improve practices in four main areas: (1) adopting comprehensive instructional reform strategies, (2) developing and increasing teacher and principal effectiveness, (3) increasing learning time and creating community-oriented schools, and (4) having operational flexibility and receiving support. The report finds minimal positive effects from the grants and no evidence that SIG had significant impacts on math and reading scores, graduation rates, or increased college enrollment.
Dragoset, L., Thomas, J., Herrmann, M., Deke, J., James-Burdumy, S., Graczewski, C., … & Giffin, J. (2017). School Improvement Grants: Implementation and Effectiveness (No. 76bce3f4bb0944f29a481fae0dbc7cdb). Mathematica Policy Research.
2020 teacher prep review: Program performance in early reading instruction
New data and analysis from the National Council on Teacher Quality finds significant progress on the science of reading instruction in teacher preparation.
Drake, G., & Walsh, K. (2020). 2020 teacher prep review: Program performance in early reading instruction. Washington, D.C.: National Council on Teacher Quality. Retrieved from www.nctq.org/publications/2020-Teacher-Prep-Review:-Program-Performance-in-Early-Reading-Instruction
Teacher prep review: Program Performance in Early Reading Instruction.
The National Council of Teacher Quality (NCTQ) review examines teacher preparation program progress in adopting the necessary components of evidence-based reading instruction. The report continues the effort of two previous reports offering educators a look at trends on preparation program progress on providing this essential training.
The bases of teacher experiences: A meta-analysis
Reports a meta-analysis of research on the bases of teacher expectancies. The following conclusions were drawn: Student attractiveness, conduct, cumulative folder information, race, and social class were related to teacher expectancies.
Dusek, J. B., & Joseph, G. (1983). The bases of teacher expectancies: A meta-analysis. Journal of Educational psychology, 75(3), 327.
Teachers, Start Your Engines: Management Tips from the Pit Crew
The editors at Education World offer 20 successful classroom management strategies to get your year off to a great start and keep your classroom running smoothly throughout the entire year.
Building strong school leadership teams to sustain reform.
Effective Instructional Leadership Teams can be integral to helping underperforming schools strengthen their leadership, professional learning systems and core instruction.
Edwards, B., & Gammell, J. (2016). Building strong school leadership teams to sustain reform. Leadership, 45(3), 20-22. https://www.shastacoe.org/uploaded/Haylie_Blalock/Building-Strong-School-Leadership-Teams-to-Sustain-Reform.pdf
Meta-analysis of the relationship between collective teacher efficacy and student achievement
This meta-analysis systematically synthesized results from 26 component studies, including dissertations and published articles, which reported at least one correlation between collective teacher efficacy and school achievement.
Eells, R. J. (2011). Meta-analysis of the relationship between collective teacher efficacy and student achievement.
Meta-analysis of the relationship between collective teacher efficacy and student achievement
Collective teacher efficacy is an emergent school level variable reflecting a faculty’s collective belief in its ability to positively affect students. It has been linked in the literature to school achievement. The research questions addressed the distribution of effect sizes for the relationship and the moderator variables that could explain any variance found among the studies.
Eells, R. J. (2011). Meta-analysis of the relationship between collective teacher efficacy and student achievement (Doctoral dissertation, Loyola University Chicago).
Detrimental effects of reward: Reality or myth?
An analysis of a quarter century of research on intrinsic task interest and creativity revealed, however, that (a) detrimental effects of reward occur under highly restricted, easily avoidable conditions; (b) mechanisms of instrumental and classical conditioning are basic for understanding incremental and decremental effects of reward on task motivation; and (c) positive effects of reward on generalized creativity are easily attainable using procedures derived from behavior theory.
Eisenberger, R., & Cameron, J. (1996). Detrimental effects of reward: Reality or myth?. American psychologist, 51(11), 1153.
Meta-analysis of early intensive behavioral intervention for children with autism
The authors concluded that early intensive behavioral intervention was associated with large to moderate improvements in IQ (intelligence quotient) and adaptive behavior in children with autism compared to no intervention or eclectic treatment.
Eldevik, S., Hastings, R. P., Hughes, J. C., Jahr, E., Eikeseth, S., & Cross, S. (2009). Meta-analysis of early intensive behavioral intervention for children with autism. Journal of Clinical Child & Adolescent Psychology, 38(3), 439-450.
Examining the Impact of Inference Instruction on the Literal and Inferential Comprehension of Skilled and Less Skilled Readers: A Meta-Analytic Review.
This research suggests a strong relationship between inference generation and reading comprehension. The study finds inference instruction was effective for increasing general comprehension (d 0.58), inferential comprehension (d 0.68), and literal comprehension (d 0.28).
Elleman, A. M. (2017). Examining the Impact of Inference Instruction on the Literal and Inferential Comprehension of Skilled and Less Skilled Readers: A Meta-Analytic Review. Journal of Educational Psychology
Handbook of classroom management: Research, practice, and contemporary issues
Classroom management is a topic of enduring concern for teachers, administrators, and the public. It consistently ranks as the first or second most serious educational problem in the eyes of the general public, and beginning teachers consistently rank it as their most pressing concern during their early teaching years. Management problems continue to be a major cause of teacher burnout and job dissatisfaction. Strangely, despite this enduring concern on the part of educators and the public, few researchers have chosen to focus on classroom management or to identify themselves with this critical field.
Evertson, C. M., & Weinstein, C. S. (Eds.). (2013). Handbook of classroom management: Research, practice, and contemporary issues. New York, NY: Routledge.
The challenges of implementing evidence based practice: Ethical considerations in practice, education, policy, and research.
This paper identified and discussed some of the more pressing challenges and associated ethical dilemmas of implementing EBP in social work and strategies to manage them, in the hopes of affirming that the process of EBP is both feasible and practicable.
Farley, A. (2009). The challenges of implementing evidence based practice: ethical considerations in practice, education, policy, and research. Social Work & Society, 7(2), 246-259.
Effective college teaching from the students' and faculty's view: Matched or mismatched priorities?
Thirty-one studies were located in each of which students and faculty specified the instructional characteristics they considered particularly important to good teaching and effective instruction.
Feldman, K. A. (1988). Effective college teaching from the students' and faculty's view: Matched or mismatched priorities?. Research in Higher Education, 28(4), 291-329.
The correlation between teacher clarity of communication and student achievement gain: A meta-analysis.
The problem was to determine the correlation between teacher clarity and the mean class student learning (achievement gain) in normal public education classes in English-speaking, industrialized countries. It is of practical and theoretical importance to know the relationship between class learning and teacher clarity.
Fendick, F. (1990). The correlation between teacher clarity of communication and student achievement gain: A meta-analysis (Doctoral dissertation, University of Florida).
The correlation between teacher clarity of communication and student achievement gain: A meta-analysis
This paper aim to determine the correlation between teacher clarity and the mean class student learning (achievement gain) in normal public-education classes in English-speaking, industrialized countries.
Fendick, F. (1992). The correlation between teacher clarity of communication and student achievement gain: A meta-analysis.
The effects of contingent teacher praise, as specified by Canter’s Assertive Discipline programme on children’s off-task behavior
The purpose of this study was to examine the effectiveness of contingent teacher praise, as specified by Canter's Assertive Discipline programme, on children's on‐task behaviour. However, observations conducted during a follow‐up phase revealed reductions in the use of praise by the teachers and in some levels of on‐task behaviour.
Ferguson, E., & Houghton, S. (1992). The effects of contingent teacher praise, as specified by Canter's Assertive Discipline Programme, on children's on‐task behaviour. Educational studies, 18(1), 83-93.
Readiness for Change
The purpose of this Brief is to define the variables a state or large district leadership team may wish to consider as they determine if they are “ready” to invest in the scaling-up of innovation in education.
Fixsen, D. L., Blase, K. A., Horner, R., & Sugai, G. (2009). Readiness for Change. Scaling-Up Brief. Number 3. FPG Child Development Institute.
Core Implementation Components
The failure of better science to readily produce better services has led to increasing interest in the science and practice of implementation. The results of recent reviews of implementation literature and best practices are summarized in this article.
Fixsen, D. L., Blase, K. A., Naoom, S. F., & Wallace, F. (2009). Core implementation components. Research on social work practice, 19(5), 531-540.
Improving Attendance in a Remote Learning Environment
In the current context, barriers to student attendance and engagement have only increased. Schools and districts are encouraged to emphasize a supportive multi-tiered model for supporting student and staff engagement and attendance rather than punitive attendance or truancy policies.
Freeman, J., Flannery, B., Sugai, G., Goodman, S., Simonsen, B., & Barrett, S. (2020). Improving Attendance in a Remote Learning Environment. Technical Assistance Center on Positive Behavioral Interventions and Supports.
Introduction to response to intervention: What, why, and how valid is it?
In this article, we explain important features of RTI, why it has been promoted as a substitute for IQ-achievement discrepancy, and what remains to be understood before it may be seen as a valid means of LD identification.
Fuchs, D., & Fuchs, L. S. (2006). Introduction to response to intervention: What, why, and how valid is it?. Reading research quarterly, 41(1), 93-99.
Is "Learning Disabilities" Just a Fancy Term for Low Achievement? A Meta-Analysis of Reading Differences between Low Achievers with and without the Label.
This paper reports the results of a study that investigated the reading differences between students who were low achieving, both with and without the label of learning disabilities (LD).
Fuchs, D., Fuchs, L. S., Mathes, P. G., Lipsey, M. W., & Roberts, P. H. (2001). Is" Learning Disabilities" Just a Fancy Term for Low Achievement?: A Meta-Analysis of Reading Differences Between Low Achievers with and Without the Label. Executive Summary. ERIC Clearinghouse.
Responsiveness‐to‐intervention: Definitions, evidence, and implications for the learning disabilities construct.
The authors describe both types of responsiveness-to-intervention (RTI), "problem solving" and "standard-protocol" then review empirical evidence bearing on their effectiveness and feasibility, and conclude that more needs to be understood before RTI may be viewed as a valid means of identifying students with Learning Disabilities
Fuchs, D., Mock, D., Morgan, P. L., & Young, C. L. (2003). Responsiveness‐to‐intervention: Definitions, evidence, and implications for the learning disabilities construct. Learning Disabilities Research & Practice, 18(3), 157-171.
Effects of Systematic Formative Evaluation: A Meta-Analysis
In this meta-analysis of studies that utilize formative assessment the authors report an effective size of .7.
Fuchs, L. S., & Fuchs, D. (1986). Effects of Systematic Formative Evaluation: A Meta-Analysis. Exceptional Children, 53(3), 199-208.
Enhancing third-grade students’ mathematical problem solving with self-regulated learning strategies
The authors assessed the contribution of self-regulated learning strategies (SRL), when combined with problem-solving transfer instruction (L. S. Fuchs et al., 2003), on 3rd-graders' mathematical problem solving. SRL incorporated goal setting and self-evaluation.
Fuchs, L. S., Fuchs, D., Prentice, K., Burch, M., Hamlett, C. L., Owen, R., & Schroeter, K. (2003). Enhancing third-grade students’ mathematical problem solving with self-regulated learning strategies. Journal of Educational Psychology, 95(2), 306–315.
Back to basics: Rules, praise, ignoring, and reprimands revisited
Research begun in the 1960s provided the impetus for teacher educators to urge classroom teachers to establish classroom rules, deliver high rates of verbal/nonverbal praise, and, whenever possible, to ignore minor student provocations. The research also discuss several newer strategies that warrant attention.
Gable, R. A., Hester, P. H., Rock, M. L., & Hughes, K. G. (2009). Back to basics: Rules, praise, ignoring, and reprimands revisited. Intervention in School and Clinic, 44(4), 195-205.
Teaching methods and students’ academic performance
The objective of this study was to investigate the differential effectiveness of teaching methods on students’ academic performance. Using the inferential statistics course, students’ assessment test scores were derived from the internal class test prepared by the lecturer.
Ganyaupfu, E. M. (2013). Teaching methods and students’ academic performance. International Journal of Humanities and Social Science Invention, 2(9), 29-35.
