What are teacher competencies? Competencies are the skills and knowledge that enable a teacher to be successful. To maximize student learning, teachers must have expertise in a wide-ranging array of competencies in an especially complex environment where hundreds of critical decisions are required each day (Jackson, 1990). Few jobs demand the integration of professional judgment and the proficient use of evidence-based competencies as does teaching.
Why is this important? The transformational power of an effective teacher is something many of us have experienced. Intuitively, the link between teaching and student academic achievement may seem obvious, but what is the evidence for it?
Research confirms this common perception of a link and reveals that of all factors under the control of a school, teachers are the most powerful influence on student success (Babu & Mendro, 2003; Sanders & Rivers, 1996). What separates effective teachers from ineffective ones, and how can this information be used to support better teaching? We can now begin to build a profile of exemplary classroom instruction derived from effectiveness research (Wenglinsky, 2002; Hattie, 2009).
Which competencies make the biggest difference? An examination of the research on education practices that make a difference shows that four classes of competencies yield the greatest results.
- Instructional delivery
- Classroom management
- Formative assessment
- Personal competencies (soft skills)
Further, the research indicates that these competencies can be used to organize the numerous specific skills and knowledge available for building effective teacher development.
Instructional delivery: Research tells us what can be expected from a teacher employing instructional strategies and practices that are proven to lead to increased mastery of lessons. Better learning happens in a dynamic setting in which teachers offer explicit active instruction than in situations in which teachers do not actively guide instruction and instead turn control over content and pace of instruction to students (Hattie, 2009).
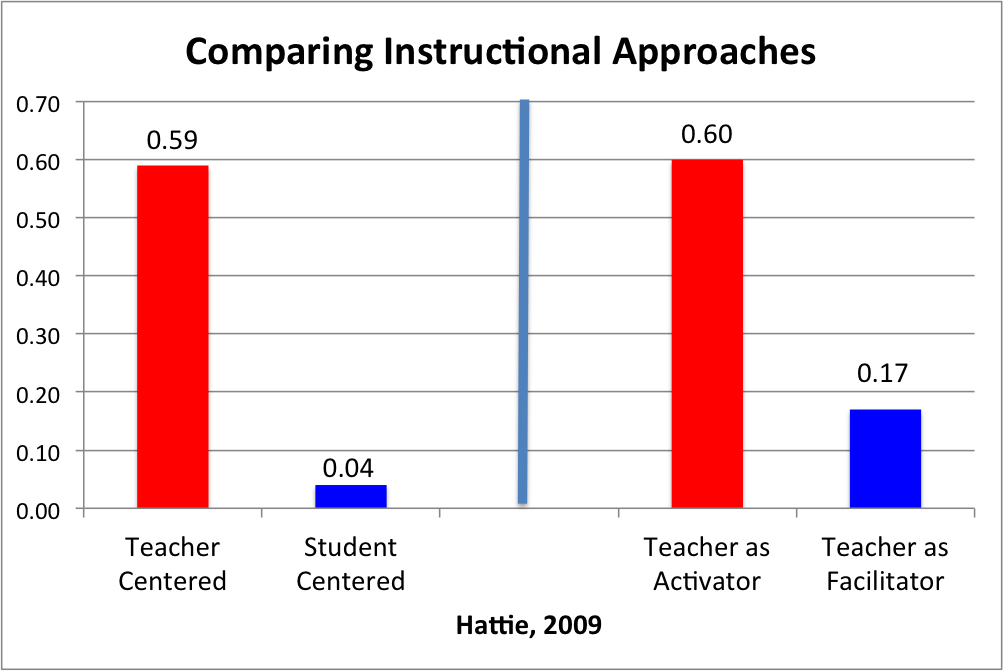
Is there a diverse set of practices that teachers can efficiently and effectively use to increase mastery of content for a variety of curricula? The structured and systematic approach of explicit instruction emphasizes mastery of the lesson to ensure that students understand what has been taught, become fluent in new material, and can generalize what they learn to novel situations they encounter in the future.
The following are hallmarks of an explicit approach for teachers (Archer & Hughes, 2011; Knight, 2012).
- Teacher selects the learning area to be taught.
- Teacher sets criteria for success.
- Teacher informs students of criteria ahead of the lesson.
- Teacher demonstrates to the students successful use of the knowledge/skills through modeling.
- Teacher evaluates student acquisition.
- Teacher provides remedial opportunities for acquiring the knowledge/skills, if necessary.
- Teacher provides closure at the end of the lesson.
A common complaint of an explicit instruction approach is that it does not offer sufficient opportunities for students to build on acquired knowledge/skills in creative and novel ways that help them to assimilate the material. The reality is that all effective instruction, regardless of philosophy, must aid students in generalizing newly taught knowledge/skills in a context that is greater than a single lesson. An explicit model accomplishes the goal of building toward “big ideas” by first emphasizing mastery of foundation skills such as reading and mathematics, and then systematically introducing opportunities to integrate these critical skills in discovery-based lessons to maximize students’ experience of success.
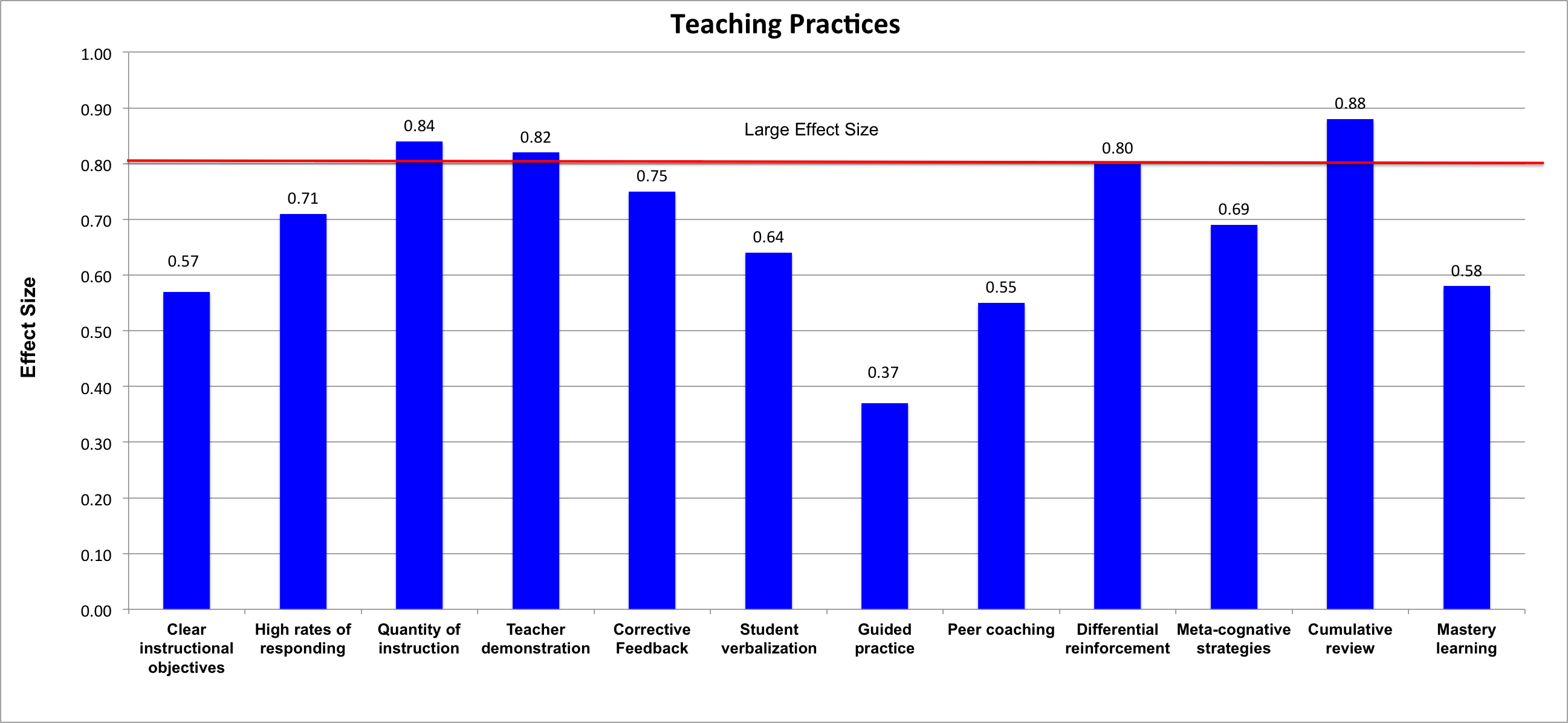
Effective explicit instruction practices include these features.
- Well-designed and planned instruction: Instruction that is well planned moves students from their current level of competency toward explicit criteria for success.
- Instructional design with clear instructional objectives: The teacher should present these objectives to students for each lesson.
- Scope and sequencing: The teacher should teach the range of related skills and the order in which they should be learned.
- Instruction that offers sufficient opportunities for successful acquisition:
- High rates of responding for each student to practice the skill: The teacher should provide sufficient opportunities for unpunished errors and ample reinforcement for success.
- Sufficient quantity of instruction: The teacher should allocate enough time to teach a topic.
- Teaching to mastery: Students need to learn the knowledge/skills to criteria that are verified by teachers or students’ peers.
- Teaching foundation knowledge/skills that become the basis for teaching big ideas: Current lessons should be built on past knowledge to increase fluency and maintain mastery of material. The teacher should relate lessons to complex issues and big ideas that provide deeper meaning and give students better understanding of the content.
View graph detail
Classroom management: Classroom management is one of the most persistent areas of concern voiced by school administrators, the public, and teachers (Evertson & Weinstein, 2013). Research consistently places classroom management among the top five issues that affect student achievement.
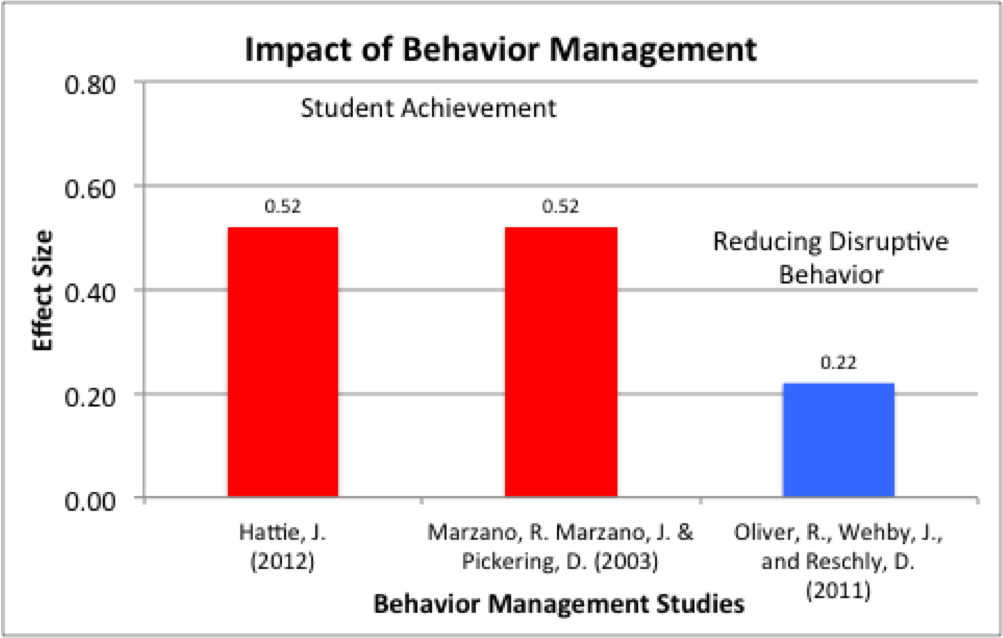
To put its in perspective, classroom management was associated with an increase of 20% in student achievement when classroom rules and procedures were applied systematically (Hattie, 2005).
A good body of research highlights four important areas that classroom teachers should be proficient in to create a climate that maximizes learning and induces a positive mood and tone.
- Rules and procedures: Effective rules and procedures identify expectations and appropriate behavior for students. To be effective, these practices must be observable and measurable.
- Schoolwide rules and procedures: Clearly stated rules identify, define, and operationalize acceptable behavior specific to a school. These rules, applicable to all students, are designed to build pro-social behavior and reduce problem behavior in a school. They distinguish appropriate from problem behavior as well as specify consequences for infractions.
- Classroom rules and procedures: Another set of clearly stated rules establishes acceptable behavior specific in a classroom. These rules need to be consistent with schoolwide rules, but may be unique to meet the needs of an individual classroom.
- Proactive classroom management: These are the practices that teachers and administrators can employ to teach and build acceptable behavior that is positive and helpful, promotes social acceptance, and leads to greater success in school. The key to proactive classroom management is active teacher supervision. The practice elements that constitute active supervision require staff to observe and interact with students regularly. The goal is to build a positive teacher-student relationship by providing timely and frequent positive feedback for appropriate behavior, and to swiftly and consistently respond to inappropriate behaviors.
- Effective classroom instruction: The key to maintaining a desirable classroom climate is to provide students with quality instructional delivery aligned to the skill level of each student. This enables students to experience success and keeps them attentive.
- Behavior reduction: These practices, designed to reduce problem and unacceptable behavior, are employed in the event the first three strategies fail. Behavior reduction strategies include giving students corrective feedback at the time of an infraction, minimizing reinforcement of a student’s unacceptable behavior, and guiding students in how to behave appropriately.
Formative assessment: Effective ongoing assessment, referred to in education literature as formative assessment and progress monitoring, is indispensable in promoting teacher and student success. It is frequently listed at the top of interventions for school improvement (Walberg, 1999).