Strategies for Effective Classroom Coaching
This article aimed to present frameworks and practices coaches can use with classroom teachers to facilitate the implementation of evidence-based interventions in schools.
Garbacz, S. A., Lannie, A. L., Jeffrey-Pearsall, J. L., & Truckenmiller, A. J. (2015). Strategies for effective classroom coaching. Preventing School Failure: Alternative Education for Children and Youth, 59(4), 263-273.
The impact of two professional development interventions on early reading instruction and achievement
To help states and districts make informed decisions about the PD they implement to improve reading instruction, the U.S. Department of Education commissioned the Early Reading PD Interventions Study to examine the impact of two research-based PD interventions for reading instruction: (1) a content-focused teacher institute series that began in the summer and continued through much of the school year (treatment A) and (2) the same institute series plus in-school coaching (treatment B).
Garet, M. S., Cronen, S., Eaton, M., Kurki, A., Ludwig, M., Jones, W., ... Zhu, P. (2008). The impact of two professional development interventions on early reading instruction and achievement. NCEE 2008-4030. Washington, DC: National Center for Education Evaluation and Regional Assistance.
Preparing for culturally responsive teaching.
In this article, a case is made for improving the school success of ethnically diverse students through culturally responsive teaching and for preparing teachers in preservice education programs with the knowledge, attitudes, and skills needed to do this.
Gay, G. (2002). Preparing for culturally responsive teaching. Journal of teacher education, 53(2), 106-116.
Culturally responsive teaching: Theory, research, and practice.
Combining insights from multicultural education theory with real-life classroom stories, this book demonstrates that all students will perform better on multiple measures of achievement when teaching is filtered through students’ own cultural experiences. This perennial bestseller continues to be the go-to resource for teacher professional learning and preservice courses.
Gay, G. (2018). Culturally responsive teaching: Theory, research, and practice. Teachers College Press.
A practical application of time management
This chapter progresses four specific components of “a practical application of time management”.
Factors enhancing sustained use of research-based instructional practices
This article reviews key findings from school-reform studies of the 1980s and explains their relevance to special education. It also highlights significant findings from more recent studies that help elucidate and flesh out the earlier findings.
Gersten, R., Chard, D., & Baker, S. (2000). Factors enhancing sustained use of research-based instructional practices. Journal of learning disabilities, 33(5), 445-456.
Incentives in organizations
The author summarizes four new strands in agency theory that help him think about incentives in real organizations. The author concludes by suggesting two avenues for further progress in agency theory: better integration with organizational economics, and cross-pollination with other fields that study organizations.
Gibbons, R. (1998). Incentives in organizations. Journal of economic perspectives, 12(4), 115-132.
Teamwork, soft skills, and research training.
This paper provide a list of soft skills that are important for collaboration and teamwork, based on the authors own experience and from an opinion survey of team leaders. This paper also outline workable short courses for graduate schools to strengthen teamwork and collaboration skills among research students.
Gibert, A., Tozer, W. C., & Westoby, M. (2017). Teamwork, soft skills, and research training. Trends in ecology & evolution, 32(2), 81-84.
Effects of quantity of instruction on time spent on learning and achievement.
This article evaluates the extent to which quantity of instruction influences time spent on self‐
study and achievement. The results suggest that time spent on self‐study is primarily a function of the degree of time allocated to instruction.
Gijselaers, W. H., & Schmidt, H. G. (1995). Effects of quantity of instruction on time spent on learning and achievement. Educational Research and Evaluation, 1(2), 183-201.
Human Competence: Engineering Worthy Performance
This book is written by Tom Gilbert who is one of the most influential theorists in building a science of performance management. Although not explicitly written for educators, it offers concrete examples principals can apply to improve the performance of teachers and other school personnel so student’s can ultimately be successful.
Gilbert, T. F. (1978). Human competence�engineering worthy performance. NSPI Journal, 17(9), 19-27.
Investigating preservice teachers’ sense of reading efficacy
Nierstheimer, Hopkins, Dillon, and Schmitt (2000) reported increased efficacy for elementary
preservice teachers participating in a corrective reading methods course and pre-requisite
tutoring practicum. Likewise, Haverback and Parault's (2011) investigation of two field
experiences, tutoring and observing, on elementary preservice teachers' self-efficacy
showed that both groups reported growth in reading teacher efficacy.
Giles, R. M., Kent, A. M., & Hibberts, M. (2013). Investigating Preservice Teachers’ Sense of Reading Efficacy. The Reading Professor, 35(1), 8.
Soft skills and technical expertise of effective project managers.
The article presents an overview of these tenets drawn from opinion positions, practical experiences, and empirical research studies. There is clear evidence that additional empirical research would be beneficial.
Gillard, S. (2009). Soft skills and technical expertise of effective project managers. Issues in informing science & information technology, 6.
Simulation and the need for practice in teacher preparation.
Recognizing the power of high quality practice in teacher preparation, a web-based simulation called Cook School District was designed to allow teacher candidates to practice the skills necessary to connect their teaching to the learning of all children employing the framework of teacher work samples (TWS). Pilot study data comparing simulation users' abilities to analyze hypothetical teaching scenarios, interviews, and reflective writing in real work samples suggest that the simulation plays a role in helping candidates become more aware of, and able to perform, several critical skills necessary to effectively connect teacher actions to the learning of each student.
Girod, M., & Girod, G. R. (2008). Simulation and the need for practice in teacher preparation. Journal of Technology and Teacher Education, 16(3), 307-337.
Impacts of comprehensive teacher induction: Final results from a randomized controlled study
To evaluate the impact of comprehensive teacher induction relative to the usual induction support, the authors conducted a randomized experiment in a set of districts that were not already implementing comprehensive induction.
Glazerman, S., Isenberg, E., Dolfin, S., Bleeker, M., Johnson, A., Grider, M., & Jacobus, M. (2010). Impacts of Comprehensive Teacher Induction: Final Results from a Randomized Controlled Study. NCEE 2010-4027. National Center for Education Evaluation and Regional Assistance.
When and why incentives (don't) work to modify behavior.
This book discuss how extrinsic incentives may come into conflict with other motivations and examine the research literature in which monetary incentives have been used in a nonemployment context to foster the desired behavior. The conclusion sums up some lessons on when extrinsic incentives are more or less likely to alter such behaviors in the desired directions.
Gneezy, U., Meier, S., & Rey-Biel, P. (2011). When and why incentives (don't) work to modify behavior. Journal of Economic Perspectives, 25(4), 191-210.
Making the most of student teaching: The importance of mentors and scope for change.
A growing literature documents the importance of student teaching placements for teacher development. Emerging evidence from this literature highlights the importance of the mentor teacher who supervises this placement, as teachers tend to be more effective when they student teach with a mentor who is a more effective teacher.
Goldhaber, D., Krieg, J., Naito, N., & Theobald, R. (2020). Making the most of student teaching: The importance of mentors and scope for change. Education Finance and Policy, 15(3), 581-591.
When Evidence-based Literacy Programs Fail.
This study examines the implementation of Leveled Literacy Intervention (LLI) for struggling readers that had been proven to work in early grades. The findings highlight the importance of considering context and implementation, in addition to evidence of effectiveness, when choosing an intervention program. Not only do schools need to adopt programs supported by evidence, but equally educators need to implement them consistently and effectively if students are to truly benefit from an intervention.
The skills Americans say kids need to succeed in life.
Pew Research Center recently asked a national sample of adults to select among a list of 10 skills: “Regardless of whether or not you think these skills are good to have, which ones do you think are most important for children to get ahead in the world today?”
Goo, S. A. R. A. (2015). The skills Americans say kids need to succeed in life. Pew Research Center.
Why marriages succeed or fail.
This breakthrough book guides you through a series of self-tests designed to help you determine what kind of marriage you have, where your strengths and weaknesses are, and what specific actions you can take to help your marriage.
Gottman, J., Gottman, J. M., & Silver, N. (1995). Why marriages succeed or fail: And how you can make yours last. Simon and Schuster.
Implicit bias: Scientific foundations.
This Article introduces implicit bias-an aspect of the new science of unconscious mental processes that has substantial bearing on discrimination law.
Greenwald, A. G., & Krieger, L. H. (2006). Implicit bias: Scientific foundations. California Law Review, 94(4), 945-967.
Adolescent trust in teachers: Implications for behavior in the high school classroom
This study examined teachers' relational approach to discipline as a predictor of high school students' behavior and their trust in teacher authority.
Gregory, A., & Ripski, M. B. (2008). Adolescent trust in teachers: Implications for behavior in the high school classroom. School Psychology Review, 37(3), 337.
Evolution of the response-to-intervention concept: Empirical foundations and recent developments
The purpose of this chapter is to present the evolution of the response to intervention (RTI) concept and discuss how that concept can be and is being used to provide more effective services to children and youth with both academic and social/behavioral difficulties
Gresham, F. M. (2007). Evolution of the response-to-intervention concept: Empirical foundations and recent developments. In Handbook of response to intervention (pp. 10-24). Springer, Boston, MA.
Decreasing Inappropriate Behavior Overview.
This overview describes strategies for how school personnel can respond when disruptive behavior occurs, including (1) negative consequences that can be applied as primary interventions, (2) functional behavior assessment, and (3) function-based, individualized interventions characteristic of the secondary or tertiary tiers of a multitiered system of support.
Guinness, K., Detrich, R., Keyworth, R. & States, J. (2020). Overview of Decreasing Inppropriate Behavior. Oakland, CA: The Wing Institute. https://www.winginstitute.org/classroom-inappropriate-behaviors.
A meta-analysis of team-efficacy, potency, and performance: Interdependence and level of analysis as moderators of observed relationships.
The purpose of the current study was to test theoretically derived hypotheses regarding the relationships between team efficacy, potency, and performance and to examine the moderating effects of level of analysis and interdependence on observed relationships.
Gully, S. M., Incalcaterra, K. A., Joshi, A., & Beaubien, J. M. (2002). A meta-analysis of team-efficacy, potency, and performance: interdependence and level of analysis as moderators of observed relationships. Journal of applied psychology, 87(5), 819.
Implementing response to intervention: A principal's guide.
This principal's guide to implementing Response to Intervention (RTI) for elementary and middle school reading emphasizes the critical role administrators play in ensuring RTI success in their schools. The author makes recommendations for putting the RTI process in motion and helps school leaders:
Hall, S. L. (Ed.). (2007). Implementing response to intervention: A principal's guide. Thousand Oaks, CA: Corwin Press.
Can comprehension be taught? A quantitative synthesis of “metacognitive” studies
To assess the effect of “metacognitive” instruction on reading comprehension, 20 studies, with a total student population of 1,553, were compiled and quantitatively synthesized. In this compilation of studies, metacognitive instruction was found particularly effective for junior high students (seventh and eighth grades). Among the metacognitive skills, awareness of textual inconsistency and the use of self-questioning as both a monitoring and a regulating strategy were most effective. Reinforcement was the most effective teaching strategy.
Haller, E. P., Child, D. A., & Walberg, H. J. (1988). Can comprehension be taught? A quantitative synthesis of “metacognitive” studies. Educational researcher, 17(9), 5-8.
Practitioner’s Guide to Curriculum-Based Evaluation in Reading
This book gives researchers and professionals the means to break this frustrating cycle, crafted by authors who have not only been there and done that, but can explain in-depth how to replicate the method
Harlacher J., Sakelaris T., Kattelman N. (2014) Practitioner’s guide to curriculum-based evaluation in reading. New York, NY: Springer.
Mediation of interpersonal expectancy effects: 31 meta-analyses.
Reviews 135 studies on mediation and classifies results into 31 behavior categories (e.g., praise, climate, asks questions). Separate meta-analyses for each mediating variable were conducted. Results were also analyzed separately for studies that examined the relation between expectations and emitted behaviors and between mediating behaviors and outcome measures.
Harris, M. J., & Rosenthal, R. (1985). Mediation of interpersonal expectancy effects: 31 meta-analyses. Psychological bulletin, 97(3), 363.
Visible learning: A synthesis of over 800 meta-analyses relating to achievement
Hattie’s book is designed as a meta-meta-study that collects, compares and analyses the findings of many previous studies in education. Hattie focuses on schools in the English-speaking world but most aspects of the underlying story should be transferable to other countries and school systems as well. Visible Learning is nothing less than a synthesis of more than 50.000 studies covering more than 80 million pupils. Hattie uses the statistical measure effect size to compare the impact of many influences on students’ achievement, e.g. class size, holidays, feedback, and learning strategies.
Hattie, J. (2008). Visible learning: A synthesis of over 800 meta-analyses relating to achievement. New York, NY: Routledge.
Visible learning: A synthesis of over 800 meta-analyses relating to achievement
Hattie’s book is designed as a meta-meta-study that collects, compares and analyses the findings of many previous studies in education. Hattie focuses on schools in the English-speaking world but most aspects of the underlying story should be transferable to other countries and school systems as well. Visible Learning is nothing less than a synthesis of more than 50.000 studies covering more than 80 million pupils. Hattie uses the statistical measure effect size to compare the impact of many influences on students’ achievement, e.g. class size, holidays, feedback, and learning strategies.
Hattie, J. (2008). Visible learning: A synthesis of over 800 meta-analyses relating to achievement. New York, NY: Routledge.
Visible Learning for Teachers: Maximizing Impact on Learning
This book takes over fifteen years of rigorous research into education practices and provides teachers in training and in-service teachers with concise summaries of the most effective interventions and offers practical guidance to successful implementation in classrooms.
Hattie, J. (2012). Visible learning for teachers: Maximizing impact on learning. Routledge.
Effective use of behavior-specific praise: A middle school case study
Teachers experience high levels of stress and emotional exhaustion while teaching in classrooms with too much student misbehavior. The two teachers in this study expressed concerns about this very issue during math instruction. They were also feeling tired and stressed due to constantly reprimanding students. Fortunately, a simple strategy was used to effectively respond to these challenging behaviors
Haydon, T., & Musti-Rao, S. (2011). Effective use of behavior-specific praise: A middle school case study. Beyond Behavior, 20(2).
Made to stick: Why some ideas survive and others die
This book reveal the anatomy of ideas that stick and explain ways to make ideas stickier, such as applying the human scale principle, using the Velcro Theory of Memory, and creating curiosity gaps. Along the way, we discover that sticky messages of all kinds draw their power from the same six traits.
Heath, C., & Heath, D. (2007). Made to stick: Why some ideas survive and others die. Random House.
Hard evidence on soft skills.
This paper summarizes recent evidence on what achievement tests measure; how achievement tests relate to other measures of "cognitive ability" like IQ and grades; the important skills that achievement tests miss or mismeasure, and how much these skills matter in life.
Heckman, J. J., & Kautz, T. (2012). Hard evidence on soft skills. Labour economics, 19(4), 451-464.
Evaluating the relationships between poverty and school.
This study examined the relationships between poverty and a school's academic performance (both student achievement and growth).
Hegedus, A. (2018). Evaluating the Relationships between Poverty and School Performance. NWEA Research. NWEA.
What do we know about time management? A review of the literature and a psychometric critique of instruments assessing time management.
The purpose of this chapter is to examine the existing time management literature.
Hellsten, L. M. (2012). What do we know about time management. A review of the literature and a psychometric critique of instruments assessing time management. Rijeka, Croatia: Intech, 21-22.
Ten faulty notions about teaching and learning that hinder the effectiveness of special education.
This article discusses 10 such notions that the author believes limit the effectiveness of special education by impeding the adoption of research-based instructional practices.
Heward, W. L. (2003). Ten faulty notions about teaching and learning that hinder the effectiveness of special education. The journal of special education, 36(4), 186-205.
Want to improve the effectiveness of your lectures? Try guided notes
This paper briefly discuss some pros and con of lecturing as a teaching method, describe how a strategy called "guided notes" can make lecturing more effective, and offer some specific suggestions for developing and using guided notes.
Heward, W. L. (2004). Want to improve the effectiveness of your lectures? Try guided notes. Talking About Teaching.
Using choral responding to increase active student response.
There are numerous practical strategies for increasing active student response during group instruction. One of these strategies, Choral Responding, is the subject of this article.
Heward, W. L., Courson, F. H., & Narayan, J. S. (1989). Using choral responding to increase active student response. Teaching Exceptional Children, 21(3), 72-75.
Global blended learning practices for teaching and learning, leadership and professional development.
This study will discuss a guiding definition for blended learning, benefits, team support, policy, management issues, rationale for expansion, professional development, purchasing, funding, evaluation, and lenses of the future and implications.
Hilliard, A. T. (2015). Global blended learning practices for teaching and learning, leadership and professional development. Journal of International Education Research, 11(3), 179–188. https://files.eric.ed.gov/fulltext/EJ1070786.pdf
Improving pedagogy in the developmental mathematics classroom
Community colleges typically offer extensive developmental education programs to students
with weak academic skills in order to prepare them for college-level coursework. Yet, for
students referred to developmental mathematics education, rates of completion in
developmental math courses and in college-level math courses required for a degree are
particularly low.
Hodara, M. (2011). Improving pedagogy in the developmental mathematics classroom. CCRC Brief, 51, 1-4.
A meta-analysis on the correlation between the implicit association test and explicit self-report measures.
A meta-analysis on the relationship between the Implicit Association Test (IAT) and corresponding explicit self-report measures was conducted.
Hofmann, W., Gawronski, B., Gschwendner, T., Le, H., & Schmitt, M. (2005). A meta-analysis on the correlation between the Implicit Association Test and explicit self-report measures. Personality and Social Psychology Bulletin, 31(10), 1369-1385.
Effects of Two Levels of Procedural Fidelity with Constant Time Delay on Children's Learning
The purpose of this study was to compare the effects of constant time delay delivered with high procedural fidelity to constant time delay with high procedural fidelity on all variables except delivery of the controlling prompt
Holcombe, A., Wolery, M., & Snyder, E. (1994). Effects of two levels of procedural fidelity with constant time delay on children's learning. Journal of Behavioral Education, 4(1), 49-73.
Education reparation: an examination of Black teacher retention
The purpose of this study was to examine the workplace factors that positively and negatively impact Black K12 teacher retention. This study utilized a mixed-method approach to examine the qualitative and quantitative data.
Hollinside, M. M. (2017). Education reparation: an examination of Black teacher retention (Doctoral dissertation).
Teacher and student behaviors in the contexts of grade-level and instructional grouping
This study aimed to examine active instruction and engagement across elementary, middle, and high schools using a large database of direct classroom observations.
Hollo, A., & Hirn, R. G. (2015). Teacher and student behaviors in the contexts of grade-level and instructional grouping. Preventing School Failure: Alternative Education for Children and Youth, 59(1), 30-39.
Early identification of learning problems: A meta-analysis
Conducted a meta-analysis of 58 studies (1960–1984) on the early prediction of learning problems that reported correlations between measures administered in kindergarten or 1st-grade and reading achievement later in elementary school.
Horn, W. F., & Packard, T. (1985). Early identification of learning problems: A meta-analysis. Journal of Educational Psychology, 77(5), 597.
Principal’s time use and school effectiveness.
This paper examines the relationship between the time principals spent on different types of activities and school outcomes including student achievement, teacher and parent assessments of the school, and teacher satisfaction.
Horng, E. L., Klasik, D., & Loeb, S. (2010). Principal's time use and school effectiveness. American journal of education, 116(4), 491-523.
The effects of limited private reprimands and increased private praise on classroom behaviour in four British secondary school classes
The results showed clearly that both minimal use of private reprimands and use of private praise statements were effective in increasing the on-task behaviour of secondary aged pupils in all classes, by an average of over 20 per cent. Follow-up observations after two months on three classes showed that improved on-task behaviour was still apparent.
Houghton, S., Wheldall, K., Jukes, R. O. D., & Sharpe, A. (1990). The effects of limited private reprimands and increased private praise on classroom behaviour in four British secondary school classes. British Journal of Educational Psychology, 60(3), 255-265.
Deaths: Final Data for 1999
This report presents final 1999 data on U.S. deaths and death rates according to demographic and medical characteristics. Trends and patterns in general mortality, life expectancy, and infant and maternal mortality are also described.
Hoyert, D. L., Kochanek, K. D., & Murphy, S. L. (1999). Deaths: final data for 1997. Natl Vital Stat Rep, 47(19), 1-104.
Defining the meaning of teacher success in Hong Kong.
This study have sought to investigate teacher success in Hong Kong. The study aims to achieve the following objectives: to acquire an initial understanding of how Hong Kong teachers conceptualize teacher success, to identify the factors hindering teacher success; to study the relationship between professional development and teacher success.
Hung, C. M., Oi, A. K., Chee, P. K., & Man, C. L. (2007). Defining the meaning of teacher success in Hong Kong. In Handbook of teacher education (pp. 415-432). Springer, Dordrecht.
Four Domains for Rapid School Improvement: An Implementation Framework. The Center on School Turnaround.
This paper describes “how” to effectively implement lasting school improvement initiatives that maximize leadership, develop talent, amplify instructional transformation, and shift the culture.
Jackson, K., R., Fixsen, D., and Ward, C. (2018). Four Domains for Rapid School Improvement: An Implementation Framework. The Center on School Turnaround.
Life in Classrooms.
Focusing on elementary classrooms, chapters include: Students' Feelings about School; Involvement and Withdrawal in the Classroom; Teachers Views; The Need for New Perspectives.
Jackson, P. W. (1990). Life in classrooms. Teachers College Press.
Life in Classrooms.
Focusing on elementary classrooms, chapters include: Students' Feelings about School; Involvement and Withdrawal in the Classroom; Teachers Views; The Need for New Perspectives.
Jackson, P. W. (1990). Life in classrooms. Teachers College Press.
Screening for at-risk readers in a response to intervention framework
This article examines universal screening, one component in a response to intervention approach for serving struggling learners.
Jenkins, J. R., Hudson, R. F., & Johnson, E. S. (2007). Screening for At-Risk Readers in a Response to. School Psychology Review, 36(4), 582-600.
Demonstrating the Experimenting Society Model with Classwide Behavior Management Interventions
Demonstrates the experimenting society model using data-based decision making and collaborative consultation to evaluate behavior-management intervention strategies in 25 seventh graders. Each intervention results in improved behavior, but active teaching of classroom rules was determined to be most effective.
Johnson, T. C., Stoner, G., & Green, S. K. (1996). Demonstrating the Experimenting Society Model with Classwide Behavior Management Interventions. School Psychology Review, 25(2), 199-214.
The existence of implicit bias is beyond reasonable doubt: A refutation of ideological and methodological objections and executive summary of ten studies that no manager should ignore
In this article, we respond at length to recent critiques of research on implicit bias, especially studies using the Implicit Association Test (IAT). These studies reveal that students, nurses, doctors, police officers, employment recruiters, and many others exhibit implicit biases with respect to race, ethnicity, nationality, gender, social status, and other distinctions.
Jost, J. T., Rudman, L. A., Blair, I. V., Carney, D. R., Dasgupta, N., Glaser, J., & Hardin, C. D. (2009). The existence of implicit bias is beyond reasonable doubt: A refutation of ideological and methodological objections and executive summary of ten studies that no manager should ignore. Research in organizational behavior, 29, 39-69.
Praise counts: Using self-monitoring to increase effective teaching practices
The authors examined the effectiveness of self-monitoring for increasing the rates of teacher praise statements and the acceptability of using this technique for teachers. This study's results support the use of self-monitoring to increase effective teaching practices, namely praise, and further demonstrates high social validity for the participant and the students.
Kalis, T. M., Vannest, K. J., & Parker, R. (2007). Praise counts: Using self-monitoring to increase effective teaching practices. Preventing School Failure: Alternative Education for Children and Youth, 51(3), 20-27.
Implicit bias in the courtroom.
What, if anything, should we do about implicit bias in the courtroom? The authors comprises legal academics, scientists, researchers, and even a sitting federal judge who seek to answer this question in accordance with behavioral realism.