Feedback, a core component of formative assessment, is recognized as an essential tool for improving performance in sports, business, and education. Hattie (2009) identified feedback as the single most powerful educational tool available for improving student performance, with a medium to large effect size ranging from 0.66 to 0.94.
Formative assessment consists of a range of formal and informal diagnostic testing procedures, conducted by teachers throughout the learning process, for modifying teaching and adapting activities to improve student attainment. Systemic interventions such as Response to Intervention (RtI) and Data-Based Decision Making depend heavily on the use of formative assessment (Hattie, 2009; Marzano, Pickering, & Pollock, 2001).
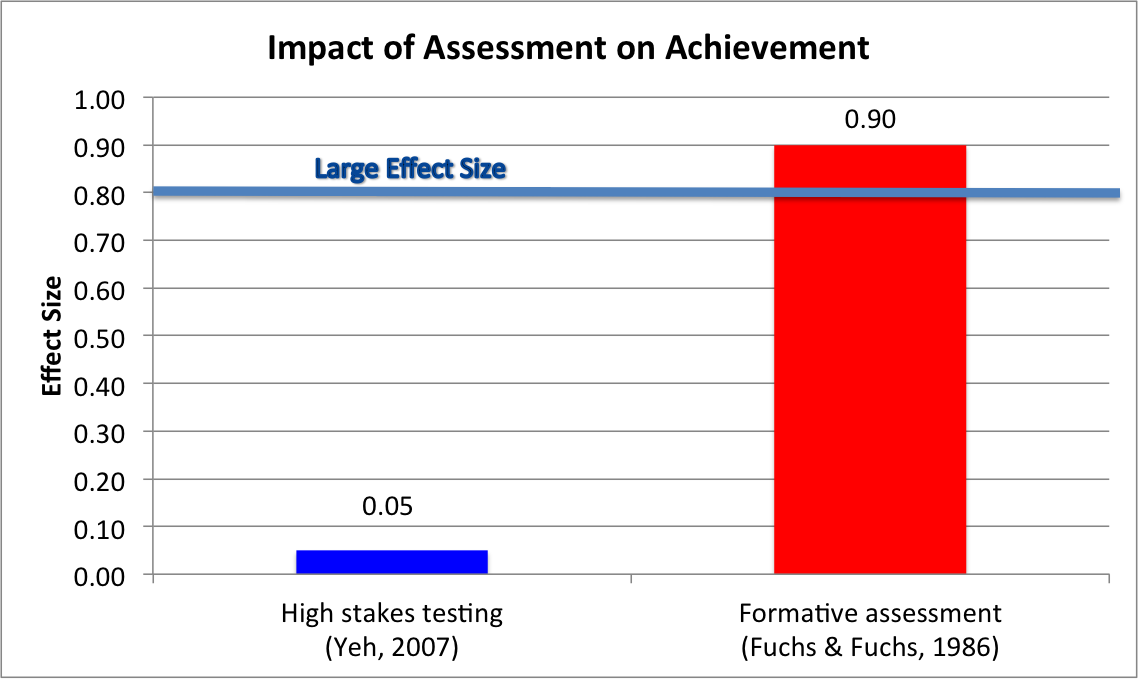
The following are the practice elements of formative assessment (Fuchs & Fuchs, 1986).
- Assessment: (Effect size 0.26) Assessing a student’s performance throughout a lesson offers a teacher insight into who is succeeding and who is falling behind. It is important that teachers collect and maintain data gained through both informal and formal assessments.
- Data display: (Effect size 0.70) Displaying the data in the form of a graphic has a surprisingly powerful effect on formative assessment’s usefulness as a tool.
- Data analysis following defined rules: (Effect size 0.90) Formative assessment is most valuable when teachers use evidence-based research and their own professional judgment to develop specific remedial interventions, before it is too late, for those falling behind.
Personable competencies (soft skills): An inspiring teacher can affect students profoundly by stimulating their interest in learning. It is equally true that most students have encountered teachers who were uninspiring and for whom they performed poorly. Unfortunately, effective and ineffective teachers have no readily discernable personality differences. Some of the very best teachers are affable, but many ineffective instructors can be personable and caring. Conversely, some of the best teachers appear as stern taskmasters, but whose influence is enormous in motivating students to accomplish things they never thought possible.
What soft skills do successful teachers have in common? Typically, the finest teachers display enthusiasm and excitement for the subjects they teach. More than just generating excitement, they provide a road map for students to reach the goals set before them. The best teachers are proficient in the technical competencies of teaching: instructional delivery, formative assessment, and classroom management. Equally significant, they are fluent in a multilayered set of social skills that students recognize and respond to, which leads to greater learning (Attakorn, Tayut, Pisitthawat, & Kanokorn, 2014). These skills must be defined as clear behaviors that teachers can master for use in classrooms.
Indispensable soft skills include:
- Establishing high but achievable expectations
- Encouraging a love for learning
- Listening to others
- Being flexible and capable of adjusting to novel situations
- Showing empathy
- Being culturally sensitive
- Embedding and encouraging higher order thinking along with teaching foundation skills
- Having a positive regard for students
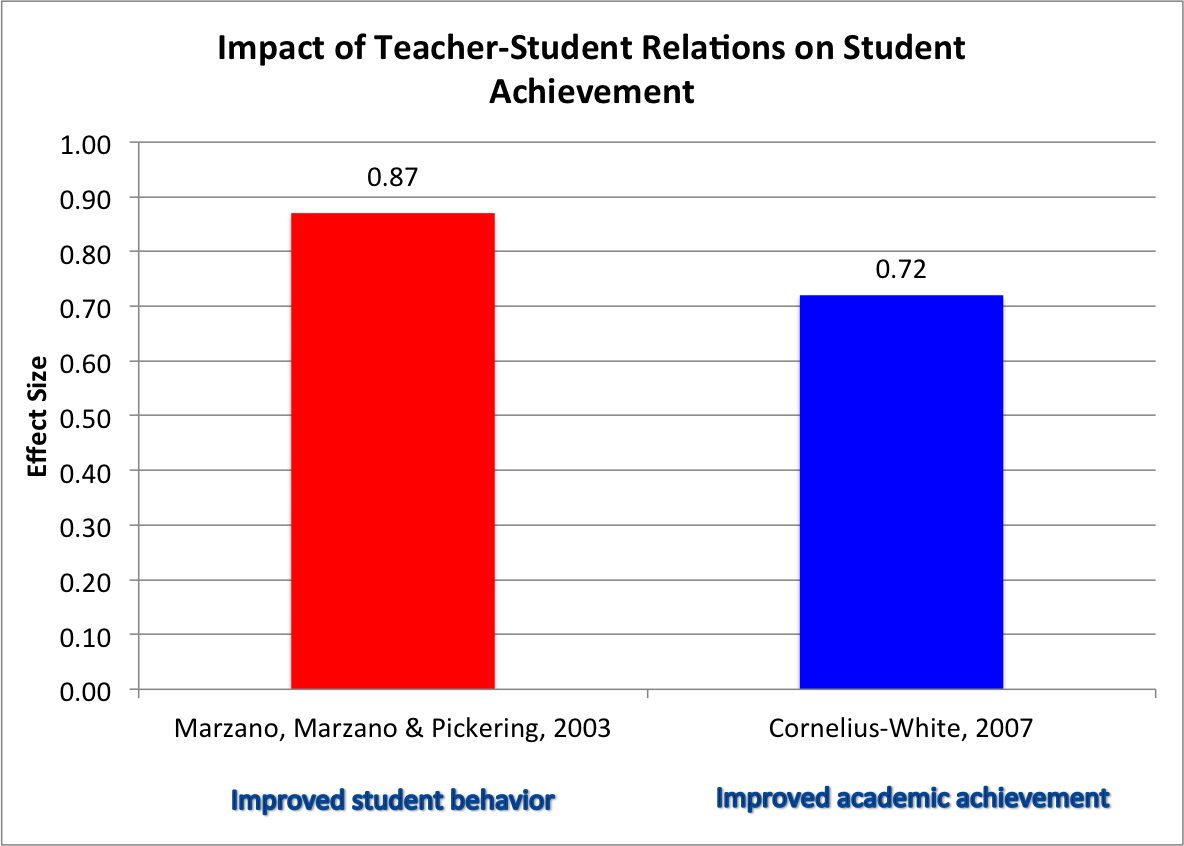
What does research tell us about personal competencies? Quantitative studies provide an overall range of effect sizes from 0.72 to 0.87 for effective teacher-student relations. Better teacher-student relations promote increased student academic performance and improve classroom climate by reducing disruptive student behavior (Cornelius-White, 2007; Marzano, Marzano & Pickering, 2003).
Conclusion
There is abundant research to support the notion that teachers play the critical role in improving student achievement in schools. What teachers do in the classroom is crucial in this process. The breadth of high-quality research accumulated over the past 40 years offers educators a clear picture of how to maximize teacher competency in four critical categories: instructional delivery, classroom management, formative assessment, and personal competencies. There is now ample evidence to recommend these competencies as the core around which to build teacher preparation, teacher hiring, teacher development, and teacher and school evaluations.
Citations
Archer, A. L., & Hughes, C. A. (2011). Explicit instruction: Efficient and effective teaching. New York, NY: Guilford Publications.
Attakorn, K., Tayut, T., Pisitthawat, K., & Kanokorn, S. (2014). Soft skills of new teachers in the secondary schools of Khon Kaen Secondary Educational Service Area 25, Thailand. Procedia—Social and Behavioral Sciences, 112, 1010–1013.
Babu, S., & Mendro, R. (2003). Teacher accountability: HLM-based teacher effectiveness indices in the investigation of teacher effects on student achievement in a state assessment program. Presented at the annual meeting of the American Educational Research Association (AERA), Chicago, IL, April.
Cornelius-White, J. (2007). Learner-centered teacher-student relationships are effective: A meta-analysis. Review of educational research, 77(1), 113–143.
Evertson, C. M., & Weinstein, C. S. (Eds.). (2013). Handbook of classroom management: Research, practice, and contemporary issues. New York, NY: Routledge.
Fuchs, L. S., & Fuchs, D. (1986). Effects of systematic formative evaluation: A meta-analysis. Exceptional Children, 53(3), 199–208.
Hattie, J., (2009). Visible learning: A synthesis of over 800 meta-analyses related to achievement. New York, NY: Routledge.
Jackson, P. W. (1990). Life in classrooms. New York, NY: Teachers College Press.
Knight, J. (2012). High-impact instruction: A framework for great teaching. Thousand Oaks, CA: Corwin Press.
Marzano, R. J., Marzano, J. S., & Pickering, D. (2003). Classroom management that works: Research-based strategies for every teacher. Alexandria, VA: Association for Supervision and Curriculum Development (ASCD).
Marzano, R. J., Pickering, D., & Pollock, J. E. (2001). Classroom instruction that works: Research-based strategies for increasing student achievement. Alexandria, VA: Association for Supervision and Curriculum Development (ASCD).
Sanders, W. L., & Rivers, J. C. (1996). Cumulative and residual effects of teachers on future student academic achievement. Knoxville, TN: University of Tennessee Value-Added Research and Assessment Center. Retrieved from http://heartland.org/policy-documents/cumulative-and-residual-effects-teachers-future-student-academic-achievement.
Walberg, H. (1999). Productive teaching. In H. C. Waxman & H. J. Walberg (Eds.), New directions for teaching practice and research (pp. 75–104). Berkeley, CA: McCutchen Publishing.
Wenglinsky, H. (2002). How schools matter: The link between teacher classroom practices and student academic performance. Education Policy Analysis Archives, 10(12).
White, W. A. T. (1988). A meta-analysis of the effects of direct instruction in special education. Education and Treatment of Children, 11(4), 364–374.
Yeh, S. S. (2007). The cost-effectiveness of five policies for improving student achievement. American Journal of Evaluation, 28(4), 416–436.
Publications
TITLE
SYNOPSIS
CITATION
LINK
Curriculum Content for Teacher Training Overview
A substantial body of evidence is available to guide teacher preparation programs in developing a pre-service curriculum based on universal skills needed for success across settings, age ranges, and subjects being taught. These skills include instructional delivery, classroom management, formative assessment, and personal competencies (soft skills)
Cleaver, S., Detrich, R., States, J. & Keyworth, R. (2021). Curriculum Content for Teacher Training Overview . Oakland, CA: The Wing Institute. https://www.winginstitute.org/pre-service-teacher-curriculum-content.
Treatment Integrity: Fundamental to Education Reform
To produce better outcomes for students two things are necessary: (1) effective, scientifically supported interventions (2) those interventions implemented with high integrity. Typically, much greater attention has been given to identifying effective practices. This review focuses on features of high quality implementation.
Detrich, R. (2014). Treatment integrity: Fundamental to education reform. Journal of Cognitive Education and Psychology, 13(2), 258-271.
Improving Educational Outcomes in America: Can A Low-Tech, Generic Teaching Practice Make A Difference
Heward and Wood consider a range of instructional practices that were identified by participants of the eighth Wing Institute summit and make an argument that Active Student Responding (ASR) has the potential to significantly improve student learning. The authors consider ASR in the context of the positive benefits and the cost considerations including equipment/materials, training, logistical fit, and the fit with the teacher's belief about effective instruction.
Heward, W.L. & Wood, C.L. (2015). Improving Educational Outcomes in America: Can A Low-Tech, Generic Teaching Practice Make A Difference Retrieved from ../../uploads/docs/2013WingSummitWH.pdf.
Introduction: Proceedings from the Wing Institute’s Fifth Annual Summit on Evidence-Based Education: Education at the Crossroads: The State of Teacher Preparation.