Kang, J., Bennett, M., Carbado, D., & Casey, P. (2011). Implicit bias in the courtroom. UCLa L. rev., 59, 1124.
Teacher attrition and mobility: Results from the 2008–09 teacher follow-up survey
The objective of TFS is to provide information about teacher mobility and attrition among elementary and secondary school teachers who teach in grades K–12 in the 50 states and the District of Columbia.
Keigher, A. (2010). Teacher Attrition and Mobility: Results from the 2008-09 Teacher Follow-Up Survey. First Look. NCES 2010-353. National Center for Education Statistics.
How Does Reading Proficiency Correlate With a Student's Socio-Economic Status?
This analysis examines the influence of poverty on student reading performance across grade levels.
Keyworth, R. (2015). How does reading proficiency correlate with a student's socio-economic status? Oakland, CA: The Wing Institute. Retrieved from https://www.winginstitute.org/how-does-reading-proficiency
District leadership for effective principal evaluation and support
Research demonstrating principals' impact on student learning outcomes has fueled the shift from principals as facilities managers to an emphasis on instructional leadership. Principals are under increasing pressure to carry out effective instructional leadership practices, including those needed to adopt college- and career-ready standards and more comprehensive teacher evaluation approaches.
Kimball, S. M., Arrigoni, J., Clifford, M., Yoder, M., & Milanowski, A. (2015). District Leadership for Effective Principal Evaluation and Support. Teacher Incentive Fund, US Department of Education.
Instructional coaching
This article discusses instructional coaching as well as the eight factors that can increase the likelihood that coaching will be a real fix for a school.
Knight, J. (2006). Instructional Coaching. School Administrator, 63(4), 36.
High-Impact Instruction: A Framework for Great Teaching.
This book offers strategies that make a difference in student learning including: content planning, instructional practices, and community building.
Knight, J. (2013). High-impact Instruction: A Framework for Great Teaching. Corwin Press.
Using Guided Notes to Enhance Instruction for All Students
The purpose of this article is to provide teachers with several suggestions for creating and using guided notes to enhance other effective teaching methods, support students’ studying, and promote higher order thinking.
Konrad, M., Joseph, L. M., & Itoi, M. (2011). Using guided notes to enhance instruction for all students. Intervention in school and clinic, 46(3), 131-140.
The testing charade: Pretending to make schools better.
For decades we’ve been studying, experimenting with, and wrangling over different approaches to improving public education, and there’s still little consensus on what works, and what to do. The one thing people seem to agree on, however, is that schools need to be held accountable—we need to know whether what they’re doing is actually working.
Koretz, D. (2017). The testing charade. University of Chicago Press.
Effect of think-pair-share in a large CS1 class: 83% sustained engagement.
Think-Pair-Share (TPS) is a classroom-based active learning strategy, in which students work on a problem posed by the instructor, first individually, then in pairs, and finally as a classwide discussion. This study investigate the quantity and quality of student engagement in a large CS1 class during the implementation of TPS activities.
Kothiyal, A., Majumdar, R., Murthy, S., & Iyer, S. (2013, August). Effect of think-pair-share in a large CS1 class: 83% sustained engagement. In Proceedings of the ninth annual international ACM conference on International computing education research (pp. 137-144). ACM.
Work groups and teams in organizations.
This review chapter examines the literature on work team effectiveness. This paper consider their nature, define them, and identify four critical conceptual issues—context, workflow, levels, and time—that serve as review themes and discuss the multitude of forms that teams may assume.
Kozlowski, S. W., & Bell, B. S. (2003). Work groups and teams in organizations. Handbook of psychology, 333-375.
Teacher-student relationship, student mental health, and dropout from upper secondary school
The purpose of this literature search study was to assess the status of knowledge regarding the association between teacher–student relationship (TSR), dropout from upper secondary school, and student mental health.
Krane, V., Karlsson, B., Ness, O., & Kim, H. S. (2016). Teacher–student relationship, student mental health, and dropout from upper secondary school: A literature review. Lærer-elev-relasjoner, elevers psykiske helse og frafall i videregående skole. En eksplorerende studie om samarbeid og den store betydningen av de små ting.
Educational testing and measurement: Classroom application and practice
An up-to-date, practical, reader-friendly resource that will help readers navigate today's seemingly ever-changing and complex world of educational testing, assessment, and measurement. The 11th edition presents a balanced perspective of educational testing and assessment, informed by developments and the ever increasing research base.
Kubiszyn, T., & Borich, G. (1987). Educational testing and measurement. Glenview, IL: Scott, Foresman.
Fluency: A review of developmental and remedial practices.
This paper provides a review of the theoretical discussions and practical studies relating to fluency instruction and reading development.
Kuhn, M. R., & Stahl, S. A. (2003). Fluency: A review of developmental and remedial practices. Journal of educational psychology, 95(1), 3.
Effectiveness of intelligent tutoring systems: A meta-analytic review.
This review describes a meta-analysis of findings from 50 controlled evaluations of
intelligent computer tutoring systems.
Kulik, J. A., & Fletcher, J. D. (2016). Effectiveness of intelligent tutoring systems: A meta-analytic review. Review of Educational Research, 86(1), 42–78.
Teacher stress and burnout: An international review
This paper reviews studies on teacher stress and burnout conducted over the past decade. The range of studies considered indicates that this topic is now of major international concern.
Kyriacou, C. (1987). Teacher stress and burnout: An international review. Educational research, 29(2), 146-152.
Toward a theory of culturally relevant pedagogy.
This article attempts to challenge notions about the intersection of culture and teaching that rely solely on microanalytic or macro analytic perspective
Ladson-Billings, G. (1995). Toward a theory of culturally relevant pedagogy. American educational research journal, 32(3), 465-491.
The differences between hard and soft skills and their relative impact on training transfer
This article discusses differences that are hypothesized to exist between hard‐ (technical) and soft‐ (intrapersonal and interpersonal) skills training that we believe impact the degree of training transfer achieved.
Laker, D. R., & Powell, J. L. (2011). The differences between hard and soft skills and their relative impact on training transfer. Human Resource Development Quarterly, 22(1), 111-122.
Academic and social integration variables and secondary student persistence in distance education.
A survey of 351 secondary distance education students (181 responses) found significant relationships between 2 academic variables (educational goals and study time) and academic persistence;
Laube, M. R. (1992). Academic and Social Integration Variables and Secondary Student Persistence in Distance Education. Research in Distance Education, 4(1), 2-9.
Performance pay and productivity
Much of the theory in personnel economics relates to effects of monetary incentives on output, but the theory was untested because appropriate data were unavailable. A new data set for the Safelite Glass Corporation tests the predictions that average productivity will rise, the firm will attract a more able workforce, and variance in output across individuals at the firm will rise when it shifts to piece rates.
Lazear, E. P. (2000). Performance pay and productivity. American Economic Review, 90(5), 1346-1361.
A meta-analysis of single-subject-design intervention research for students with LD
This article summarizes single-subject-design intervention studies that include students with learning disabilities. The results are supportive of the pervasive influence of cognitive strategy and direct instruction models across treatment domains and of the notion that variations in sample definition moderate treatment outcomes.
Lee Swanson, H., & Sachse-Lee, C. (2000). A meta-analysis of single-subject-design intervention research for students with LD. Journal of learning disabilities, 33(2), 114-136.
Forgotten racial equality: Implicit bias, decision-making, and misremembering
In this article, the author claim that judges and jurors unknowingly misremember case facts in racially biased ways. Drawing upon studies from implicit social cognition, human memory research, and legal decisionmaking, I argue that implicit racial biases affect the way judges and jurors encode, store, and recall relevant case facts.
Levinson, J. D. (2007). Forgotten racial equality: Implicit bias, decisionmaking, and misremembering. Duke LJ, 57, 345.
Does Peer Assessment Promote Student Learning? A Meta-Analysis.
Peer assessment has become a popular education intervention. A review of the literature finds few studies on the impact of Peer Review on student outcomes. This meta-analysis examines the effect sizes found in 58 studies.
Li, H., Xiong, Y., Hunter, C. V., Guo, X., & Tywoniw, R. (2020). Does peer assessment promote student learning? A meta-analysis. Assessment & Evaluation in Higher Education, 45(2), 193-211.
Teaching anti-bias curriculum in teacher education programs: What and how.
In this article, the authors discuss what an anti-bias curriculum is, provide the theoretical framework and rationale for involving teacher candidates in certain activities that promote the anti-bias curriculum, and offer additional anti-bias strategies for teacher candidates and teacher educators to implement in their classrooms.
Lin, M., Lake, V. E., & Rice, D. (2008). Teaching anti-bias curriculum in teacher education programs: What and how. Teacher Education Quarterly, 35(2), 187-200.
11 Million Days Lost: Race, Discipline, and Safety at U.S. Public Schools: Part I
This descriptive summary is one of the first reviews to examine the number of days of “lost instruction” resulting from student suspensions. The study examines the total number of days lost nationwide, disparities among different student subgroups, and differences across individual states. The impact of loss of instruction due to suspensions has a lifelong impact on students, including: lower graduation rates (Rumberger and Losen, 2017), increased involvement in the juvenile justice system (Mowicki, 2018), and arrests as adults Rosenbaum (2018).
Losen, D. J., & Whitaker, A. 11 Million Days Lost. Joint Report by the Center for Civil Rights Remedies of UCLA's Civil Rights Project and the American Civil Liberties Union of Southern California.
The strange case of the disappearing NAEP
The long term trend test of the National Assessment of Educational Progress (LTT NAEP) is the longest running test of student achievement that provides a scientifically valid estimate of what American students have learned.
Loveless, T., (2016, October 17). The strange case of the disappearing NAEP. Brookings Institution
Expectations for students.
The evidence in this paper suggest that schools can improve student learning by encouraging teachers and students to set their sights high.
Lumsden, L. (1997). Expectations for students (pp. 1-4). ERIC Clearinghouse on Educational Management, University of Oregon.
Effects of performance feedback and coaching on the problem-solving process: Improving the integrity of implementation and enhancing student outcomes
the present study was designed to learn more about how to strengthen the integrity of the problem-solving process
Lundahl, A. A. (2010). Effects of Performance Feedback and Coaching on the Problem-Solving Process: Improving the Integrity of Implementation and Enhancing Student Outcomes. ProQuest LLC. 789 East Eisenhower Parkway, PO Box 1346, Ann Arbor, MI 48106.
Using habit reversal to decrease filled pauses in public speaking.
This study evaluated the effectiveness of simplified habit reversal in reducing filled pauses that occur during public speaking. Filled pauses consist of “uh,” “um,” or “er”; clicking sounds; and misuse of the word “like.” During post-intervention assessments, all 6 participants exhibited an immediate decrease in filled pauses.
Mancuso, C., & Miltenberger, R. G. (2016). Using habit reversal to decrease filled pauses in public speaking. Journal of applied behavior analysis, 49(1), 188-192.
Leadership: The key concepts.
Leadership: The Key Concepts is an indispensable and authoritative guide to the most crucial ideas, concepts and debates surrounding the study and exercise of leadership
Marturano, A., & Gosling, J. (2007). Leadership: The key concepts. Routledge.
A Theory-Based Meta-Analysis of Research on Instruction.
This research synthesis examines instructional research in a functional manner to provide guidance for classroom practitioners.
Marzano, R. J. (1998). A Theory-Based Meta-Analysis of Research on Instruction.
The Key to Effective Classroom Management
A three-phase process helps build strong teacher-student bonds, which can reduce disruptive behavior.
Classroom management that works: Research-based strategies for every teacher
How does classroom management affect student achievement? What techniques do
teachers find most effective? How important are schoolwide policies and practices in setting
the tone for individual classroom management? In this follow-up to What Works in Schools,
Robert J. Marzano analyzes research from more than 100 studies on classroom
management to discover the answers to these questions and more. He then applies these
findings to a series of" Action Steps"--specific strategies.
Marzano, R. J., Marzano, J. S., & Pickering, D. (2003). Classroom management that works: Research-based strategies for every teacher. Alexandria, VA: Association for Supervision and Curriculum Development (ASCD).