This article shared information about the Wing Institute and demographics of the Summit participants. It introduced the Summit topic, sharing performance data on past efforts of school reform that focused on structural changes rather than teaching improvement. The conclusion is that the system has spent enormous resources with virtually no positive results. The focus needs to be on teaching improvement.
Keyworth, R., Detrich, R., & States, J. (2012). Introduction: Proceedings from the Wing Institute’s Fifth Annual Summit on Evidence-Based Education: Education at the Crossroads: The State of Teacher Preparation. In Education at the Crossroads: The State of Teacher Preparation (Vol. 2, pp. ix-xxx). Oakland, CA: The Wing
Proceedings from the Wing Institute’s Fifth Annual Summit on Evidence-Based Education: Education at the Crossroads: The State of Teacher Preparation
This article shared information about the Wing Institute and demographics of the Summit participants. It introduced the Summit topic, sharing performance data on past efforts of school reform that focused on structural changes rather than teaching improvement. The conclusion is that the system has spent enormous resources with virtually no positive results. The focus needs to be on teaching improvement.
Keyworth, R., Detrich, R., & States, J. (2012). Introduction: Proceedings from the Wing Institute’s Fifth Annual Summit on Evidence-Based Education: Education at the Crossroads: The State of Teacher Preparation. In Education at the Crossroads: The State of Teacher Preparation (Vol. 2, pp. ix-xxx). Oakland, CA: The Wing
Classroom Management
In this overview, classroom management strategies have been grouped into four essential areas: rules and procedures, proactive management, well-designed and delivered instruction, and disruptive behavior management. These strategies are devised for use at both school and classroom levels.
States, J., Detrich, R. & Keyworth, R. (2017). Overview of Classroom Management.Oakland, CA: The Wing Institute. https://www.winginstitute.org/effective-instruction-classroom.
Effective Teachers Make a Difference
This analysis examines the available research on effective teaching, how to impart these skills, and how to best transition teachers from pre-service to classroom with an emphasis on improving student achievement. It reviews current preparation practices and examine the research evidence on how well they are preparing teachers
States, J., Detrich, R. & Keywroth, R. (2012). Effective Teachers Make a Difference. In Education at the Crossroads: The State of Teacher Preparation (Vol. 2, pp. 1-46). Oakland, CA: The Wing Institute.
Seven Habits of Superhero Teachers
This commentary review the critical competencies for teacher success in the classroom.
Twyman, J. S. (2013) Seven Habits of Superhero Teachers. Wing Institute. Date accessed: 5/7/14.
Are we making the differences that matter in education?
This paper argues that ineffective practices in schools carry a high price for consumers and suggests that school systems consider the measurable yield in terms of gains in student achievement for their schooling effort.
VanDerHeyden, A. (2013). Are we making the differences that matter in education. In R. Detrich, R. Keyworth, & J. States (Eds.),Advances in evidence-‐based education: Vol 3(pp. 119–138). Oakland, CA: The Wing Institute. Retrieved from http://www.winginstitute.org/uploads/docs/Vol3Ch4.pdf
Data Mining
TITLE
SYNOPSIS
CITATION
LINK
How Much Formal Training Do Teachers Get?
The analysis reviews school teacher earned degree data obtained from the National Center for Education Statistics (NCES) Digest of Education Statistics (2008).
Keyworth, R. (2010). How Much Formal Training Do Teachers Get? Retrieved from how-much-formal-training.
How important is it for teachers to receive subject matter training in order to obtain a teaching credential?
This inquiry lookes at two meta-analyses on the importance of subject matter training in teacher pre-service instruction.
States, J. (2010). How important is it for teachers to receive subject matter training in order to obtain a teaching credential? Retrieved from how-important-is-it.
How important in increasing student achievement is the training of teachers in the subject matter they will teach students?
This literature review tries to answer the question; does the quality and amount of subject matter pre-service training translate into better qualified teachers?
States, J. (2011). How important in increasing student achievement is the training of teachers in the subject matter they will teach students? Retrieved from how-important-in-increasing.
How Effective Are Principals in Assessing Teacher Skills?
This is an examination of a tool used for assessing principal's accuracy in determining teacher’s abilities to effectively deliver instruction in a classroom.
States, J. (2012). How Effective Are Principals in Assessing Teacher Skills? Retrieved from how-effective-are-principals.
What are the key factors that influence student achievement?
This is an analysis of a meta-analysis by Marzano, Waters, and McNulty undertaken to ascertain crticial factors that lead to higher student achievement.
States, J. (2012). What are the key factors that influence student achievement? Retrieved from what-are-key-factors.
Presentations
TITLE
SYNOPSIS
CITATION
LINK
Effective Teaching Practices: Narrowing the Field
This paper distills the research on effective teaching practices to basic assumptions and core practices. It presents a impact-cost paradigm for rating and prioritizing such practices.
Heward, W. (2013). Effective Teaching Practices: Narrowing the Field [Powerpoint Slides]. Retrieved from 2013-wing-presentation-william-heward.
What We Know About Teacher Preparation Programs
This paper examines effective teaching, how to impart these skills, and how to best transition teachers into the classroom. Preparation practices are analyzed to determine how well we are succeeding in preparing teachers.
States, J. (2010). What We Know About Teacher Preparation Programs [Powerpoint Slides]. Retrieved from 2010-aba-presentation-jack-states.
TITLE
SYNOPSIS
CITATION
LINK
Behavioral Consultation and Therapy
The book is written for individuals interested in procedures for increasing consultation skills to assist parents, teachers, and other socialization agents to solve mental health and educational problems of children and youths.
Bergan, J. R., & Kratochwill, T. R. (1990). Applied clinical psychology. Behavioral consultation and therapy. New York, NY, US: Plenum Press.
Relationships matter: Linking teacher support to student engagement and achievement
This study was guided by a reduced version of the Self-System Process Model developed by Connell. This paper report the optimal and risk thresholds for the Student Performance and Commitment Index (SPCI) and engagement, and then data on how much engagement matters for later success in school are presented.
Klem, A. M., & Connell, J. P. (2004). Relationships matter: Linking teacher support to student engagement and achievement. Journal of school health, 74(7), 262-273.
Learner-centered teacher-student relationships are effective: A meta-analysis
This is a meta-analysis that examines teacher-student relations impact on student performance.
Learner-centered teacher-student relationships are effective: A meta-analysis Retrieved from http://rer.sagepub.com/content/77/1/113.full?patientinform-links=yes&legid=sprer;77/1/113.
The relative impact of long and short reprimands on children's off-task behavior in the classroom.
This study compared the impact of long and short reprimands on children's off-task behavior in a classroom.
Abramowitz, A. J., O'Leary, S. G., & Futtersak, M. W. (1988). The relative impact of long and short reprimands on children's off-task behavior in the classroom. Behavior Therapy, 19(2), 243-247.
Teachers’ subject matter knowledge as a teacher qualification: A synthesis of the quantitative literature on students’ mathematics achievement
The main focus of this study is to find different kinds of variables that might contribute to variations in the strength and direction of the relationship by examining quantitative studies that relate mathematics teachers’ subject matter knowledge to student achievement in mathematics.
Ahn, S., & Choi, J. (2004). Teachers' Subject Matter Knowledge as a Teacher Qualification: A Synthesis of the Quantitative Literature on Students' Mathematics Achievement. Online Submission.
Distraction, privacy, and classroom design
Environmental features of elementary school classrooms are examined in relation to distraction and privacy. Teachers' adjustments of their activities to make their settings less distracting are also explored.
Ahrentzen, S., & Evans, G. W. (1984). Distraction, privacy, and classroom design. Environment and Behavior, 16(4), 437-454.
Teaching naming relatives to individuals with autism using simultaneous prompting
This study examines the effectiveness of simultaneous prompting in teaching naming relatives to
Akmanoglu-Uludag, N., & Batu, S. (2005). Teaching naming relatives to individuals with autism using simultaneous prompting. Education and Training in Developmental Disabilities, 40(4), 401.
Teachers Matter: Evidence from Value-Added Assessments.
Value-added assessment proves that very good teaching can boost student learning and that family background does not determine a student's destiny. Students taught by highly effective teachers several years in a row earn higher test scores than students assigned to particularly ineffective teachers.
American Education Research Association (AERA). (2004). Teachers matter: Evidence from value-added assessments. Research Points, 2(2). Retrieved from http://www.aera.net/ Portals/38/docs/Publications/Teachers%20Matter.pdf
K–12 online and blended teacher licensure: Striking a balance between policy and preparedness.
This article explores the theoretical underpinnings surrounding quality teaching in online settings as well as practical considerations for what teachers should know and be able to do in online environments.
Archambault, L., DeBruler, K., & Freidhoff, J. (2014). K-12 online and blended teacher licensure: Striking a balance between policy and preparedness. Journal of Technology and Teacher Education, 22(1), 83-106. Retrieved from
https://www.academia.edu/6459023/K-12_Online_ and_blended _Teacher_licensure_Striking_a_balance_between_Policy_ and_Preparedness
Explicit Instruction: Effective and Efficient Teaching
This book gives special and general education teachers the tools to implement explicit instruction in any grade level or content area. The authors provide clear guidelines for identifying key concepts, skills, and routines to teach; designing and delivering effective lessons; and giving students opportunities to practice and master new material.
Archer, A., & Hughes, C. A. (2011). Explicit instruction: Efficient and effective teaching. New York, NY: Guilford Publications.
Soft skills of new teachers in the secondary schools of Khon Kaen Secondary Educational Service Area 25, Thailand.
This research objective was to study soft skills of new teachers in the secondary schools of Khon Kaen Secondary Educational Service Area 25, Thailand. The data were collected from 60 purposive samples of new teachers by interviewing and questionnaires. The results of this study were informed that new teachers have all of soft skills at high level totally. Communicative skills were highest among seven of soft skills and next Life-long learning and information management skills, Critical and problem solving skills, Team work skills, Ethics, moral and professional skills, Leadership skills and Innovation invention and development skills were lowest in all skills. Based on the research findings obtained, the sub-skills of seven soft skills will be considered and utilized in the package of teacher development program of next research.
Attakorn, K., Tayut, T., Pisitthawat, K., & Kanokorn, S. (2014). Soft skills of new teachers in the secondary schools of Khon Kaen Secondary Educational Service Area 25, Thailand. Procedia-Social and Behavioral Sciences, 112, 1010-1013.
Soft skills of new teachers in the secondary schools of Khon Kaen Secondary Educational Service Area 25, Thailand.
This research objective was to study soft skills of new teachers in the secondary schools of Khon Kaen Secondary Educational Service Area 25, Thailand. The data were collected from 60 purposive samples of new teachers by interviewing and questionnaires. The results of this study were informed that new teachers have all of soft skills at high level totally. Communicative skills were highest among seven of soft skills and next Life-long learning and information management skills, Critical and problem solving skills, Team work skills, Ethics, moral and professional skills, Leadership skills and Innovation invention and development skills were lowest in all skills. Based on the research findings obtained, the sub-skills of seven soft skills will be considered and utilized in the package of teacher development program of next research.
Attakorn, K., Tayut, T., Pisitthawat, K., & Kanokorn, S. (2014). Soft skills of new teachers in the secondary schools of Khon Kaen Secondary Educational Service Area 25, Thailand. Procedia-Social and Behavioral Sciences, 112, 1010-1013.
Teacher–Student Relationship Climate and School Outcomes: Implications for Educational Policy Initiatives
This study examined whether associations between teacher policies and student achievement were mediated by the teacher–student relationship climate. Results of this study were threefold. These findings are discussed in light of their educational policy implications.
Barile, J. P., Donohue, D. K., Anthony, E. R., Baker, A. M., Weaver, S. R., & Henrich, C. C. (2012). Teacher–student relationship climate and school outcomes: Implications for educational policy initiatives. Journal of Youth and Adolescence, 41(3), 256-267.
A follow-up of Follow Through: The later effects of the Direct Instruction model on children in fifth and sixth grades.
The later effects of the Direct Instruction Follow Through program were assessed at five diverse sites. Low-income fifth and sixth graders who had completed the full 3 years of this first- through third-grade program were tested on the Metropolitan Achievement Test (Intermediate level) and the Wide Range Achievement Test (WRAT).
Becker, W. C., & Gersten, R. (1982). A follow-up of Follow Through: The later effects of the Direct Instruction Model on children in fifth and sixth grades. American Educational Research Journal, 19(1), 75-92.
Exploring the lecture method: An empirical study.
In this article aspects of lecturing are explored. Attention is given to explaining and to other strategies of lecturing and to the possibility of demarcating certain lecturing styles.
Behr, A. L. (1988). Exploring the lecture method: An empirical study. Studies in Higher Education, 13(2), 189-200.
Assertive supervision: Building involved teamwork.
This well-written book on assertiveness clearly describes the non assertive, assertive, and aggressive styles of supervision. Each chapter provides numerous examples, practice exercises, and self-tests. The author identifies feelings and beliefs that support aggressiveness, non aggressiveness, or non assertiveness which help the reader "look beyond the words themselves."
Black, M. K. (1991). Assertive Supervision-Building Involved Teamwork. The Journal of Continuing Education in Nursing, 22(5), 224-224.
Assessment and classroom learning
This paper is a review of the literature on classroom formative assessment.
Black, P., & Wiliam, D. (1998). Assessment and classroom learning. Assessment in education, 5(1), 7-74.
Assessment and classroom learning. Assessment in Education: principles, policy & practice
This is a review of the literature on classroom formative assessment. Several studies show firm evidence that innovations designed to strengthen the frequent feedback that students receive about their learning yield substantial learning gains.
Black, P., & Wiliam, D. (1998). Assessment and classroom learning. Assessment in Education: principles, policy & practice, 5(1), 7-74.
Human characteristics and school learning
This paper theorizes that variations in learning and the level of learning of students are determined by the students' learning histories and the quality of instruction they receive.
Bloom, B. (1976). Human characteristics and school learning. New York: McGraw-Hill.
Development and validation of the clarity indicators scale
This study was conducted to create a reliable and valid low- to medium-inference, multidimensional measure of instructor clarity from seminal work across several academic fields. The five factors were explored in regards to their ability to predict the outcomes. Implications for instructional communication researchers are discussed.
Bolkan, S. (2017). Development and validation of the clarity indicators scale. Communication Education, 66(1), 19-36.
Nine Competencies for Teaching Empathy.
The author shares nine teachable competencies that can serve as a principal's guide for empathy education. This paper will help answer which practices enhance empathy and how will principals know if teachers are implementing them effectively.
Borba, M. (2018). Nine Competencies for Teaching Empathy. Educational Leadership, 76(2), 22-28.
Achieving Equitable Accessing to Strong Teachers: A Guide for District Leaders
The purpose of this guide is to help district leaders take on the challenge of ensuring that students have equitable access to excellent teachers. It shares some early lessons the Education Trust has learned from districts about the levers available to prioritize low-income students and students of color in teacher quality initiatives. The guide outlines a seven-stage process that can help leaders define their own challenges, explore underlying causes, and develop strategies to ensure all schools and students have equitable access to effective teachers.
Bromberg, M. (2016). Achieving Equitable Access to Strong Teachers: A Guide for District Leaders. Education Trust.
Teacher behavior and student achievement
This paper, prepared as a chapter for the "Handbook of Research on Teaching" (third edition), reviews correlational and experimental research linking teacher behavior to student achievement. It focuses on research done in K-12 classrooms during 1973-83, highlighting several large-scale, programmatic efforts.
Brophy, J., & Good, T. L. (1984). Teacher Behavior and Student Achievement. Occasional Paper No. 73.
Amazing Results! Teacher Expectations and Student Achievement (TESA) Follow-Up Survey of TESA-Trained Teachers in 45 States and the District of Columbia.
This paper describes a survey of teachers trained in Teacher Expectations and Student Achievement (TESA). The study examined whether teachers: agreed that TESA interactions were useful with today's children; continued to practice the TESA coding and observation process after being trained; and would recommend TESA to colleagues.
Cantor, J., Kester, D., & Miller, A. (2000). Amazing Results! Teacher Expectations and Student Achievement (TESA) Follow-Up Survey of TESA-Trained Teachers in 45 States and the District of Columbia.
Direct Instruction Reading
This book provide detailed information on how to systematically and explicitly teach essential reading skills. The procedures describe in this text have been shown to benefit all student, especially powerful with the most vulnerable learners, children who are at risk because of poverty, disability, or limited knowledge of English.
Carnine, D., Silbert, J., Kameenui, E. J., & Tarver, S. G. (1997). Direct instruction reading. Columbus, OH: Merrill.
The Teacher's Craft: The 10 Essential Skills of Effective Teaching
This book provides evidence-based principles of effective teaching. College students preparing to teach, new teachers struggling to find their way, and experienced teachers eager to hone their skills will benefit from this set of commonsense principles that, when practiced together, will markedly improve student performance.
Chance, P. (2008). The teacher's craft: The 10 essential skills of effective teaching. Waveland PressInc.
Effectiveness of the practice style and reciprocal style of teaching: A meta-analysis
This meta-analysis looks at the effectiveness of two strategies in teaching motor skills to students: practice and reciprocal. The research examined two of the 11 teaching strategies identified in Mosston’s Spectrum of Teaching Styles designed for teachers in physical education. Six studies met the criteria for inclusion in this paper. The practice strategy involves the student in the decision-making process. The reciprocal strategy assigns each learner to a specific role: One learner performs the task and the other is the observer who offers immediate and ongoing feedback using a criteria sheet designed by the teacher. At the end of the practice, the students switch roles.
The study showed a very large effect size of 1.16 for the practice strategy, and a large effect size of 0.94 for the reciprocal strategy. It would not be surprising to see these particularly large effect sizes moderated in subsequent replication studies (Makel & Plucker, 2014; van Aert & van Assen, 2018). The study confirms previous research on reciprocal teaching as an effective instructional strategy. Reciprocal teaching has been found to be a powerful strategy for teaching reading and other academic subjects. John Hattie (1995) reported an effect size of 0.74 for reciprocal teaching. The takeaway from this meta-analysis is that practice and reciprocal styles have positive effects on motor skill acquisition.
Chatoupis, C., & Vagenas, G. (2018). Effectiveness of the practice style and reciprocal style of teaching: A meta-analysis. Physical Educator, 75(2), 175–194.
The Development of The Teacher Clarity Short Inventory (TCSI) to Measure Clear Teaching in The Classroom
This study presents the Teacher Clarity Short Inventory (TCSI) as an alternative to existing measures of teacher clarity. Analyses revealed a 10 item scale with an acceptable factor structure, acceptable reliability and validity.
Chesebro, J. L., & McCroskey, J. C. (1998). The development of the teacher clarity short inventory (TCSI) to measure clear teaching in the classroom. Communication Research Reports, 15(3), 262-266.
It’s easier to pick a good teacher than to train one: Familiar and new results on the correlates of teacher effectiveness
Neither holding a college major in education nor acquiring a master's degree is correlated with elementary and middle school teaching effectiveness, regardless of the university at which the degree was earned. Teachers generally do become more effective with a few years of teaching experience, but we also find evidence that teachers may become less effective with experience, particularly later in their careers.
Chingos, M. M., & Peterson, P. E. (2011). It's easier to pick a good teacher than to train one: Familiar and new results on the correlates of teacher effectiveness. Economics of Education Review, 30(3), 449-465.
A review of the time management literature. Personnel Review
The purpose of this article is to provide an overview for those interested in the current state‐of‐the‐art in time management research. The review demonstrates that time management behaviours relate positively to perceived control of time, job satisfaction, and health, and negatively to stress.
Claessens, B. J., Van Eerde, W., Rutte, C. G., & Roe, R. A. (2007). A review of the time management literature. Personnel Review, 36(2), 255–276.
Reconceptualizing behavior management and school-wide discipline in general education.
The purpose of this appear is to describe a school-wide staff development model that is based on a proactive instructional approach to solving problem behavior on a school-wide basis and utilizes effective staff development procedures.
Colvin, G., Kameenui, E. J., & Sugai, G. (1993). Reconceptualizing behavior management and school-wide discipline in general education. Education and treatment of children, 361-381.
Teacher-Delivered Strategies to Increase Students’ Opportunities to Respond: A Systematic Methodological Review.
This systematic review of the literature examines the evidence behind teacher-directed strategies to increase students’ opportunities to respond (OTR) during whole-group instruction.
Common, E. A., Lane, K. L., Cantwell, E. D., Brunsting, N. C., Oakes, W. P., Germer, K. A., & Bross, L. A. (2019). Teacher-delivered strategies to increase students’ opportunities to respond: A systematic methodological review. Behavioral Disorders, 0198742919828310.
Impact of the script in a supplemental reading program on instructional opportunities for student practice of specified skills
This study sought to investigate the impact of a supplemental program’s script on the rate of on-task and off-task instructional opportunities offered by the instructor for students to practice the specific skills targeted in lesson exercises.
Cooke, N. L., Galloway, T. W., Kretlow, A. G., & Helf, S. (2011). Impact of the script in a supplemental reading program on instructional opportunities for student practice of specified skills. The Journal of Special Education, 45(1), 28-42.
Applied Behavior Analysis
This book is a comprehensive description of the principles and procedures for systematic change of socially significant behavior. It includes basic principles, applications, and behavioral research methods.
Cooper, J. O., Heron, T. E., & Heward, W. L. (2007). Applied behavior analysis.
Learner-centered teacher-student relationships are effective: A meta-analysis.
The author reviewed about 1,000 articles to synthesize 119 studies from 1948 to 2004 with 1,450 findings and 355,325 students. The meta-analysis design followed Mackay, Barkham, Rees, and Stiles’s guidelines, including comprehensive search mechanisms, accuracy and bias control, and primary study validity assessment.
Cornelius-White, J. (2007). Learner-centered teacher-student relationships are effective: A meta-analysis. Review of educational research, 77(1), 113-143.
Learner-centered teacher-student relationships are effective: A meta-analysis.
The author reviewed about 1,000 articles to synthesize 119 studies from 1948 to 2004 with 1,450 findings and 355,325 students. The meta-analysis design followed Mackay, Barkham, Rees, and Stiles’s guidelines, including comprehensive search mechanisms, accuracy and bias control, and primary study validity assessment.
Cornelius-White, J. (2007). Learner-centered teacher-student relationships are effective: A meta-analysis. Review of educational research, 77(1), 113-143.
What Works in Education
This monograph summarizes a sample of programs and procedures demonstrated to work. Each program included in the monograph has been validated through solid scientific research.
Crandall, J., & Sloane, H. (1997). What works in education. Cambridge Center for Behavioral Studies.
On the teachability of communication strategies.
This article describes what communication strategies are and provides an overview of the teachability issue, discussing the arguments for and against strategy instruction, and suggests three possible reasons for the existing controversy.
Dörnyei, Z. (1995). On the teachability of communication strategies. TESOL quarterly, 29(1), 55-85.
Enhancing Professional Practice: A Framework for Teaching
The framework for teaching is a research-based set of components of instruction that are grounded in a constructivist view of learning and teaching. The framework defines four levels of performance--Unsatisfactory, Basic, Proficient, and Distinguished--for each element, providing a valuable tool that all teachers can use.
Danielson, C. (2007). Enhancing professional practice: A framework for teaching. ASCD.
Does teacher certification matter? Evaluating the evidence
The authors respond to Dan Goldhaber and Dominic Brewer’s article in the Summer 2000 issue of Educational Evaluation and Policy Analysis that claimed from an analysis of NELS teacher and student data that teacher certification has little bearing on student achievement. Goldhaber and Brewer found strong and consistent evidence that, as compared with students whose teachers are uncertified, students achieve at higher levels in mathematics when they have teachers who hold standard certification in mathematics.
Darling-Hammond, L., Berry, B., & Thoreson, A. (2001). Does teacher certification matter? Evaluating the evidence. Educational evaluation and policy analysis, 23(1), 57-77.
Does teacher preparation matter? Evidence about teacher certification, Teach For America, and teacher effectiveness.
Recent debates about the utility of teacher education have raised questions about whether certified teachers are, in general, more effective than those who have not met the testing and training requirements for certification, and whether some candidates with strong liberal arts backgrounds might be at least as effective as teacher education graduates.
Darling-Hammond, L., Holtzman, D. J., Gatlin, S. J., & Heilig, J. V. (2005). Does teacher preparation matter? Evidence about teacher certification, Teach for America, and teacher effectiveness. Education Policy Analysis Archives/Archivos Analíticos de Políticas Educativas, 13, 1-48.
School Improvement Grants: Implementation and Effectiveness
The Institute of Education Sciences (IES) recently released a summary report of the impact of School Improvement Grants (SIG). The American Recovery and Reinvestment Act of 2009 provided states and school districts with $3 Billion for SIG. By accepting SIG grants states agreed to implement one of four interventions to improve the lowest performing schools: transformation, turnaround, restart, or closure. The goals of SIG were to improve practices in four main areas: (1) adopting comprehensive instructional reform strategies, (2) developing and increasing teacher and principal effectiveness, (3) increasing learning time and creating community-oriented schools, and (4) having operational flexibility and receiving support. The report finds minimal positive effects from the grants and no evidence that SIG had significant impacts on math and reading scores, graduation rates, or increased college enrollment.
Dragoset, L., Thomas, J., Herrmann, M., Deke, J., James-Burdumy, S., Graczewski, C., … & Giffin, J. (2017). School Improvement Grants: Implementation and Effectiveness (No. 76bce3f4bb0944f29a481fae0dbc7cdb). Mathematica Policy Research.
The bases of teacher experiences: A meta-analysis
Reports a meta-analysis of research on the bases of teacher expectancies. The following conclusions were drawn: Student attractiveness, conduct, cumulative folder information, race, and social class were related to teacher expectancies.
Dusek, J. B., & Joseph, G. (1983). The bases of teacher expectancies: A meta-analysis. Journal of Educational psychology, 75(3), 327.
Meta-analysis of the relationship between collective teacher efficacy and student achievement
Collective teacher efficacy is an emergent school level variable reflecting a faculty’s collective belief in its ability to positively affect students. It has been linked in the literature to school achievement. The research questions addressed the distribution of effect sizes for the relationship and the moderator variables that could explain any variance found among the studies.
Eells, R. J. (2011). Meta-analysis of the relationship between collective teacher efficacy and student achievement (Doctoral dissertation, Loyola University Chicago).
Effective Teaching Principles and the Design of Quality Tools for Educators
This monograph presents a synthesis of the literature on empirically supported effective teaching principles that have been derived from research on behavioral, cognitive, social-learning, and other theories.
Ellis, E. S., Worthington, L. A., & Larkin, M. J. (1994). research synthesis on effective teaching principles and the design of quality tools for educators.(Tech. Rep. No. 6). Eugene, OR: University of Oregon, National Center to Improve the Tools of Educators.
Handbook of classroom management: Research, practice, and contemporary issues
Classroom management is a topic of enduring concern for teachers, administrators, and the public. It consistently ranks as the first or second most serious educational problem in the eyes of the general public, and beginning teachers consistently rank it as their most pressing concern during their early teaching years. Management problems continue to be a major cause of teacher burnout and job dissatisfaction. Strangely, despite this enduring concern on the part of educators and the public, few researchers have chosen to focus on classroom management or to identify themselves with this critical field.