Classroom Instruction That Works: Research Based Strategies For Increasing Student Achievement
This is a study of classroom management on student engagement and achievement.
Marzano, R. J., Pickering, D., & Pollock, J. E. (2001). Classroom instruction that works: Research-based strategies for increasing student achievement. Ascd
Team effectiveness 1997–2007: A review of recent advancements and a glimpse into the future
The authors review team research that has been conducted over the past 10 years. They discuss the nature of work teams in context and note the substantive differences underlying different types of teams.
Mathieu, J., Maynard, M. T., Rapp, T., & Gilson, L. (2008). Team effectiveness 1997-2007: A review of recent advancements and a glimpse into the future. Journal of management, 34(3), 410-476.
“Soft Skills”: A phrase in search of meaning
This literature review explores the definition of soft skills; contrasts skills with related concepts, such as personality traits, attitudes, beliefs, and values; and compares a set of soft skill typologies
Matteson, M. L., Anderson, L., & Boyden, C. (2016). " Soft Skills": A Phrase in Search of Meaning. portal: Libraries and the Academy, 16(1), 71-88.
Teaching spelling through prompting and review procedures using computer-based instruction
Computer-based instruction (CBI) was used to teach 3 sets of 20 spelling words to two 6th graders in a multiple baseline design. The CBI presented a voice recording of each spelling word and prompted the students to type the word. If they spelled the word incorrectly, a training procedure was initiated that included prompt fading and systematic review practice.
Mayfield, K. H., Glenn, I. M., & Vollmer, T. R. (2008). Teaching spelling through prompting and review procedures using computer-based instruction. Journal of Behavioral Education, 17(3), 303-312.
The role of empathy in teaching culturally diverse students: A qualitative study of teachers’ beliefs.
This study provides a description of 34 practicing teachers' beliefs regarding the role of empathy as an attribute in their effectiveness with culturally diverse students. Empathy involves cognitive, affective, and behavioral components that teachers believed were manifested in their practice.
McAllister, G., & Irvine, J. J. (2002). The role of empathy in teaching culturally diverse students: A qualitative study of teachers’ beliefs. Journal of teacher education, 53(5), 433-443.
Evaluating Value-Added Models for Teacher Accountability. Monograph.
Value added modeling has become of interest to policymakers interested in evaluating teacher performance. The authors argue that the models work well when the schools in the sample are homogenous but as heterogeneity of the student population increases estimates of teacher effects are likely to confounded.
McCaffrey, D. F., Lockwood, J. R., Koretz, D. M., & Hamilton, L. S. (2003). Evaluating Value-Added Models for Teacher Accountability. Monograph. ERIC. Retrieved from http://eric.ed.gov/?id=ED529961
Teaching high-expectation strategies to teachers through an intervention process.
This study describes the outcomes of an intervention focused on the strategies and practices of high expectation teachers. Findings revealed that teachers involved in the intervention refined and changed their practices by creating flexible grouping, enhancing the class climate, and supporting students’ goal setting.
McDonald, L., Flint, A., Rubie-Davies, C. M., Peterson, E. R., Watson, P., & Garrett, L. (2016). Teaching high-expectation strategies to teachers through an intervention process. Professional Development in education, 42(2), 290-307.
Forewarning and forearming stereotype-threatened students.
This study investigated communicative strategies for helping female students cope with ‘‘stereotype threat’’. The results demonstrate that priming a positive achieved identity (e.g., private college student) can subdue stereotype threat associated with an ascribed identity (e.g., female).
McGlone, M. S., & Aronson, J. (2007). Forewarning and forearming stereotype-threatened students. Communication Education, 56(2), 119-133.
Monitoring Response to General Education Instruction
The purpose of this chapter is to describe a critical component of the response-to-
intervention (RTI) process: monitoring student response to general education instruction.
McMaster, K. L., & Wagner, D. (2007). Monitoring response to general education instruction. In Handbook of response to intervention (pp. 223-233). Springer, Boston, MA.
Exploring the Use of Social Media Network Methods in Designing Healthcare Quality Improvement Teams.
In this paper, the authors use tools from social network analysis (SNA) to derive principles for the design of effective clinical quality improvement teams and explore the implementation of these principles using social network data collected from the inpatient general medicine services at a large academic medical center in Chicago, USA
Meltzer, D., Chung, J., Khalili, P., Marlow, E., Arora, V., Schumock, G., & Burt, R. (2010). Exploring the use of social network methods in designing healthcare quality improvement teams. Social science & medicine, 71(6), 1119-1130.
Falling off track: How teacher-student relationships predict early high school failure rates
This paper examines the relationship between the climate of teacher-student relations within a school and individual student's likelihood of freshman year success. Results find that teacher-student climate does have a significant effect.
Miller, S. R. (2000). Falling Off Track: How Teacher-Student Relationships Predict Early High School Failure Rates.
Literature synthesis on curriculum-based measurement in reading
In this article, the authors review the research on curriculum-based measurement (CBM) in reading published since the time of Marston’s 1989 review
Miura Wayman, M., Wallace, T., Wiley, H. I., Tichá, R., & Espin, C. A. (2007). Literature synthesis on curriculum-based measurement in reading. The Journal of Special Education, 41(2), 85-120.
Whole language lives on: The illusion of “balanced” reading instruction.
This position paper contends that the whole language approach to reading instruction has been disproved by research and evaluation but still pervades textbooks for teachers, instructional materials for classroom use, some states' language-arts standards and other policy documents, teacher licensing requirements and preparation programs, and the professional context in which teachers work.
Moats, L. C. (2000). Whole language lives on: The illusion of “balanced” reading instruction. Washington, DC: DIANE Publishing.
Child study team decision making in special education: Improving the process.
Child study teams (CSTs) are involved in making decisions about many aspects of the delivery of special services to handicapped students. However, a number of factors inhibit the decision-making process within CSTs. These factors have their origins in the implementation of the team process at the local education agency (LEA) level, the preparation of CST members to participate in team decision making, and in the difficulties encountered in communicating discipline-specific information.
Moore, K. J., Fifield, M. B., Spira, D. A., & Scarlato, M. (1989). Child study team decision making in special education: Improving the process. Remedial and Special Education, 10(4), 50-58.
Classroom social climate and student absences and grades
this paper investigated the relationship between student and teacher perceptions of the social environments of 19 high school classes and student absenteeism rates and the average final grades given by the teacher.
Moos, R. H., & Moos, B. S. (1978). Classroom social climate and student absences and grades. Journal of Educational Psychology, 70(2), 263.
A systematic review of single-case research on video analysis as professional development for special educators.
This meta-analysis reports on the overall effectiveness of video analysis when used with special educators, as well as on moderator analyses related to participant and instructional characteristics.
Morin, K. L., Ganz, J. B., Vannest, K. J., Haas, A. N., Nagro, S. A., Peltier, C. J., … & Ura, S. K. (2019). A systematic review of single-case research on video analysis as professional development for special educators. The Journal of Special Education, 53(1), 3-14.
Updating the Project Management Bodies of Knowledge
This paper reviews the status of BOKs and reports research on what topics should be included in the BOK (1) conducted at the Center of Research in the Management of Projects (CRMP) using data from 117 companies and (2) through ongoing work on a Global framework sponsored by the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) and others.
Morris, P. W. (2001). Updating the project management bodies of knowledge. Project Management Journal, 32(3), 21-30.
Radical equations: Math literacy and civil rights
Begun in 1982, the Algebra Project is transforming math education in twenty-five cities. The Project works with entire communities-parents, teachers, and especially students-to create a culture of literacy around algebra, a crucial stepping-stone to college math and opportunity.
Moses, R., & Cobb, C. E. (2002). Radical equations: Civil rights from Mississippi to the Algebra Project. Beacon Press.
Institute of Medicine report on prevention of mental disorders: Summary and commentary.
A comprehensive report mandated by the US Congress on the state of the science of prevention recommends a stricter definition of the term prevention; summarizes specific preventive intervention research programs across the life span; and specifies funding, personnel, and coordination priorities to build a national prevention research infrastructure
Munoz, R. F., Mrazek, P. J., & Haggerty, R. J. (1996). Institute of Medicine report on prevention of mental disorders: summary and commentary. American Psychologist, 51(11), 1116.
Fast facts: Expenditures
Current expenditures for education can be expressed in terms of the percentage of funds going toward salaries, employee benefits, purchased services, tuition, supplies, or other expenditures.
National Center for Education Statistics. (n.d.). Fast facts: Expenditures
A closer look at student teaching: Undergraduate secondary programs
Programs leave too much of student teaching to chance. Only six percent of programs incorporate two essential elements that contribute to an effective student teaching experience: providing frequent feedback to student teachers and evaluating the quality of the cooperating teachers who open their classrooms to student teachers. A quarter of programs fail to take either of these basic steps.
National Council on Teacher Quality. (2017). A closer look at student teaching: Undergraduate secondary programs.
Professional Standards for Educational Leaders 2015
This document updates a set of voluntary school leadership standards first developed in 1996, then revised in 2008 and long known by the initials of the creator of the original document, ISLLC. The 2015 document differs from its predecessors by focusing more strongly and clearly on students and student learning.
National Policy Board for Educational Administration. (2015). Professional standards for educational leaders 2015.
K–12 education: Discipline disparities for black students, boys, and students with disabilities.
This report examines: (1) patterns in disciplinary actions among public K-12 schools; (2) challenges selected school districts have with student behavior and how they approach school discipline; and (3) actions the Departments of Education and Justice have taken to identify and address disparities or discrimination in school discipline.
Nowicki, J. M. (2018). K-12 Education: Discipline Disparities for Black Students, Boys, and Students with Disabilities. Report to Congressional Requesters. GAO-18-258. US Government Accountability Office.
Teachers’ perceptions of their preparation for teaching linguistically and culturally diverse learners in rural eastern North Carolina
The number of English language learners (ELL) students in the US is increasing dramatically. Teachers were interviewed regarding their perceptions of their preparedness to teach English language learners in the mainstream classrooms. Findings revealed that teacher training programs have not prepared these individuals for the student population they face today regardless of the year in which they received their teaching licenses.
O'Neal, D. D., Ringler, M., & Rodriguez, D. (2008). Teachers’ perceptions of their preparation for teaching linguistically and culturally diverse learners in rural eastern North Carolina. The Rural Educator, 30(1).
Examination of the relation between academic procrastination and time management skills of undergraduate students in terms of some variables
Academic procrastination is seen to be quite common among undergraduates and time management is thought to be one of the possible reasons of it. Two surveys, academic procrastination and time management, were given to 332 undergraduate students in this correlational research.
Ocak, G., & Boyraz, S. (2016). Examination of the relation between academic procrastination and time management skills of undergraduate students in terms of some variables. Journal of Education and Training Studies, 4(5), 76-84.
Relating communication competence to teaching effectiveness: Implication for teacher education
This paper posits that teacher education should emphasize both content knowledge and communication skills. It follows up the contention by conceptualizing communication, exploring teacher communication competence, and finally suggesting the introduction of Teacher Communication Skills (TCS) course in the curricula of teacher education across levels.
Okoli, A. C. (2017). Relating Communication Competence to Teaching Effectiveness: Implication for Teacher Education. Journal of Education and Practice, 8(3), 150-154.
Losing our future: How minority youth are being left behind by the graduation rate crisis
This report seeks to highlight some disparities to draw the public’s and policymakers’ attention to the urgent need to address this educational and civil rights crisis. Using a more accurate method for calculating graduation rates, they provide estimates of high school graduation rates, distinguished at the state and district level, and disaggregated by race.
Orfield, G., Losen, D., Wald, J., & Swanson, C. B. (2004). Losing our future: How minority youth are being left behind by the graduation rate crisis. Civil Rights Project at Harvard University (The).
Predicting ethnic and racial discrimination: A meta-analysis of IAT criterion studies
This article reports a meta-analysis of studies examining the predictive validity of the Implicit Association Test (IAT) and explicit measures of bias for a wide range of criterion measures of discrimination.
Oswald, F. L., Mitchell, G., Blanton, H., Jaccard, J., & Tetlock, P. E. (2013). Predicting ethnic and racial discrimination: A meta-analysis of IAT criterion studies. Journal of personality and social psychology, 105(2), 171.
Work Teams in Schools
"More is better"--this precept lies behind the burgeoning use of work teams to handle problem-solving and decision-making in schools and school districts. Teams are said to build stronger relationships among those involved in education and, ultimately, to benefit students because more people with broader perspectives help to shape a stronger educational program.
Oswald, L. J. (1996). Work Teams in Schools. ERIC Digest, Number 103.
Organizing instruction and study to improve student learning
Much of teaching is about helping students master new knowledge and skills and then helping students not to forget what they have learned. The recommendations in this practice guide are intended to provide teachers with specific strategies for organizing both instruction and students' studying of material to facilitate learning and remembering information, and to enable students to use what they have learned in new situations.
Pashler, H., Bain, P. M., Bottge, B. A., Graesser, A., Koedinger, K., McDaniel, M., & Metcalfe, J. (2007). Organizing Instruction and Study to Improve Student Learning. IES Practice Guide. NCER 2007-2004. National Center for Education Research.
Time Management Behavior as a Moderator for the Job Demand-Control Interaction.
The interaction effects of time management, work demands, and autonomy on burnout were investigated in a survey study of 123 elementary teachers.
Peeters, M. A., & Rutte, C. G. (2005). Time management behavior as a moderator for the job demand-control interaction. Journal of occupational health psychology, 10(1), 64.
Classroom Assessment Scoring System (CLASS) Manual
Positive teacher-student interactions are a primary ingredient of quality early educational experiences that launch future school success. With CLASS, educators finally have an observational tool to assess classroom quality in pre-kindergarten through grade 3 based on teacher-student interactions rather than the physical environment or a specific curriculum
Pianta, R. C., La Paro, K. M., & Hamre, B. K. (2008). Classroom Assessment Scoring System™: Manual K-3. Baltimore, MD, US: Paul H Brookes Publishing.
Teacher Prep Review: Clinical Practice and Classroom Management
The COVID pandemic has meant that large numbers of students are learning by Zoom instead of in classrooms, and schools are struggling to reach students who don't have sufficient access to the internet or computers. In all this disruption, there is still one constant: the importance of effective, skilled teachers.
Pomerance, L., & Walsh, K. (2020). 2020 Teacher Prep Review: Clinical Practice & Classroom Management. National Council on Teacher Quality.
Elementary school-wide implementation of a blended learning program for reading intervention.
The authors examined the implementation of a blended learning program for literacy instruction across kindergarten through Grade 5 in a Title I urban elementary school, including a population of students (18%) who are English learners.
Prescott, J. E., Bundschuh, K., Kazakoff, E. R., & Macaruso, P. (2018). Elementary school-wide implementation of a blended learning program for reading intervention. Journal of Educational Research, 111(4), 497–506.
Meta-analysis of field experiments shows no change in racial discrimination in hiring over time
This study investigates change over time in the level of hiring discrimination in US labor markets.
Quillian, L., Pager, D., Hexel, O., & Midtbøen, A. H. (2017). Meta-analysis of field experiments shows no change in racial discrimination in hiring over time. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 114(41), 10870–10875.
Reading fluency instruction: Moving beyond accuracy, automaticity, and prosody.
Reading fluency instruction: Moving beyond accuracy, automaticity, and prosody.
Rasinski, T. (2006). Reading fluency instruction: Moving beyond accuracy, automaticity, and prosody. The Reading Teacher, 59(7), 704-706.
Instructional-design Theories and Models: A New Paradigm of Instructional Theory,
Instructional theory describes a variety of methods of instruction (different ways of facilitating human learning and development) and when to use--and not use--each of those methods. It is about how to help people learn better.
Reigeluth, C. M. (1999). The elaboration theory: Guidance for scope and sequence decisions. Instructional design theories and models: A new paradigm of instructional theory, 2, 425-453.
The effectiveness of teams in organizations: a meta-analysis
The proposed meta-analysis of 61 independent samples aims to identify whether, and if so under what conditions, team working in organizations is related to organizational effectiveness.
Richter, A. W., Dawson, J. F., & West, M. A. (2011). The effectiveness of teams in organizations: A meta-analysis.International Journal of Human Resource Management, 22(13), 2749–2769.
The relation between DIBELS, reading comprehension, and vocabulary in urban first-grade students
The relation between DIBELS, reading comprehension, and vocabulary in urban first-grade students
Riedel, B. W. (2007). The relation between DIBELS, reading comprehension, and vocabulary in urban first‐grade students. Reading research quarterly, 42(4), 546-567.
Dilemmas in a general theory of planning
In this paper, it is argued that Critical Planning Theory is inadequate as a planning theory.
Rittel, H. W., & Webber, M. M. (1973). Dilemmas in a general theory of planning. Policy sciences, 4(2), 155-169.
The Impact of Leadership On Student Outcomes: an Analysis Of The Differential Effects Of Leadership Types
The purpose of this study is to examine the relative impact of different types of leadership on students’ academic and nonacademic outcomes.
Robinson, V. M., Lloyd, C. A., & Rowe, K. J. (2008). The impact of leadership on student outcomes: An analysis of the differential effects of leadership types. Educational administration quarterly.
Executive perceptions of the top 10 soft skills needed in
This study identified the top 10 soft skills as perceived the most important by business executives: integrity, communication, courtesy, responsibility, social skills, positive attitude, professionalism, flexibility, teamwork, and work ethic.
Robles, M. M. (2012). Executive perceptions of the top 10 soft skills needed in today’s workplace. Business and Professional Communication Quarterly, 75(4), 453–465.
Executive perceptions of the top 10 soft skills needed in today’s workplace
This study identified the top 10 soft skills as perceived the most important by business executives: integrity, communication, courtesy, responsibility, social skills, positive attitude, professionalism, flexibility, teamwork, and work ethic.
Robles, M. M. (2012). Executive perceptions of the top 10 soft skills needed in today’s workplace. Business and Professional Communication Quarterly, 75(4), 453–465.
More or better student teachers
Drawing from data on over 1000 prospective teachers in a large urban district including pre and post-student teaching survey data, this study investigates whether lengthening student teaching improves teachers’ perceptions of instructional preparedness, efficacy, and career plans. The findings suggest that the duration of student teaching has little effect on teacher outcomes; however, the quality of student teaching has significant and positive effects.
Ronfeldt, M., & Reininger, M. (2012). More or better student teaching?. Teaching and teacher education, 28(8), 1091-1106.
Interpersonal expectancy effects: The first 345 studies
This paper general purpose is to summarize the results of 345 experiments investigating interpersonal expectancy effects. These studies fall into eight broad categories of research: reaction time, inkblot tests, animal learning, laboratory interviews, psychophysical judgments, learning and ability, person perception, and everyday life situations.
Rosenthal, R., & Rubin, D. (1978). Interpersonal expectancy effects: The first 345 studies. Behavioral and Brain Sciences, 3, 377–415.
Expecting the best: Instructional practices, teacher beliefs and student outcomes
The current study aimed to track the self‐perception outcomes of students (N = 256) whose teachers had high or low class‐level expectations. Students completed the Reading, Mathematics, Physical Abilities, and Peer Relations subscales of the Self Description Questionnaire‐1 (SDQ‐1; Marsh, 1990) at the beginning and end of 1 year.
Rubie, C. M. (2004). Expecting the best: Instructional practices, teacher beliefs and student outcomes (Unpublished doctoral dissertation). University of Auckland, New Zealand,database (UoA1207968).
Expecting the best for students: Teacher expectations and academic outcomes
This study aimed to explore differences in teachers’ expectations and judgments of student reading performance for Maori, Pacific Island, Asian and New Zealand European students. A further objective was to compare teacher expectations and judgments with actual student achievement.
Rubie‐Davies, C., Hattie, J., & Hamilton, R. (2006). Expecting the best for students: Teacher expectations and academic outcomes. British Journal of Educational Psychology, 76(3), 429-444.
Improving Performance: How To Manage The White Space On The Chart
Improving Performance has been a pivotal book in the creation of the performance management movement by showing how to bridge the gap between organization strategy and the individual. It can be used as guide for principals to link planning to action, implementation of organization change, and offering ways to redesign processes to overcome obstacles that impede implementation.
Rummler, G. A., & Brache, A. P. (2012). Improving performance: How to manage the white space on the organization chart. John Wiley & Sons.
Developing and enhancing teamwork in organizations: Evidence-based best practices and guidelines
This latest volume in the SIOP Professional Practice Series was inspired by a Leading Edge Conference sponsored by the Society for Industrial and Organizational Psychology to bring together leading-edge practitioners and academics to exchange views and knowledge about effective teams and help lead to better practice in that area.
Salas, E., Tannenbaum, S., Cohen, D., & Latham, G. (Eds.). (2013). Developing and enhancing teamwork in organizations: Evidence-based best practices and guidelines (Vol. 33). John Wiley & Sons.
Cumulative and residual effects of teachers on future student academic achievement.
The Tennessee Value-Added Assessment System determines the effectiveness of school systems, schools, and teachers based on student academic growth over time. Research conducted utilizing data from the TVAAS database has shown that race, socioeconomic level, class size, and classroom heterogeneity are poor predictors of student academic growth. Rather, the effectiveness of the teacher is the major determinant of student academic progress.
Sanders, W. L., & Rivers, J. C. (1996). Cumulative and residual effects of teachers on future student academic achievement.
Exploration of a blended learning approach to reading instruction for low SES students in early elementary grades.
This study investigated the potential benefits of a blended learning approach on the reading skills of low socioeconomic status students in Grades 1 and 2.
Schechter, R., Macaruso, P., Kazakoff, E. R., & Brooke, E. (2015). Exploration of a blended learning approach to reading instruction for low SES students in early elementary grades. Computers in the Schools, 32, 183–200.
The Foundations of Educational Effectiveness
In this book, recent research and theoretical interpretations are used in a critical analysis of the knowledge base on educational effectiveness.
Scheerens, J., & Bosker, B. (1997). The foundations of education effectiveness. New York: Pergamon.
Interest as a predictor of academic achievement: A meta-analysis of research.
This paper provides an overview of previous research results pertaining to the relation between interest and academic achievement. focus on the conceptualization and operationalization of interest.
Schiefele, U., Krapp, A., & Winteler, A. (1992). Interest as a predictor of academic achievement: A meta-analysis of research.
A meta‐analysis of national research: Effects of teaching strategies on student achievement in science in the United States
This project consisted of a meta-analysis of U.S. research published from 1980 to 2004 on the effect of specific science teaching strategies on student achievement. T
Schroeder, C. M., Scott, T. P., Tolson, H., Huang, T. Y., & Lee, Y. H. (2007). A meta‐analysis of national research: Effects of teaching strategies on student achievement in science in the United States. Journal of Research in Science Teaching: The Official Journal of the National Association for Research in Science Teaching, 44(10), 1436-1460.
The importance of soft skills: Education beyond academic knowledge.
This paper makes a survey of the importance of soft skills in students’ lives both at college and after college. It discusses how soft skills complement hard skills, which are the technical requirements of a job the student is trained to do.
Schulz, B. (2008). The importance of soft skills: Education beyond academic knowledge.
Preparing a pipeline of effective principals: A legislative approach
Using examples from states throughout the country, this guidebook from the National Conference of State Legislatures describes six key areas in which state legislators can take action to improve the quality of leadership in public schools
Shelton, S. V. (2012). Preparing a pipeline of effective principals: A legislative approach. National Conference of State Legislatures.
Teams in the Military: A Review and Emerging Challenges
the purpose of this chapter is to review the science of teams and their effectiveness, extrapolate critical lessons learned, and highlight several future challenges critical for military psychology to address in order to prepare future military teams for success.
Shuffler, M. L., Pavlas, D., & Salas, E. (2012). Teams in the military: A review and emerging challenges. In J. H. Laurence & M. D. Matthews (Eds.), The Oxford handbook of military psychology(pp. 282–310). Oxford, UK: Oxford University Press.