Evertson, C. M., & Weinstein, C. S. (Eds.). (2013). Handbook of classroom management: Research, practice, and contemporary issues. New York, NY: Routledge.
Applied behavior analysis for educators: Teacher centered and classroom based
The purpose of this commentary is to consider the crisis in education and the complex role teachers play in our society; to examine critically major aspects of the traditional modus operandi of behavior analysis that are counterproductive to teacher use; and to identify practices related to promoting greater teacher use and thereby enhancing the relevance of behavioral technology in education.
Fantuzzo, J., & Atkins, M. (1992). Applied behavior analysis for educators: Teacher centered and classroom based. Journal of Applied Behavior Analysis, 25(1), 37.
Effective college teaching from the students' and faculty's view: Matched or mismatched priorities?
Thirty-one studies were located in each of which students and faculty specified the instructional characteristics they considered particularly important to good teaching and effective instruction.
Feldman, K. A. (1988). Effective college teaching from the students' and faculty's view: Matched or mismatched priorities?. Research in Higher Education, 28(4), 291-329.
The correlation between teacher clarity of communication and student achievement gain: A meta-analysis
This paper aim to determine the correlation between teacher clarity and the mean class student learning (achievement gain) in normal public-education classes in English-speaking, industrialized countries.
Fendick, F. (1992). The correlation between teacher clarity of communication and student achievement gain: A meta-analysis.
The effects of contingent teacher praise, as specified by Canter's Assertive Discipline programme, on children's on-task behaviour
The purpose of this study was to examine the effectiveness of contingent teacher praise, as specified by Canter's Assertive Discipline programme, on children's on task behaviour. Continuous data collection indicated that following training in the appropriate use of praise, as specified by Canter, all three teachers successfully increased their rates of praising. Of the 24 children, all but one evidenced increases in levels of on‐task behaviour.
Ferguson, E. & Houghton, S. (1992). The effects of contingent teacher praise, as specified by Canter's Assertive Discipline programme, on children's on-task behaviour. Educational Studies, 18(1), 83-93.
Implementation Research: A Synthesis of the Literature
This is a comprehensive literature review of the topic of Implementation examining all stages beginning with adoption and ending with sustainability.
Fixsen, D. L., Naoom, S. F., Blase, K. A., & Friedman, R. M. (2005). Implementation research: A synthesis of the literature.
The lecture as a transmedial pedagogical form: A historical analysis.
This article examines the lecture as a pedagogical genre, as “a site where differences between media are negotiated” (Franzel) as these media coevolve. This examination shows the lecture as bridging oral communication with writing and newer media technologies, rather than as being superseded by newer electronic and digital forms.
Friesen, N. (2011). The lecture as a transmedial pedagogical form: A historical analysis. Educational researcher, 40(3), 95-102.
Researchers and teachers working together to adapt instruction for diverse learners
This paper explain a three-stage process of Pilot Research, Formal Evaluation, and Scaling Up. Finally, we discuss several misconceptions about empirical research and researchers.
Fuchs, D., & Fuchs, L. S. (1998). Researchers and teachers working together to adapt instruction for diverse learners. Learning Disabilities Research & Practice.
Effects of Systematic Formative Evaluation: A Meta-Analysis
In this meta-analysis of studies that utilize formative assessment the authors report an effective size of .7.
Fuchs, L. S., & Fuchs, D. (1986). Effects of Systematic Formative Evaluation: A Meta-Analysis. Exceptional Children, 53(3), 199-208.
Back to basics: Rules, praise, ignoring, and reprimands revisited
Research begun in the 1960s provided the impetus for teacher educators to urge classroom teachers to establish classroom rules, deliver high rates of verbal/nonverbal praise, and, whenever possible, to ignore minor student provocations. The research also discuss several newer strategies that warrant attention.
Gable, R. A., Hester, P. H., Rock, M. L., & Hughes, K. G. (2009). Back to basics: Rules, praise, ignoring, and reprimands revisited. Intervention in School and Clinic, 44(4), 195-205.
Preparing for culturally responsive teaching.
In this article, a case is made for improving the school success of ethnically diverse students through culturally responsive teaching and for preparing teachers in preservice education programs with the knowledge, attitudes, and skills needed to do this.
Gay, G. (2002). Preparing for culturally responsive teaching. Journal of teacher education, 53(2), 106-116.
Culturally responsive teaching: Theory, research, and practice.
Combining insights from multicultural education theory with real-life classroom stories, this book demonstrates that all students will perform better on multiple measures of achievement when teaching is filtered through students’ own cultural experiences. This perennial bestseller continues to be the go-to resource for teacher professional learning and preservice courses.
Gay, G. (2018). Culturally responsive teaching: Theory, research, and practice. Teachers College Press.
Validity of High-School Grades in Predicting Student Success beyond the Freshman Year: High-School Record vs. Standardized Tests as Indicators of Four-Year College Outcomes
High-school grades are often viewed as an unreliable criterion for college admissions, owing to differences in grading standards across high schools, while standardized tests are seen as methodologically rigorous, providing a more uniform and valid yardstick for assessing student ability and achievement. The present study challenges that conventional view. The study finds that high-school grade point average (HSGPA) is consistently the best predictor not only of freshman grades in college, the outcome indicator most often employed in predictive-validity studies, but of four-year college outcomes as well.
Geiser, S., & Santelices, M. V. (2007). Validity of High-School Grades in Predicting Student Success beyond the Freshman Year: High-School Record vs. Standardized Tests as Indicators of Four-Year College Outcomes. Research & Occasional Paper Series: CSHE. 6.07. Center for studies in higher education.
A practical application of time management
This chapter progresses four specific components of “a practical application of time management”.
Teamwork, soft skills, and research training.
This paper provide a list of soft skills that are important for collaboration and teamwork, based on the authors own experience and from an opinion survey of team leaders. This paper also outline workable short courses for graduate schools to strengthen teamwork and collaboration skills among research students.
Gibert, A., Tozer, W. C., & Westoby, M. (2017). Teamwork, soft skills, and research training. Trends in ecology & evolution, 32(2), 81-84.
Effects of quantity of instruction on time spent on learning and achievement.
This article evaluates the extent to which quantity of instruction influences time spent on self‐
study and achievement. The results suggest that time spent on self‐study is primarily a function of the degree of time allocated to instruction.
Gijselaers, W. H., & Schmidt, H. G. (1995). Effects of quantity of instruction on time spent on learning and achievement. Educational Research and Evaluation, 1(2), 183-201.
Soft skills and technical expertise of effective project managers.
The article presents an overview of these tenets drawn from opinion positions, practical experiences, and empirical research studies. There is clear evidence that additional empirical research would be beneficial.
Gillard, S. (2009). Soft skills and technical expertise of effective project managers. Issues in informing science & information technology, 6.
When and why incentives (don't) work to modify behavior.
This book discuss how extrinsic incentives may come into conflict with other motivations and examine the research literature in which monetary incentives have been used in a nonemployment context to foster the desired behavior. The conclusion sums up some lessons on when extrinsic incentives are more or less likely to alter such behaviors in the desired directions.
Gneezy, U., Meier, S., & Rey-Biel, P. (2011). When and why incentives (don't) work to modify behavior. Journal of Economic Perspectives, 25(4), 191-210.
The teacher preparation→ teacher practices→ student outcomes relationship in special education: Missing links and next steps: A research synthesis
The goal of this paper was to document and analyze the research on the connection between teachers' preparation to teach special education students, their instructional practices once in the classroom, and their students' eventual learning achievement
Goe, L. (2006). The teacher preparation→ teacher practices→ student outcomes relationship in special education: Missing links and next steps: A research synthesis. Washington, DC: National Comprehensive Center for Teacher Quality. Retrieved September, 3, 2009.
In school, teacher quality matters most. Education Next
FIFTY YEARS after the release of "Equality of Educational Opportunity"--widely known as the Coleman Report--much of what James Coleman and his colleagues reported holds up well to scrutiny. It is, in fact, remarkable to read through the 700-plus pages and see how little has changed about what the empirical evidence says matters. The report's conclusions about the importance of teacher quality, in particular, have stood the test of time, which is noteworthy, given that today's studies of the impacts of teachers use more-sophisticated statistical methods and employ far better data.
Goldhaber, D. (2016). In schools, teacher quality matters most: today's research reinforces Coleman's findings. Education Next, 16(2), 56-63.
Exploring the Impact of Student Teaching Apprenticeships on Student Achievement and Mentor Teachers
This paper examines the consequences of having an apprentice teacher for 4-8 graders in the state of Washington.
Goldhaber, D., Krieg, J. M., & Theobald, R. (2020). Exploring the impact of student teaching apprenticeships on student achievement and mentor teachers. Journal of Research on Educational Effectiveness, 1-22.
Teacher preparation experiences and early teacher effectiveness
This report provides information about new teachers' preparation experiences and explores
whether particular types of experiences are related to teachers' effectiveness in improving
their students' test scores. Prior research indicates that teaching effectiveness is the largest
in-school factor affecting student achievement.
Goodson, B., Caswell, L., Price, C., Litwok, D., Dynarski, M., Crowe, E., ... & Rice, A. (2019). Teacher Preparation Experiences and Early Teaching Effectiveness. Executive Summary. NCEE 2019-4010. National Center for Education Evaluation and Regional Assistance.
Teaching Elementary School Students to Be Effective Writers: A Practice Guide.
The report analyzes the evidence supporting those teaching methods commonly employed to increase student competency in becoming a fluent writer. The guide is for teachers, literacy coaches, principals, districts, and curriculum developers, and other educators.
Graham, S., Bollinger, A., Olson, C. B., D’Aoust, C., MacArthur, C., McCutchen, D., & Olinghouse, N. (2012). Teaching Elementary School Students to Be Effective Writers: A Practice Guide. NCEE 2012-4058. What Works Clearinghouse.
Adolescent trust in teachers: Implications for behavior in the high school classroom
This study examined teachers' relational approach to discipline as a predictor of high school students' behavior and their trust in teacher authority.
Gregory, A., & Ripski, M. B. (2008). Adolescent trust in teachers: Implications for behavior in the high school classroom. School Psychology Review, 37(3), 337.
Can comprehension be taught? A quantitative synthesis of “metacognitive” studies
This quantitative review examines 20 studies to establish an effect size of .71 for the impact of “metacognitive” instruction on reading comprehension.
Haller, E. P., Child, D. A., & Walberg, H. J. (1988). Can comprehension be taught? A quantitative synthesis of “metacognitive” studies. Educational researcher, 17(9), 5-8.
Hard Words: Why aren’t kids being taught to read?
This report and podcast examines the scientific basis for how to teach reading to children. This investigation reveals how children learn to read, emphasizing the five critical components of reading instruction.
Teacher Quality
This chapter of Handbook of The Economics of Education reviews research on teacher labor markets, the importance of teacher quality in the determination of student achievement, and the extent to which specific observable characteristics often related to hiring decisions and salary explain the variation in the quality of instruction.
Hanushek, E. A., & Rivkin, S. G. (2006). Teacher quality. In E. A. Hanushek & F. Welch (Eds.), Handbook of the economics of education, vol. 2 (pp. 1051–1078). Amsterdam, Netherlands: North Holland.
The Value of Smarter Teachers: International Evidence on Teacher Cognitive Skills and Student Performance
This new research addresses a number of critical questions: Are a teacher’s cognitive skills a good predictor of teacher quality? This study examines the student achievement of 36 developed countries in the context of teacher cognitive skills. This study finds substantial differences in teacher cognitive skills across countries that are strongly related to student performance.
Hanushek, E. A., Piopiunik, M., & Wiederhold, S. (2014). The value of smarter teachers: International evidence on teacher cognitive skills and student performance (No. w20727). National Bureau of Economic Research.
Teacher training, teacher quality and student achievement
The authors study the effects of various types of education and training on the ability of teachers to promote student achievement.
Harris, D. N., & Sass, T. R. (2011). Teacher training, teacher quality and student achievement. Journal of Public Economics, 95(7–8), 798-812.
Visible learning: A synthesis of over 800 meta-analyses relating to achievement
Hattie’s book is designed as a meta-meta-study that collects, compares and analyses the findings of many previous studies in education. Hattie focuses on schools in the English-speaking world but most aspects of the underlying story should be transferable to other countries and school systems as well. Visible Learning is nothing less than a synthesis of more than 50.000 studies covering more than 80 million pupils. Hattie uses the statistical measure effect size to compare the impact of many influences on students’ achievement, e.g. class size, holidays, feedback, and learning strategies.
Hattie, J. (2008). Visible learning: A synthesis of over 800 meta-analyses relating to achievement. New York, NY: Routledge.
Visible learning
This influential book is the result of 15 years research that includes over 800 meta-analyses on the influences on achievement in school-aged students. This is a great resource for any stakeholder interested in conducting a serious search of evidence behind common models and practices used in schools.
Hattie, J. (2009). Visible learning. A synthesis of over, 800.
Visible Learning Insights
Offering a concise introduction into the ‘Visible Learning Story’, the book provides busy teachers with a guide to why the Visible Learning research is so vital and the difference it can make to learning outcomes.
Hattie, J., & Zierer, K. (2019). Visible Learning Insights. Routledge.
Made to stick: Why some ideas survive and others die
This book reveal the anatomy of ideas that stick and explain ways to make ideas stickier, such as applying the human scale principle, using the Velcro Theory of Memory, and creating curiosity gaps. Along the way, we discover that sticky messages of all kinds draw their power from the same six traits.
Heath, C., & Heath, D. (2007). Made to stick: Why some ideas survive and others die. Random House.
Exceptional Children: An Introduction To Special Education.
This book for teachers in the area of Special Education looks at highly effective, research-based practices described in a very step-by-step, applied manner.
Heward, W. L. (2012). Exceptional Children: An Introduction to Special Education. Pearson.
Community Treatment for Youth: Evidence-Based Interventions for Severe Emotional and Behavioral Disorders
This outstanding textbook presents innovative interventions for youth with severe emotional and behavioral disorders. Community Treatment for Youth is designed to fill a gap between the knowledge base and clinical practice through its presentation of theory, practice parameters, training requirements, and research evidence.
Hoagwood, K. I. M. B. E. R. L. Y., Burns, B. J., & Weisz, J. R. (2002). A profitable conjunction: From science to service in children’s mental health. Community treatment for youth: Evidence-based interventions for severe emotional and behavioral disorders, 327-338.
Complexity, accuracy and fluency in second language acquisition
This special issue addresses a general question that is at the heart of much research in applied linguistics and second language acquisition (SLA): What makes a second or foreign language (L2) user, or a native speaker for that matter, a more or less proficient language user?
Housen, A., & Kuiken, F. (2009). Complexity, accuracy, and fluency in second language acquisition. Applied linguistics, 30(4), 461-473. Retrieved from https://pure.uva.nl/ws/files/806510/74786_AL_SI_Housen_Kuiken.pdf
Teacher turnover and teacher shortages: An organizational analysis
This paper investigates organizational characteristics and conditions in schools that drive staffing problems and teacher turnover.
Ingersoll, R. (2001). Teacher turnover and teacher shortages: An organizational analysis. American Educational Research Journal, 38(3), 499-534.
Life in Classrooms.
Focusing on elementary classrooms, chapters include: Students' Feelings about School; Involvement and Withdrawal in the Classroom; Teachers Views; The Need for New Perspectives.
Jackson, P. W. (1990). Life in classrooms. Teachers College Press.
Life in Classrooms.
Focusing on elementary classrooms, chapters include: Students' Feelings about School; Involvement and Withdrawal in the Classroom; Teachers Views; The Need for New Perspectives.
Jackson, P. W. (1990). Life in classrooms. Teachers College Press.
Not so elementary: Primary school teacher quality in high-performing systems
This report analyses whether and how highperforming systems have supported the subject expertise of their elementary school teachers.
Jensen, B., Roberts-Hull, K., Magee, J., & Ginnivan, L. (2016). Not so elementary: Primary school teacher quality in high-performing systems. Washington, DC: National Center on Education and the Economy. http://ncee.org/wp-content/uploads/2016/05/169726_Not_So_Elementary_Report_FINAL.pdf
Demonstrating the Experimenting Society Model with Classwide Behavior Management Interventions
Demonstrates the experimenting society model using data-based decision making and collaborative consultation to evaluate behavior-management intervention strategies in 25 seventh graders. Each intervention results in improved behavior, but active teaching of classroom rules was determined to be most effective.
Johnson, T. C., Stoner, G., & Green, S. K. (1996). Demonstrating the Experimenting Society Model with Classwide Behavior Management Interventions. School Psychology Review, 25(2), 199-214.
Training Teachers to Use Environmental Arrangement and Milieu Teaching with Nonvocal Preschool Children
This study investigated the effects of training preschool teachers to use environmental arrangement and milieu teaching in interactions with children using augmented communication systems. Three teachers were taught seven environmental strategies and four milieu teaching procedures through written materials, lecture, modeling, role-playing, and feedback.
Kaiser, A. P., Ostrosky, M. M., & Alpert, C. L. (1993). Training teachers to use environmental arrangement and milieu teaching with nonvocal preschool children. Journal of the Association for Persons with Severe Handicaps, 18(3), 188-199.
Praise counts: Using self-monitoring to increase effective teaching practices
The authors examined the effectiveness of self-monitoring for increasing the rates of teacher praise statements and the acceptability of using this technique for teachers. This study's results support the use of self-monitoring to increase effective teaching practices, namely praise, and further demonstrates high social validity for the participant and the students.
Kalis, T. M., Vannest, K. J., & Parker, R. (2007). Praise counts: Using self-monitoring to increase effective teaching practices. Preventing School Failure: Alternative Education for Children and Youth, 51(3), 20-27.
Effective Intervention for Students with Specific Learning Disability: The Nature of Special Education.
The nature of effective instruction for students with specific learning disability is explored.
Kavale, K. A. (2005). Effective Intervention for Students with Specific Learning Disability: The Nature of Special Education. Learning Disabilities: A Multidisciplinary Journal, 13(4), 127-138.
Identifying Specific Learning Disability: Is Responsiveness to Intervention the Answer?
Responsiveness to intervention (RTI) is being proposed as an alternative model for making decisions about the presence or absence of specific learning disability. The author argue that there are many questions about RTI that remain unanswered, and radical changes in proposed regulations are not warranted at this time.
Kavale, K. A. (2005). Identifying specific learning disability: Is responsiveness to intervention the answer?. Journal of Learning Disabilities, 38(6), 553-562.
Proceedings from the Wing Institute’s Fifth Annual Summit on Evidence-Based Education: Education at the Crossroads: The State of Teacher Preparation
This article shared information about the Wing Institute and demographics of the Summit participants. It introduced the Summit topic, sharing performance data on past efforts of school reform that focused on structural changes rather than teaching improvement. The conclusion is that the system has spent enormous resources with virtually no positive results. The focus needs to be on teaching improvement.
Keyworth, R., Detrich, R., & States, J. (2012). Introduction: Proceedings from the Wing Institute’s Fifth Annual Summit on Evidence-Based Education: Education at the Crossroads: The State of Teacher Preparation. In Education at the Crossroads: The State of Teacher Preparation (Vol. 2, pp. ix-xxx). Oakland, CA: The Wing
Formative Assessment: A Meta?Analysis And A Call For Research
This meta-analysis examines the impact of formative assessment.
Kingston, N., & Nash, B. (2011). Formative assessment: A meta?analysis and a call for research. Educational Measurement: Issues and Practice, 30(4), 28-37.
The Effects of Feedback Interventions on Performance: A Historical Review, a Meta-Analysis, and a Preliminary Feedback Intervention Theory
The authors proposed a preliminary FI theory (FIT) and tested it with moderator analyses. The central assumption of FIT is that FIs change the locus of attention among 3 general and hierarchically organized levels of control: task learning, task motivation, and meta-tasks (including self-related) processes.
Kluger, A. N., & DeNisi, A. (1996). The effects of feedback interventions on performance: A historical review, a meta-analysis, and a preliminary feedback intervention theory. Psychological bulletin, 119(2), 254.
High-Impact Instruction: A Framework for Great Teaching.
This book offers strategies that make a difference in student learning including: content planning, instructional practices, and community building.
Knight, J. (2013). High-impact Instruction: A Framework for Great Teaching. Corwin Press.
What happens when teachers design educational technology? The development of technological pedagogical content knowledge.
The authors introduce Technological Pedagogical Content Knowledge (TPCK) as a way of representing what teachers need to know about technology and argue for the role of authentic design-based activities in the development of this knowledge.
Effectiveness of mastery learning programs: A meta-analysis
This meta-analysis of findings from 108 studies shows mastery learning programs have positive effects on the examination performance of students in colleges, high schools, and the upper grades in elementary schools.
Kulik, C. L. C., Kulik, J. A., & Bangert-Drowns, R. L. (1990). Effectiveness of mastery learning programs: A meta-analysis. Review of educational research, 60(2), 265-299.
The differences between hard and soft skills and their relative impact on training transfer
This article discusses differences that are hypothesized to exist between hard‐ (technical) and soft‐ (intrapersonal and interpersonal) skills training that we believe impact the degree of training transfer achieved.
Laker, D. R., & Powell, J. L. (2011). The differences between hard and soft skills and their relative impact on training transfer. Human Resource Development Quarterly, 22(1), 111-122.
Social skills instruction for students at risk for
antisocial behavior: The effects of small-group instruction.
This study examined the effectiveness of social skills instruction for seven elementary-age students at risk for antisocial behavior who were unresponsive to a school wide primary intervention program
Lane, K. L., Wehby, J., Menzies, H. M., Doukas, G. L., Munton, S. M., & Gregg, R. M. (2003). Social skills instruction for students at risk for antisocial behavior: The effects of small-group instruction. Behavioral Disorders, 28(3), 229-248.
Reading on grade level in third grade: How is it related to high school performance and college enrollment.
This study uses longitudinal administrative data to examine the relationship between third- grade reading level and four educational outcomes: eighth-grade reading performance, ninth-grade course performance, high school graduation, and college attendance.
Lesnick, J., Goerge, R., Smithgall, C., & Gwynne, J. (2010). Reading on grade level in third grade: How is it related to high school performance and college enrollment. Chicago: Chapin Hall at the University of Chicago, 1, 12.
Precision Teaching: By Teachers for Children
in this article, the author describes the policies of precision teaching.
Lindsley, O. R. (1990). Precision teaching: By teachers for children. Teaching Exceptional Children, 22(3), 10-15.
The effects of social skills instruction on the social behaviors of students at risk for emotional or behavioral disorders
The authors examined the effects of pullout small-group and teacher-directed classroom-based social skills instruction on the social behaviors of five third- and fourth-grade students at risk for emotional or behavioral disorders.
Lo, Y. Y., Loe, S. A., & Cartledge, G. (2002). The effects of social skills instruction on the social behaviors of students at risk for emotional or behavioral disorders. Behavioral Disorders, 27(4), 371-385.
The Reporting of Core ProgramComponents: An Overlooked Barrier for Moving Research Into Practice
The successful implementation of school-based behavioral interventions requires school personnel to be competent with program content and procedures. An unfortunate trend within school-based behavioral intervention research is that the core intervention components and implementation features are often not fully described.
Maggin, D. M., & Johnson, A. H. (2015). The reporting of core program components: an overlooked barrier for moving research into practice. Preventing School Failure: Alternative Education for Children and Youth, 59(2), 73-82.
Four Classwide Peer Tutoring Models: Similarities, Differences, and Implications for Research and Practice
In this special issue, this Journal introduce a fourth peer teaching model, Classwide Student Tutoring Teams. This journal also provide a comprehensive analysis of common and divergent programmatic components across all four models and discuss the implications of this analysis for researchers and practitioners alike.
Maheady, L., Mallette, B., & Harper, G. F. (2006). Four classwide peer tutoring models: Similarities, differences, and implications for research and practice. Reading & Writing Quarterly, 22(1), 65-89.
A Theoretical Framework for Data-Driven Decision Making
The purpose of this paper is to provide a model for more effective data-driven decision making in classrooms, schools, and districts.
Mandinach, E. B., Honey, M., & Light, D. (2006, April). A theoretical framework for data-driven decision making. In annual meeting of the American Educational Research Association, San Francisco, CA.
A Theory-Based Meta-Analysis of Research on Instruction.
This research synthesis examines instructional research in a functional manner to provide guidance for classroom practitioners.
Marzano, R. J. (1998). A Theory-Based Meta-Analysis of Research on Instruction.
Classroom management that works: Research-based strategies for every teacher
How does classroom management affect student achievement? What techniques do
teachers find most effective? How important are schoolwide policies and practices in setting
the tone for individual classroom management? In this follow-up to What Works in Schools,
Robert J. Marzano analyzes research from more than 100 studies on classroom
management to discover the answers to these questions and more. He then applies these
findings to a series of" Action Steps"--specific strategies.
Marzano, R. J., Marzano, J. S., & Pickering, D. (2003). Classroom management that works: Research-based strategies for every teacher. Alexandria, VA: Association for Supervision and Curriculum Development (ASCD).
Classroom Instruction That Works: Research Based Strategies For Increasing Student Achievement
This is a study of classroom management on student engagement and achievement.
Marzano, R. J., Pickering, D., & Pollock, J. E. (2001). Classroom instruction that works: Research-based strategies for increasing student achievement. Ascd
Classroom Instruction That Works: Research Based Strategies For Increasing Student Achievement
This is a study of classroom management on student engagement and achievement.
Marzano, R. J., Pickering, D., & Pollock, J. E. (2001). Classroom instruction that works: Research-based strategies for increasing student achievement. Ascd
What Works Clearinghouse Intervention Report: National Board for Professional Teaching Standards Certification.
The What Works Clearinghouse (WWC) identified five studies of NBPTS certification that both fall within the scope of the Teacher Training, Evaluation, and Compensation topic area and meet WWC group design standards.
Mathematica Policy Research (2018). What Works Clearinghouse Intervention Report: National Board for Professional Teaching Standards Certification. Washington, DC: U.S. Department of Education, National Center for Education Statistics, National Assessment of Educational Progress (NAEP). Retrieved from https://ies.ed.gov/ncee/wwc/Docs/InterventionReports/wwc_nbpts_021318.pdf.
Multiple effects of home and daycare crowding.
This research examines the relationship between noise and preschool children's acquisition of prereading skills, environmental factors in preschool inclusive classrooms, and children's use of outdoorplay equipment.
Maxwell, L. E. (1996). Multiple effects of home and day care crowding. Environment and Behavior, 28(4), 494-511.
The role of empathy in teaching culturally diverse students: A qualitative study of teachers’ beliefs.
This study provides a description of 34 practicing teachers' beliefs regarding the role of empathy as an attribute in their effectiveness with culturally diverse students. Empathy involves cognitive, affective, and behavioral components that teachers believed were manifested in their practice.
McAllister, G., & Irvine, J. J. (2002). The role of empathy in teaching culturally diverse students: A qualitative study of teachers’ beliefs. Journal of teacher education, 53(5), 433-443.