Evidence-based practices in classroom management: Considerations for research to practice.
The purpose of this paper is to describe a systematic literature search to identify evidence-based classroom management practices.
Simonsen, B., Fairbanks, S., Briesch, A., Myers, D., & Sugai, G. (2008). Evidence-based practices in classroom management: Considerations for research to practice. Education and Treatment of Children, 31(3), 351-380.
Initial validation of the Classroom Management Observation Tool
Effective classroom management is critical for student and teacher success. Because teachers receive limited preservice preparation and in-service support in classroom management, educational leaders (e.g., school psychologists, behavior coaches, mentor teachers, and administrators) need efficient and effective tools to identify teachers’ strengths and needs and to guide professional development.
Simonsen, B., Freeman, J., Kooken, J., Dooley, K., Gambino, A. J., Wilkinson, S., ... & Kern, L. (2020). Initial validation of the Classroom Management Observation Tool (CMOT). School Psychology, 35(3), 179.
Teacher self-efficacy and teacher burnout: A study of relations
The purpose of this study was partly to test the factor structure of a recently developed Norwegian scale for measuring teacher self-efficacy and partly to explore relations between teachers' perception of the school context, teacher self-efficacy, collective teacher efficacy, teacher burnout, teacher job satisfaction, and teachers' beliefs that factors external to teaching puts limitations to what they can accomplish.
Skaalvik, E. M., & Skaalvik, S. (2010). Teacher self-efficacy and teacher burnout: A study of relations. Teaching and teacher education, 26(4), 1059-1069.
Teacher job satisfaction and motivation to leave the teaching profession: Relations with school context, feeling of belonging, and emotional exhaustion.
This study examines the relations between school context variables and teachers’ feeling of belonging, emotional exhaustion, job satisfaction, and motivation to leave the teaching profession. Six aspects of the school context were measured: value consonance, supervisory support, relations with colleagues, relations with parents, time pressure, and discipline problems.
Skaalvik, E. M., & Skaalvik, S. (2011). Teacher job satisfaction and motivation to leave the teaching profession: Relations with school context, feeling of belonging, and emotional exhaustion. Teaching and teacher education, 27(6), 1029-1038.
Science and human behavior
The psychology classic—a detailed study of scientific theories of human nature and the possible ways in which human behavior can be predicted and controlled.
Skinner, B. F. (1965). Science and human behavior (No. 92904). Simon and Schuster.
Retrieval practice protects memory against acute stress.
A commentary on: Retrieval practice protects memory against acute stress
Smith, A. M., Floerke, V. A., & Thomas, A. K. (2016). Retrieval practice protects memory against acute stress. Science, 354(6315), 1046-1048.
Teacher expectations.
The purpose of this paper is to integrate statistically the results of the literature on teacher expectations.
Smith, M. L. (1980). Teacher expectations. Evaluation in Education, 4, 53-55.
Teaching critical thinking and problem solving skills.
Several barriers can impede critical thinking instruction. However, actively engaging students in project-based or collaborative activities can encourage students’ critical thinking development if instructors model the thinking process, use effective questioning techniques, and guide students’ critical thinking processes.
Snyder, L. G., & Snyder, M. J. (2008). Teaching critical thinking and problem solving skills. The Journal of Research in Business Education, 50(2), 90.
Managing conflict in school teams: The impact of task and goal interdependence on conflict management and team effectiveness
The present study explores conflict management as a team phenomenon in schools. The author examined how the contextual variables (task interdependence, goal interdependence) are related to team conflict management style (integrating vs. dominating) and school team effectiveness (team performance).
Somech, A. (2008). Managing conflict in school teams: The impact of task and goal interdependence on conflict management and team effectiveness. Educational administration quarterly, 44(3), 359-390.
What Science Offers Teachers of Reading
This article examine what science offers general and special educators who teach reading then review some well‐established scientific findings about reading and their practical implications, not only for children with reading disabilities, but for other children as well.
Spear‐Swerling, L., & Sternberg, R. J. (2001). What science offers teachers of reading. Learning Disabilities Research & Practice, 16(1), 51-57.
Evidence-based Practice: A Framework for Making Effective Decisions.
Evidence-based practice is a decision-making framework. This paper describes the relationships among the three cornerstones of this framework.
Spencer, T. D., Detrich, R., & Slocum, T. A. (2012). Evidence-based Practice: A Framework for Making Effective Decisions. Education & Treatment of Children (West Virginia University Press), 35(2), 127-151.
Does a longer school year or longer school day improve student achievement scores?
This reviews looks at the issue, do longer school days and longer school years improve student achievement?
States, J. (2011). Does a longer school year or longer school day improve student achievement scores? Retrieved from does-longer-school-year.
Why Education Practices Fail?
This paper examines a range of education failures: common mistakes in how new practices are selected, implemented, and monitored. The goal is not a comprehensive listing of all education failures but rather to provide education stakeholders with an understanding of the importance of vigilance when implementing new practices.
States, J., & Keyworth, R. (2020). Why Practices Fail. Oakland, CA: The Wing Institute. https://www.winginstitute.org/roadmap-overview
Classroom Management
In this overview, classroom management strategies have been grouped into four essential areas: rules and procedures, proactive management, well-designed and delivered instruction, and disruptive behavior management. These strategies are devised for use at both school and classroom levels.
States, J., Detrich, R. & Keyworth, R. (2017). Overview of Classroom Management.Oakland, CA: The Wing Institute. https://www.winginstitute.org/effective-instruction-classroom.
Classroom Management
In this overview, classroom management strategies have been grouped into four essential areas: rules and procedures, proactive management, well-designed and delivered instruction, and disruptive behavior management. These strategies are devised for use at both school and classroom levels.
States, J., Detrich, R. & Keyworth, R. (2017). Overview of Classroom Management.Oakland, CA: The Wing Institute. https://www.winginstitute.org/effective-instruction-classroom.
Effective Instruction Overview
A summary of the available studies accumulated over the past 40 years on a key education driver, teacher competencies offers practical strategies, practices, and rules to guide teachers in ways to improve instruction that improves student performance and the quality of the work experience.
States, J., Detrich, R. & Keyworth, R. (2017). Effective Instruction Overview. Oakland, CA: The Wing Institute. Retrieved from https://www.winginstitute.org/effective-instruction-overview
Teacher Soft Skills Overview
This overview examines the available research on the topic of soft skills (personal competencies) and how these proficiencies support the technical competencies required for success in school
States, J., Detrich, R. & Keyworth, R. (2018). Overview of Teacher Soft Skills.Oakland, CA: The Wing Institute. https://www.winginstitute.org/teacher-compentencies-soft-skills.
Active Student Responding (ASR)
Active Student Responding (ASR) is a strategies that designed to engage all students regardless of class size. ASR avoids the common problem of having only high achievers answer questions while low achievers remain silent, thus escaping detection. ASR strategies include; guided notes, response slates, response cards, and choral responding.
States, J., Detrich, R. & Keyworth, R. (2019). Active Student Responding (ASR) Overview.Oakland, CA: The Wing Institute. https://www.winginstitute.org/instructional-delivery-student-respond
Effective Teachers Make a Difference
This analysis examines the available research on effective teaching, how to impart these skills, and how to best transition teachers from pre-service to classroom with an emphasis on improving student achievement. It reviews current preparation practices and examine the research evidence on how well they are preparing teachers
States, J., Detrich, R. & Keywroth, R. (2012). Effective Teachers Make a Difference. In Education at the Crossroads: The State of Teacher Preparation (Vol. 2, pp. 1-46). Oakland, CA: The Wing Institute.
Multi-tiered systems of support and evidence-based practices
The purpose of this chapter is to present a combined research- and practice-based framework for integrating a comprehensive MTSS model with EBP, and thus, optimize the results stemming from school improvement efforts.
Stoiber, K. C., & Gettinger, M. (2016). Multi-tiered systems of support and evidence-based practices. In Handbook of response to intervention (pp. 121-141). Springer, Boston, MA.
Role of Leadership and culture in PBIS Implementation
This presentation slide describes the important role of leadership in effective, efficient, and relevant PBIS implementation
Sugai, G. (2013). Role of Leadership and culture in PBIS Implementation [PowerPoint slides]. Retrieved from http://www.pbis.org/common/cms/files/pbisresources/PBIS_Implementation_leadership_braiding_apr_11_2013_HAND.pdf
A contextual consideration of culture and school-wide positive behavior support
This article considers culture within the context of School-wide Positive Behavior Support. The paper provides an overview of culture and working definitions to assist educators to more effectively implement evidence-based practices.
Sugai, G., O’Keeffe, B. V., & Fallon, L. M. (2012). A contextual consideration of culture and school-wide positive behavior support. Journal of Positive Behavior Interventions, 14(4), 197-208. Can pd
Targeted reading intervention: A coaching model to help classroom teachers with struggling readers
This study examined the effectiveness of a classroom teacher intervention, the Targeted Reading Intervention (TRI), in helping struggling readers in kindergarten and first grade. This intervention used biweekly literacy coaching in the general education classroom to help classroom teachers use diagnostic strategies with struggling readers in one-on-one 15-min sessions.
Targeted reading intervention: A coaching model to help classroom teachers with struggling readers. Learning Disability Quarterly, 35, 102-114.
Best practices in school psychology III.
Increasingly, school services are being guided by a problem solving approach and are evaluated by the achievement of positive outcomes. This shift is explored here in 96 chapters and 11 appendices. The volume provides a comprehensive reference relating contemporary research and thought to quality professional services
Thomas, A., & Grimes, J. (Eds.). (1995). Best practices in school psychology III.Washington, DC: National Association of School Psychologists.
The evolution of school psychology to science-based practice: Problem solving and the three-tiered model.
This chapter chronicles some of the major steps school psychology has taken toward adopting science as the basis of practice. Each step has yielded benefits for students as well as practice challenges to be overcome.
Tilly, W. D. (2008). The evolution of school psychology to science-based practice: Problem solving and the three-tiered model. In A. Thomas & J. Grimes (Eds.), Best practices in school psychology–5(pp. 17–36). Bethesda, MD: National Association of School Psychologists.
Two meta-analyses exploring the relationship between teacher clarity and student learning.
This article reports the findings of two meta-analyses that explored the relationship between teacher clarity and student learning. Combined, the results suggest that teacher clarity has a larger effect for student affective learning than for cognitive learning. However, neither the effects for cognitive learning nor affective learning were homogeneous.
Titsworth, S., Mazer, J. P., Goodboy, A. K., Bolkan, S., & Myers, S. A. (2015). Two meta-analyses exploring the relationship between teacher clarity and student learning. Communication Education, 64(4), 385-418.
Reconcilable differences: Standards-based teaching and differentiation.
Standards-based instruction and differentiated learning can be compatible approaches in today's classrooms.
Tomlinson, C. A. (2000). Reconcilable differences: Standards-based teaching and differentiation. Educational Leadership, 58(1), 6–11. http://eric.ed.gov/?id=EJ614602
Virtual schools: The changing landscape of K–12 education in the U.S.
This paper examines some of the challenges and strengths of virtual schools, it offers questions to consider when deciding whether or not a virtual school option would be ideal, and it draws conclusions, which provide an outlook for the future of virtual schools in k-12 education.
Toppin, I. N., & Toppin, S. M. (2016). Virtual schools: The changing landscape of K–12 education in the U.S. Education and Information Technologies, 21(6), 1571–1581.
Individual Differences in Response to Early Interventions in Reading: The Lingering Problem of Treatment Resisters
Five recent studies of methods to prevent reading difficulties were examined in light of the goal that every child should acquire adequate word reading skills during early elementary school.
Torgesen, J. K. (2000). Individual differences in response to early interventions in reading: The lingering problem of treatment resisters. Learning Disabilities Research & Practice, 15(1), 55-64.
Managing Classroom Behavior to Maximize Student Learning
This is a detailed guide on managing classroom behavior to maximize student learning.
Teacher efficacy: It’s meaning and measure
The theoretical and empirical underpinnings of teacher efficacy are examined to bring coherence to the construct and its measurement. First, we explore the correlates of teacher efficacy revealed using various instruments and search for patterns that suggest a better understanding of the construct.
Tschannen-Moran, M., Hoy, A. W., & Hoy, W. K. (1998). Teacher efficacy: Its meaning and measure. Review of educational research, 68(2), 202-248.
A blueprint for schoolwide positive behavior support: Implementation of three components.
This article provides a case study (focus on an eighth-grader with autism) within a case study (focus on an urban middle school) in terms of the implementation of positive behavior support (PBS).
Turnbull, A., Bohanon, H., Griggs, P., Wickham, D., Sailor, W., Freeman, R., ... & Warren, J. (2002). A blueprint for schoolwide positive behavior support: Implementation of three components. Exceptional Children, 68(3), 377–402.
States granted waivers from No Child Left Behind allowed to reapply for renewal for 2014 and 2015 school years
As students and educators go back to school across the country, and as Congress continues to debate how to fix the law commonly known as No Child Left Behind, the U.S. Department of Education announced today that states whose waivers from certain provisions of federal education law will expire at the end of the 2013-2014 school year will soon be able to request renewals of their reform plans, for up to two more years.
U.S. Department of Education (2017). States granted waivers from No Child Left Behind allowed to reapply for renewal for 2014 and 2015 school years.
Preservice teachers’ perceived barriers to the implementation of a multicultural curriculum.
This study investigated preservice teachers' perceived barriers for implementing multicultural curriculum with preservice teachers as they began their teacher education program.
Van Hook, C. W. (2002). Preservice teachers' perceived barriers to the implementation of a multicultural curriculum. Journal of Instructional Psychology, 29(4), 254-265.
Are we making the differences that matter in education?
This paper argues that ineffective practices in schools carry a high price for consumers and suggests that school systems consider the measurable yield in terms of gains in student achievement for their schooling effort.
VanDerHeyden, A. (2013). Are we making the differences that matter in education. In R. Detrich, R. Keyworth, & J. States (Eds.),Advances in evidence-‐based education: Vol 3(pp. 119–138). Oakland, CA: The Wing Institute. Retrieved from http://www.winginstitute.org/uploads/docs/Vol3Ch4.pdf
Using data to advance learning outcomes in schools
This article describes the emergence and influence of evidence-based practice and data-based decision making in educational systems. This article describes the ways in which evidence-based practice (EBP) and response to intervention (RtI) can be used to improve efficacy, efficiency, and equity of educational services.
VanDerHeyden, A., & Harvey, M. (2013). Using data to advance learning outcomes in schools. Journal of Positive Behavior Interventions, 15(4), 205-213.
Redefining Learning Disabilities as Inadequate Response to Instruction: The Promise and Potential Problems
In this introduction to the special issue, a response-to-instruction approach to learning disabilities (LD) identification is discussed
Vaughn, S., & Fuchs, L. S. (2003). Redefining learning disabilities as inadequate response to instruction: The promise and potential problems. Learning disabilities research & practice, 18(3), 137-146.
Productive teaching
This literature review examines the impact of various instructional methods
Walberg H. J. (1999). Productive teaching. In H. C. Waxman & H. J. Walberg (Eds.) New directions for teaching, practice, and research (pp. 75-104). Berkeley, CA: McCutchen Publishing.
What Influences Learning? A Content Analysis Of Review Literature.
This is a meta-review and synthesis of the research on the variables related learning.
Wang, M. C., Haertel, G. D., & Walberg, H. J. (1990). What influences learning? A content analysis of review literature. The Journal of Educational Research, 30-43.
Leadership for data-based decision-making: Collaborative data teams, 2006
This article offers practical suggestions on how to build a data-based culture in schools.
Wayman, J. C., Midgley, S., & Stringfield, S. (2006). Leadership for data-based decision-making: Collaborative educator teams. Learner centered leadership: Research, policy, and practice, 189-206.
Impact of highly and less job-related diversity on work group cohesion and performance: A meta-analysis.
A meta-analysis of the data from empirical investigations of diversity in work groups was used to examine the impact of two types of diversity attributes, highly job-related and less-related, on work group cohesion and performance.
Webber, S. S., & Donahue, L. M. (2001). Impact of highly and less job-related diversity on work group cohesion and performance: A meta-analysis. Journal of management, 27(2), 141-162.
How schools matter: The link between teacher classroom practices and student academic performance
Quantitative studies of school effects have generally supported the notion that the problems of U.S. education lie outside of the school. Yet such studies neglect the primary venue through which students learn, the classroom. The current study explores the link between classroom practices and student academic performance by applying multilevel modeling to the 1996 National Assessment of Educational Progress in mathematics. The study finds that the effects of classroom practices, when added to those of other teacher characteristics, are comparable in size to those of student background, suggesting that teachers can contribute as much to student learning as the students themselves.
Wenglinsky, H. (2002). How schools matter: The link between teacher classroom practices and student academic performance. Education Policy Analysis Archives, 10(12).
An assessment of treatment integrity in behavioral intervention studies conducted with persons with mental retardation
The purpose of this study was to assess the degree to which behavioral intervention studies conducted with persons with mental retardation operationally defined the independent variables and evaluated and reported measures of treatment integrity. The study expands the previous work in this area reported by Gresham, Gansle, and Noell (1993) and Wheeler, Baggett, Fox, and Blevins (2006) by providing an evaluation of empirical investigations published in multiple journals in the fields of applied behavior analysis and mental retardation from 1996–2006. Results of the review indicated that relatively few of the studies fully reported data on treatment integrity.
Wheeler, J. J., Mayton, M. R., Carter, S. L., Chitiyo, M., Menendez, A. L., & Huang, A. (2009). An assessment of treatment integrity in behavioral intervention studies conducted with persons with mental retardation. Education and Training in Developmental Disabilities, 187-195.
A meta-analysis of the effects of direct instruction in special education
Studies of the effectiveness of Direct Instruction programs with special education students
were examined in a meta-analysis comparison. To be included, the outcomes had to be
compared with outcomes for some other treatment to which students were assigned prior to
any interventions. Not one of 25 studies showed results favoring the comparison groups.
Fifty-three percent of the outcomes significantly favored DI with an average magnitude of
effect of. 84 standard deviation units. The effects were not restricted to a particular handicapping condition, age group or skill area.
White, W. A. T. (1988). A meta-analysis of the effects of direct instruction in special education. Education and Treatment of Children, 11(4), 364–374.
Hard Thinking on Soft Skill
A prudent way forward for educators given the many acknowledged unknowns in soft skills reform is to substantially enhance efforts that fall within traditional school practices and responsibilities rather than to boldly make risky bets on unproven programs and measures. This paper breakdown the steps for school and district administrators.
Whitehurst, G. J. (2016). Hard thinking on soft skills. Evidence Speaks Reports, 1(14), 1-10.
The effects of extrinsic rewards in intrinsic motivation: A meta‐analysis.
Results of this meta‐analysis research, testing for a moderator effect, show that support for the overjustification effect occurs only when intrinsic motivation is operationalized as task behaviour during a free‐time measure.
Wiersma, U. (1992). The effects of extrinsic rewards in intrinsic motivation: A meta-analysis.
Scoping and sequencing educational resources and speech acts: A unified design framework for learning objects and educational discourse.
This paper looks at scope and sequence as essential to effective instruction Instructional.
Wiley, D., & Waters, S. (2005). Scoping and sequencing educational resources and speech acts: A unified design framework for learning objects and educational discourse. Interdisciplinary Journal of E-Learning and Learning Objects, 1(1), 143-150.
The Current Controversy About Teaching Reading: Comments for Those Left with Questions After Reading the New York Times Article.
This Op-Ed commentary by Daniel Willingham discusses the current knowledge base on effective reading instruction in the context of a recent New York Times article on the topic.
4 proven strategies for teaching empathy.
Help your students understand the perspectives of other people with these tried-and-tested methods.
Wilson, D., & Conyers, M. (2017). 4 proven strategies for teaching empathy.Edutopia. Retrieved from https://www.edutopia.org/article/4-proven-strategies-teaching-empathy-donna-wilson-marcus-conyers
Instructional Time Trends
In this Education Trends report, Education Commission of the States addresses some of the more frequent questions, including the impact of instructional time on achievement, variation in school start dates, and trends in school day and year length.
Woods, J. R. (2015). Instructional Time Trends. Education Trends. Education Commission of the States.
Time management: An experimental investigation.
Four groups of preservice teachers participating in student teaching seminars were randomly assigned to one of three conditions to test the effectiveness of brief training in time-management techniques.
Woolfolk, A. E., & Woolfolk, R. L. (1986). Time management: An experimental investigation. Journal of school Psychology, 24(3), 267-275.
Failing Teachers?
This book describes the research undertaken during the Teaching Competence Project, a two-year research project funded by the Gatsby Charitable Foundation. There were five interlinked studies in the research.
Wragg, E. C., Chamberlin, R. P., & Haynes, G. S. (2005). Failing teachers?. Routledge.
Decreased class size, increased active learning? Intended and enacted teaching strategies in smaller classrooms
Small class size is often used as an indicator of quality in higher education, and some research suggests that instructors in smaller classes more often use activities that are learner-centered and that involve physical and mental activity on the part of learners, such as group work, simulations, and case studies. However, we have little information on how instructors change their pedagogical practice when they teach in large- versus small-class settings.
Wright, M. C., Bergom, I., & Bartholomew, T. (2019). Decreased class size, increased active learning? Intended and enacted teaching strategies in smaller classes. Active Learning in Higher Education, 20(1), 51-62.
Educational battlefields in America: The tug-of-war over students' engagement with instruction.
This study shows that gaps between opportunities to learn and students' appropriation of those opportunities are instructionally produced and socially distributed via mechanism that affect engagement and lead to alienation from instruction - the dissociation between students' physical presence in academic classes and their thoughts while in class.
Yair, G. (2000). Educational battlefields in America: The tug-of-war over students' engagement with instruction. Sociology of Education, 247-269.
The Cost-Effectiveness of Five Policies for Improving Student Achievement
This study compares the effect size and return on investment for rapid assessment, between, increased spending, voucher programs, charter schools, and increased accountability.
Yeh, S. S. (2007). The cost-effectiveness of five policies for improving student achievement. American Journal of Evaluation, 28(4), 416-436.
Encouraging active learning can improve students’ performance on examinations
We tested the hypothesis that students in psychology of women classes would perform better on materials covered by multiple-choice exams when the first author presented these materials with active learning versus lecture, autonomous readings, and video presentations alone. Across 3 classes, we coded exam items according to how the instructor presented relevant materials and recorded classwide performance.
Yoder, J. D., & Hochevar, C. M. (2005). Encouraging active learning can improve students' performance on examinations. Teaching of psychology, 32(2), 91-95.
Using a curriculum-based instructional management system to enhance math achievement in urban schools
More than two-thirds of students living in U.S. low-income urban areas have not demonstrated basic levels of math achievement. Teachers are confronted with a difficult task of meeting the needs of an increasingly academically diverse population of urban students. There is a well-confirmed knowledge base on effective instruction, but teachers need massive amounts of information for effective, sustainable improvement and data-driven decision making.
Ysseldyke, J., Spicuzza, R., Kosciolek, S., Teelucksingh, E., Boys, C., & Lemkuil, A. (2003). Using a curriculum-based instructional management system to enhance math achievement in urban schools. Journal of Education for Students Placed at Risk, 8(2), 247-265.
National Institute of Child Health and Human Development
The panel was charged with providing a report that “should present the panel’s conclusions, an indication of the readiness for application in the classroom of the results of this research, and, if appropriate, a strategy for rapidly disseminating this information to facilitate effective reading instruction in the schools. If found warranted, the panel should also recommend a plan for additional research regarding early reading development and instruction.”
|
Eunice Kennedy Shriver National Institute of Child Health and Human Development, National Institutes of Health, Department of Health and Human Services. (2000). Report of the National Reading Panel: Teaching children to read: Reports of the subgroups (00-4754).
|
| |
|