Improving education through standards-based reform.
This report offers recommendations for the implementation of standards-based reform and outlines possible consequences for policy changes. It summarizes both the vision and intentions of standards-based reform and the arguments of its critics.
McLaughlin, M. W., & Shepard, L. A. (1995). Improving Education through Standards-Based Reform. A Report by the National Academy of Education Panel on Standards-Based Education Reform. National Academy of Education, Stanford University, CERAS Building, Room 108, Stanford, CA 94305-3084..
The reduction of disruptive behaviour in two secondary school classes.
The constituent parts of a five component behavioural intervention package are described and the effect of the intervention on the on‐task behaviour of two “disruptive” secondary school classes reported.
McNamara, E., Evans, M., & Hill, W. (1986). The reduction of disruptive behaviour in two secondary school classes. British Journal of Educational Psychology, 56(2), 209-215.
The reduction of disruptive behaviour in two secondary school classes.
The constituent parts of a five component behavioural intervention package are described and the effect of the intervention on the on‐task behaviour of two “disruptive” secondary school classes reported.
McNamara, E., Evans, M., & Hill, W. (1986). The reduction of disruptive behaviour in two secondary school classes. British Journal of Educational Psychology, 56(2), 209-215.
Most classroom teachers feel unprepared to support students with disabilities.
Less than 1 in 5 general education teachers feel “very well prepared” to teach students with mild to moderate learning disabilities, including ADHD and dyslexia, according to a new survey from two national advocacy groups.
Mitchell, C. (2019, May 29). Most classroom teachers feel unprepared to support students with disabilities. Education Week.
Teacher acquisition of functional analysis methodology
The current study examined methods for training teachers to use functional analysis methods.
Moore, J. W., Edwards, R. P., Sterling‐Turner, H. E., Riley, J., DuBard, M., & McGeorge, A. (2002). Teacher acquisition of functional analysis methodology. Journal of Applied Behavior Analysis, 35(1), 73-77.
Training Head Start Teachers to Use Incidental Teaching
The purpose of this study was to investigate the effects of group inservice training plus written and verbal feedback on four Head Start teachers’ use of incidental teaching. D
Mudd, J. M., & Wolery, M. (1987). Training head start teachers to use incidental teaching. Journal of the Division for Early Childhood, 11(2), 124-134.
Connecting teacher leadership and school improvement.
This book is designed to help the reader fully comprehend teacher leadership as a pathway to school improvement.
Murphy, J. (2005). Connecting teacher leadership and school improvement. Thousand Oaks, CA: Corwin Press.
Professional standards for educational leaders
This book introduces the foundations of the recently revised professional educational leadership standards and provides an in-depth explanation and application of each one.
Murphy, J. F. (2016). Professional standards for educational leaders: The empirical, moral, and experiential foundations. Corwin Press.
No Child Left Behind Act of 2001
No Child Left Behind Act of 2001 ESEA Reauthorization
No child left behind act of 2001. Publ. L, 107-110. (2002)
Teacher classroom management practices: Effects on disruptive or aggressive student behavior.
This Campbell systematic review examines the effect of multi‐component teacher classroom management programmes on disruptive or aggressive student behaviour and which management components are most effective.
Oliver, R. M., Wehby, J. H., & Reschly, D. J. (2011). Teacher classroom management practices: Effects on disruptive or aggressive student behavior. Campbell Systematic Reviews, 7(1), 1-55.
Reciprocal Teaching of Comprehension Fostering and Comprehension Monitoring Activities
Two instructional studies directed at the comprehension-fostering and comprehension-monitoringactivitiesof seventhgrade poor comprehendersare reported
Palinscar, A. S., & Brown, A. L. (1984). Reciprocal teaching of comprehension-fostering and comprehension-monitoring activities. Cognition and instruction, 1(2), 117-175.
The Learning Styles Educational Neuromyth: Lack of Agreement Between Teachers’ Judgments, Self-Assessment, and Students’ Intelligence.
This study examined the hypothesis that teachers’ and students’ assessment of preferred LS correspond. The study found no relationship between pupils’ self-assessment and teachers’ assessment. Teachers’ and students’ answers didn’t match up. The study suggests that teachers cannot assess the LS of their students accurately.
Papadatou-Pastou, M., Gritzal, M., & Barrable, A. (2018). The Learning Styles educational neuromyth: Lack of agreement between teachers’ judgments, self-assessment, and students’ intelligence. Frontiers in Education, 3, 1-5. [105]. https://doi.org/10.3389/feduc.2018.00105
Effective programs in elementary mathematics: A best-evidence synthesis
This research synthesis examines randomized controlled trials and quasi-experimental research on the mathematics achievement outcomes for elementary school programs. The best outcomes were found for tutoring programs. The findings suggest that programs emphasizing personalization, engagement, and motivation are most impactful in elementary mathematics instruction.
Pellegrini, M., Lake, C., Inns, A, & , Slavin, R. (2018). Effective programs in elementary mathematics: A best-evidence synthesis. Best Evidence Encyclopedia. Retrieved from http://www.bestevidence.org/word/elem_math_Oct_8_2018.pdf
Teachers matter: Understanding teachers’ impact on student achievement,
Research using student scores on standardized tests confirms the common perception that some teachers are more effective than others. It also reveals that being taught by an effective teacher has important consequences for student achievement. The best way to assess a teacher's effectiveness is to look at his or her on-the-job performance.
RAND Education. (2012).Teachers matter: Understanding teachers’ impact on student achievement, Santa Monica, Calif.: Author. Retrieved from https://www.rand.org/pubs/corporate_pubs/CP693z1-2012-09.html
A brief history of teacher professionalism
Our nation faces a daunting challenge in making sure that we have a sufficient supply of well-educated, well-prepared teachers for our children. There is surely widespread agreement that good teachers are vital to our future. However, there is not widespread agreement about how we accomplish this goal. Some propose that we raise standards for entry into the teaching profession, while others suggest that we lower unnecessary barriers.
Ravitch, D. (2003, August 23). A brief history of teacher professionalism. U. S. Department of Education, White House Conference on Preparing Tomorrow’s Teachers.
Cloze Procedure and the Teaching of Reading
The terms cloze procedure and cohesion are associated with reading development. Specifically, doze applies to the testing and teaching of reading while cohesion applies to a description of how the way in which reading material is written can affect reading development.
Raymond, P. (1988). Cloze procedure in the teaching of reading. TESL Canada Journal, 6(1), 91–97.
The impact of individual teachers on student achievement: Evidence from panel data
In order to provide accurate estimates of how much teachers affect the achievement of their students, this study used panel data covering over a decade of elementary student test scores and teacher assignment in two contiguous New Jersey school districts.
Rockoff, J. E. (2004). The impact of individual teachers on student achievement: Evidence from panel data. American economic review, 94(2), 247-252.
Maximizing the effectiveness of structured classroom management programs: Implementing rule-review procedures with disruptive and distractible students.
The present study assessed the relative strength of daily rule review and rehearsal on student behavior when such procedures were added to a token economy. The token program was designed to increase appropriate classroom behaviors of disruptive boys attending a multi categorical resource room.
Rosenberg, M. S. (1986). Maximizing the effectiveness of structured classroom management programs: Implementing rule-review procedures with disruptive and distractible students. Behavioral Disorders, 11(4), 239-248.
What research has to say about fluency instruction.
The editors of What Research Has to Say About Reading Instruction present the most recent research on fluency and show how you can put it into practice.
Samuels, S. J., & Farstrup, A. E. (Eds.). (2006). What research has to say about fluency instruction. International Reading Association.
Cumulative and residual effects of teachers on future student academic achievement.
The Tennessee Value-Added Assessment System determines the effectiveness of school systems, schools, and teachers based on student academic growth over time. Research conducted utilizing data from the TVAAS database has shown that race, socioeconomic level, class size, and classroom heterogeneity are poor predictors of student academic growth. Rather, the effectiveness of the teacher is the major determinant of student academic progress.
Sanders, W. L., & Rivers, J. C. (1996). Cumulative and residual effects of teachers on future student academic achievement.
Cumulative and residual effects of teachers on future student academic achievement.
The Tennessee Value-Added Assessment System determines the effectiveness of school systems, schools, and teachers based on student academic growth over time. Research conducted utilizing data from the TVAAS database has shown that race, socioeconomic level, class size, and classroom heterogeneity are poor predictors of student academic growth. Rather, the effectiveness of the teacher is the major determinant of student academic progress.
Sanders, W. L., & Rivers, J. C. (1996). Cumulative and residual effects of teachers on future student academic achievement.
Can "Micro-Credentialing" Salvage Teacher PD?
This article discuss how "Micro-Credentialing" offer an opportunity to shift away from credit-hour and continuing-education requirements that dominate the PD apparatus in most states, toward a system based on evidence of progress in specific instructional skills.
The Foundations of Educational Effectiveness
This book looks at research and theoretical models used to define educational effectiveness with the intent on providing educators with evidence-based options for implementing school improvement initiatives that make a difference in student performance.
Scheerens, J. and Bosker, R. (1997). The Foundations of Educational Effectiveness. Oxford:Pergmon
The Foundations of Educational Effectiveness
This book looks at research and theoretical models used to define educational effectiveness with the intent on providing educators with evidence-based options for implementing school improvement initiatives that make a difference in student performance.
Scheerens, J. and Bosker, R. (1997). The Foundations of Educational Effectiveness. Oxford:Pergmon
A meta- analysis of national research: Effects of teaching strategies on student achievement in science in the United States
This is a meta-analysis of research published from 1980 to 2004 on the effect of specific science teaching strategies on student achievement.
Schroeder, C. M., Scott, T. P., Tolson, H., Huang, T. Y., & Lee, Y. H. (2007). A meta?analysis of national research: Effects of teaching strategies on student achievement in science in the United States. Journal of Research in Science Teaching, 44(10), 1436-1460.
Teacher-centered instruction: The Rodney Dangerfield of social studies.
Teacher-centered instruction implies a high degree of teacher direction and a focus of students on academic tasks. And it vividly contrasts with student-centered or constructivist approaches in establishing a leadership role for the teacher
Schug, M. C. (2003). Teacher-centereed instruction. Where did social studies go wrong, 94-110.
Academic skills problems: Direct assessment and intervention
This popular practitioner guide and text presents an effective, problem-solving-based approach to evaluating and remediating academic skills problems. The author provides practical strategies for working with students across all grade levels (K–12) who are struggling with reading, spelling, written language, or math.
Shapiro, E. S. (2011). Academic skills problems: Direct assessment and intervention. Guilford Press.
Description and effects of prosocial instruction in an elementary physical education setting.
The purpose of this article was to describe the developmental effects of one elementary physical education teacher's proactive teaching of prosocial behavior. An ABA (B) design coupled with a control group comparison across six matched urban physical education classes was used to assess the teaching strategy.
Sharpe, T., Crider, K., Vyhlidal, T., & Brown, M. (1996). Description and effects of prosocial instruction in an elementary physical education setting. Education & Treatment of Children, 19(4), 435.
Understanding validity and reliability in classroom, school-wide, or district-wide assessments to be used in teacher/principal evaluations
The goal of this paper is to provide a general understanding for teachers and administrators of the concepts of validity and reliability; thereby, giving them the confidence to develop their own assessments with clarity of these terms.
Shillingburg. W. (2016). Understanding validity and reliability in classroom, school-wide, or district-wide assessments to be used in teacher/principal evaluations. Retrieved from https://cms.azed.gov/home/GetDocumentFile?id=57f6d9b3aadebf0a04b2691a
Interventions for academic and behavior problems II: Preventive and remedial approaches
As the successor to one of NASP's most popular publications, Interventions for Academic and Behavior Problems II offers the latest in evidence-based measures that have proven to create safer, more effective schools.
Shinn, M. R., Walker, H. M., & Stoner, G. E. (2002). Interventions for academic and behavior problems II: Preventive and remedial approaches. National Association of School Psychologists.
Using the think-pair-share technique.
In this strategy guide, you will learn how to organize students and classroom topics to encourage a high degree of classroom participation and assist students in developing a conceptual understanding of a topic through the use of the Think-Pair-Share technique.
Simon, C. A. (2019). National Council of Teachers of English. Using the think-pair-share technique. Retrieved from http://www.readwritethink.org/professional-development/strategy-guides/using-think-pair-share-30626.html
A grounded theory of behavior management strategy selection, implementation, and perceived effectiveness reported by first-year elementary teachers.
In this grounded theory study, 19 teachers were interviewed and then, in constant comparative fashion, the interview data were analyzed. The theoretical model that emerged from the data describes novice teachers' tendencies to select and implement differing strategies related to the severity of student behavior.
Smart, J. B., & Igo, L. B. (2010). A grounded theory of behavior management strategy selection, implementation, and perceived effectiveness reported by first-year elementary teachers. The Elementary School Journal, 110(4), 567-584.
Teaching critical thinking and problem solving skills.
Several barriers can impede critical thinking instruction. However, actively engaging students in project-based or collaborative activities can encourage students’ critical thinking development if instructors model the thinking process, use effective questioning techniques, and guide students’ critical thinking processes.
Snyder, L. G., & Snyder, M. J. (2008). Teaching critical thinking and problem solving skills. The Journal of Research in Business Education, 50(2), 90.
Coaching Classroom Management: Strategies & Tools for Administrators & Coaches
This book is written for school administrators, staff developers, behavior specialists, and instructional coaches to offer guidance in implementing research-based practices that establish effective classroom management in schools. The book provides administrators with practical strategies to maximize the impact of professional development.
Sprick, et al. (2010). Coaching Classroom Management: Strategies & Tools for Administrators & Coaches. Pacific Northwest Publishing.
Effective Teachers Make a Difference
This analysis examines the available research on effective teaching, how to impart these skills, and how to best transition teachers from pre-service to classroom with an emphasis on improving student achievement. It reviews current preparation practices and examine the research evidence on how well they are preparing teachers
States, J., Detrich, R. & Keywroth, R. (2012). Effective Teachers Make a Difference. In Education at the Crossroads: The State of Teacher Preparation (Vol. 2, pp. 1-46). Oakland, CA: The Wing Institute.
Teacher Quality Index
This book examines issues pertaining to making effective hiring decisions. The authors present a research-based interview protocol built on quality indicators.
Stronge, J. and Hindman, J., (2006). Teacher Quality Index. Association for Supervision and Curriculum Development
Effect on varying rates of behavior-specific praise on the on-task behavior of students with EBD.
This study has 2 purposes: examine the effect of an observation-feedback intervention on the rate of a teacher's behavior-specific praise of students with emotional and behavioral disorders (EBD) and the effect of increased rates of a teacher's behavior-specific praise on the on-task behavior of a class of students with EBD.
Sutherland, K. S., Wehby, J. H., & Copeland, S. R. (2000). Effect of varying rates of behavior-specific praise on the on-task behavior of students with EBD. Journal of Emotional and Behavioral Disorders, 8(1), 2-8.
Individuals with Disabilities Education Improvement Act of 2004 and IDEA Regulations of 2006: Implications for Educators, Administrators, and Teacher Trainers
This article summarize changes and challenges that school personnel will face in order to implement The Individuals with Disabilities Education Improvement Act of 2004 (IDEIA).
The Mirage: Confronting the truth about our quest for teacher development
"The Mirage" describes the widely held perception among education leaders that they already know how to help teachers improve, and that they could achieve their goal of great teaching in far more classrooms if they just applied what they knew more widely.
TNTP. (2015). The Mirage: Confronting the truth about our quest for teacher development. Retrieved from: https://tntp.org/publications/view/the-mirage-confronting-the-truth-about-our-quest-for-teacher-development
Preservice teachers’ perceived barriers to the implementation of a multicultural curriculum.
This study investigated preservice teachers' perceived barriers for implementing multicultural curriculum with preservice teachers as they began their teacher education program.
Van Hook, C. W. (2002). Preservice teachers' perceived barriers to the implementation of a multicultural curriculum. Journal of Instructional Psychology, 29(4), 254-265.
Are we making the differences that matter in education?
This paper argues that ineffective practices in schools carry a high price for consumers and suggests that school systems consider the measurable yield in terms of gains in student achievement for their schooling effort.
VanDerHeyden, A. (2013). Are we making the differences that matter in education. In R. Detrich, R. Keyworth, & J. States (Eds.),Advances in evidence-‐based education: Vol 3(pp. 119–138). Oakland, CA: The Wing Institute. Retrieved from http://www.winginstitute.org/uploads/docs/Vol3Ch4.pdf
Keeping RTI on track: How to identify, repair and prevent mistakes that derail implementation
Keeping RTI on Track is a resource to assist educators overcome the biggest problems associated with false starts or implementation failure. Each chapter in this book calls attention to a common error, describing how to avoid the pitfalls that lead to false starts, how to determine when you're in one, and how to get back on the right track.
Vanderheyden, A. M., & Tilly, W. D. (2010). Keeping RTI on track: How to identify, repair and prevent mistakes that derail implementation. LRP Publications.
Productive teaching
This literature review examines the impact of various instructional methods
Walberg H. J. (1999). Productive teaching. In H. C. Waxman & H. J. Walberg (Eds.) New directions for teaching, practice, and research (pp. 75-104). Berkeley, CA: McCutchen Publishing.
Productive teaching
This literature review examines the impact of various instructional methods
Walberg H. J. (1999). Productive teaching. In H. C. Waxman & H. J. Walberg (Eds.) New directions for teaching, practice, and research (pp. 75-104). Berkeley, CA: McCutchen Publishing.
Assessing cross-cultural sensitivity awareness: A basis for curriculum change
This study examined the social attitudes related to race, gender, age, and ability among senior level health education students at a mid-sized university in the southeast by means of a personally experienced critical incident involving a cross-cultural incident.
Wasson, D. H., & Jackson, M. H. (2002). Assessing cross-cultural sensitivity awareness: A basis for curriculum change. Journal of Instructional Psychology, 29(4), 265-277.
How schools matter: The link between teacher classroom practices and student academic performance
Quantitative studies of school effects have generally supported the notion that the problems of U.S. education lie outside of the school. Yet such studies neglect the primary venue through which students learn, the classroom. The current study explores the link between classroom practices and student academic performance by applying multilevel modeling to the 1996 National Assessment of Educational Progress in mathematics. The study finds that the effects of classroom practices, when added to those of other teacher characteristics, are comparable in size to those of student background, suggesting that teachers can contribute as much to student learning as the students themselves.
Wenglinsky, H. (2002). How schools matter: The link between teacher classroom practices and student academic performance. Education Policy Analysis Archives, 10(12).
A meta-analysis of the effects of direct instruction in special education
Studies of the effectiveness of Direct Instruction programs with special education students
were examined in a meta-analysis comparison. To be included, the outcomes had to be
compared with outcomes for some other treatment to which students were assigned prior to
any interventions. Not one of 25 studies showed results favoring the comparison groups.
Fifty-three percent of the outcomes significantly favored DI with an average magnitude of
effect of. 84 standard deviation units. The effects were not restricted to a particular handicapping condition, age group or skill area.
White, W. A. T. (1988). A meta-analysis of the effects of direct instruction in special education. Education and Treatment of Children, 11(4), 364–374.
How to teach critical thinking.
This paper considers what the research can tell us about how critical thinking is acquired, and the implications for how education might best develop young people’s critical thinking capabilities.
Willingham, D. (2019). How to teach critical thinking. New South Wales (NSW) Department of Education.
4 proven strategies for teaching empathy.
Help your students understand the perspectives of other people with these tried-and-tested methods.
Wilson, D., & Conyers, M. (2017). 4 proven strategies for teaching empathy.Edutopia. Retrieved from https://www.edutopia.org/article/4-proven-strategies-teaching-empathy-donna-wilson-marcus-conyers
Teacher use of interventions in general education settings: Measurement and analysis of? the independent variable
This study evaluated the effects of performance feedback on increasing the quality of implementation of interventions by teachers in a public school setting.
Witt, J. C., Noell, G. H., LaFleur, L. H., & Mortenson, B. P. (1997). Teacher use of interventions in general education settings: Measurement and analysis of ?the independent variable. Journal of Applied Behavior Analysis, 30(4), 693.
Time management: An experimental investigation.
Four groups of preservice teachers participating in student teaching seminars were randomly assigned to one of three conditions to test the effectiveness of brief training in time-management techniques.
Woolfolk, A. E., & Woolfolk, R. L. (1986). Time management: An experimental investigation. Journal of school Psychology, 24(3), 267-275.
The Cost-Effectiveness of Five Policies for Improving Student Achievement
This study compares the effect size and return on investment for rapid assessment, between, increased spending, voucher programs, charter schools, and increased accountability.
Yeh, S. S. (2007). The cost-effectiveness of five policies for improving student achievement. American Journal of Evaluation, 28(4), 416-436.
Independent Teacher Education Programs: Apocryphal Claims, Illusory Evidence
This policy brief surveys historical and contemporary trends in teacher preparation, and explores what is known about the quality of five of the most prominent independent teacher education programs in the U.S., including their impact on teacher quality and student learning. The author's analysis demonstrates that claims regarding the success of such programs are not substantiated by peer-reviewed research and program evaluations.
Zeichner, K. (2016). Independent Teacher Education Programs: Apocryphal Claims, Illusory Evi-dence. Boulder, CO: National Education Policy Center. Retrieved from http://nepc.colorado.edu/publication/teacher-education
Training Teachers to Increase Behavior-Specific Praise: A Meta-Analysis.
The purpose of this study was to synthesize the literature in support of training teachers to use behavior-specific praise, which is a strategy used to reduce students’ disruptive and off-task behavior as well as prevent students’ problem behaviors from occurring.
Zoder-Martell, K. A., Floress, M. T., Bernas, R. S., Dufrene, B. A., & Foulks, S. L. (2019). Training Teachers to Increase Behavior-Specific Praise: A Meta-Analysis. Journal of Applied School Psychology, 1-30.
CLEAR TEACHING: With Direct Instruction, Siegfried Engelmann Discovered a Better Way of Teaching
This is a well-researched, highly readable introduction to Direct Instruction (DI)
Barbash, S. (2012). Clear teaching: With direct instruction, Siegfried Engelmann discovered a better way of teaching. Education Consumers Foundation.
Effective Teaching Methods
The is a practical yet theoretically substantive book that aims to provide teachers with research-based, effective teaching practices.
Borich, G. D. (1988). Effective teaching methods. Pearson Education India.
Effects of Pre-Teaching and Re-Teaching on Math Achievement and Academic Self-Concept of Students with Low Achievement in Math
This study examines and compares the effectiveness of pre-teaching and re-teaching on math achievement and academic self-concept of third grade students identified as low achievers.
Lalley, J. P., & Miller, R. H. (2006). Effects of Pre-Teaching and Re-Teaching on Math Achievement and Academic Self-Concept of Students with Low Achievement in Math. Education, 126(4), 747-755.
Evidence-Based Teaching: A Practical Approach
This book offers a thorough array of practical teaching methods backed by rigorous research to have the greatest effect along with practical techniques to apply these in actual classroom settings.
Petty. G. (2009). Evidence-Based Teaching: A Practical Approach. Nelson Thornes, Cheltenham, United Kingdom.
Personal Competency: A Framework for Building Students’ Capacity to Learn
This research synthesis examines complex issues that must be addressed in the building student personal competencies.
Redding, S. (2014). Personal Competency: A Framework for Building Students’ Capacity to Learn. The Center on Innovations in Learning. Retrieved June 2, 2015 from http://www.centeril.org/publications/Personal_Compentency_Framework.pdf
The effects of teacher questioning levels on student achievement: A quantitative synthesis.
This meta-analysis examines the effects of teachers use of higher order questions on student achievement.
Samson, G. E., Strykowski, B., Weinstein, T., & Walberg, H. J. (1987). The effects of teacher questioning levels on student achievement: A quantitative synthesis. The Journal of Educational Research, 290-295.
What Helps Students Learn? Spotlight on Student Success
This study is a research synthesis comprised of 11,000 statistical findings that shows a consensus on the most significant influences on student learning.
Wang, M. C., Haertel, G. D., & Walberg, H. J. (1997). What Helps Students Learn? Spotlight on Student Success.
A Meta-Analytic Review of Guided Notes
The purpose of this review is to summarize research on the effectiveness of guided notes.
Calder: Longitudinal Data in Education Research
CALDER is a National Research and Development Center that utilizes longitudinal state and district data on student and teachers to examine the effects of real policies and practices on the learning gains of students over time.
Center for Educational Leadership
The Center for Educational Leadership provides research and training in teaching effectiveness and school leadership.
Center on Great Teachers and Leaders
The Center on Great Teachers and Leaders (GTL Center) is dedicated to supporting state education leaders in their efforts to grow, respect, and retain great teachers and leaders for all students.
Center on Teaching and Learning (CTL)
CTL is research center that conducts and disseminates research that focuses on practical solutions to serious problems in school systems.
Council of Chief State School Officers (CCSSO)
CCSSO is a nonpartisan, nationwide, nonprofit organization of public officials who head departments of elementary and secondary education in the states, provides leadership, advocacy, and technical assistance on major educational issues.
Edutopia
Edutopia focuses on practices and programs that help students acquire and effectively apply the knowledge, attitudes, skills and beliefs to achieve their full potential.
How to Survive Your First Year Teaching
You’ve graduated college, completed your student teaching, earned your teaching credential, been offered a position, and are ready to jump into the classroom head first. But before your first day, it’s important to recognize the challenges that await many new teachers. According to the Learning Policy Institute, studies show that between 19 and 30 percent of teachers leave within their first five years due to low pay, lack of administrative support, poor work conditions, and other reasons. And the first year can be the most challenging of all. Teachers like you are the cornerstone of our educational system, but often lack the resources needed to succeed – or aren’t sure where to find them.
We’re here to fill that gap with this guide, which provides meaningful support through helpful resources and expert tips, whether you’re teaching Pre-K children or college freshmen. Read on to learn how you and other teachers can make it through your first year and come out stronger on the other side.
Joyce Foundation
The Joyce Foundation invests in and focuses on today's most pressing problems while also informing the public policy decisions critical to creating opportunity and achieving long-term solutions. The work is based on sound research and is focused on where it can add the most value.
K-12 Education: Gates Foundation
K-12 Education works to make sure tools, curriculum, and supports are designed using teacher insights.
National Commission on Teaching & America's Future (NCTAF)
NCTAF is a bipartisan endeavor to engage experienced policymakers and practitioners in researching the entrenched national challenge of recruiting, developing, and retaining teachers.
National Council on Teacher Quality (NCTQ)
The National Council on Teacher Quality works to achieve fundamental changes in the policy and practices of teacher preparation programs, school districts, state governments, and teachers unions.
Schools and Staffing Survey (SASS)
The SASS is a system of related questionnaires that provide descriptive data on the context of elementary and secondary education and policymakers a variety of statistics on the condition of education in the United States.
What Works Clearinghouse (WWC)
The goal of the WWC is a resource for informed education decision-making. The WWC identifies evidence-based practice, program, or policy, and disseminates summary information on the WWC website.





